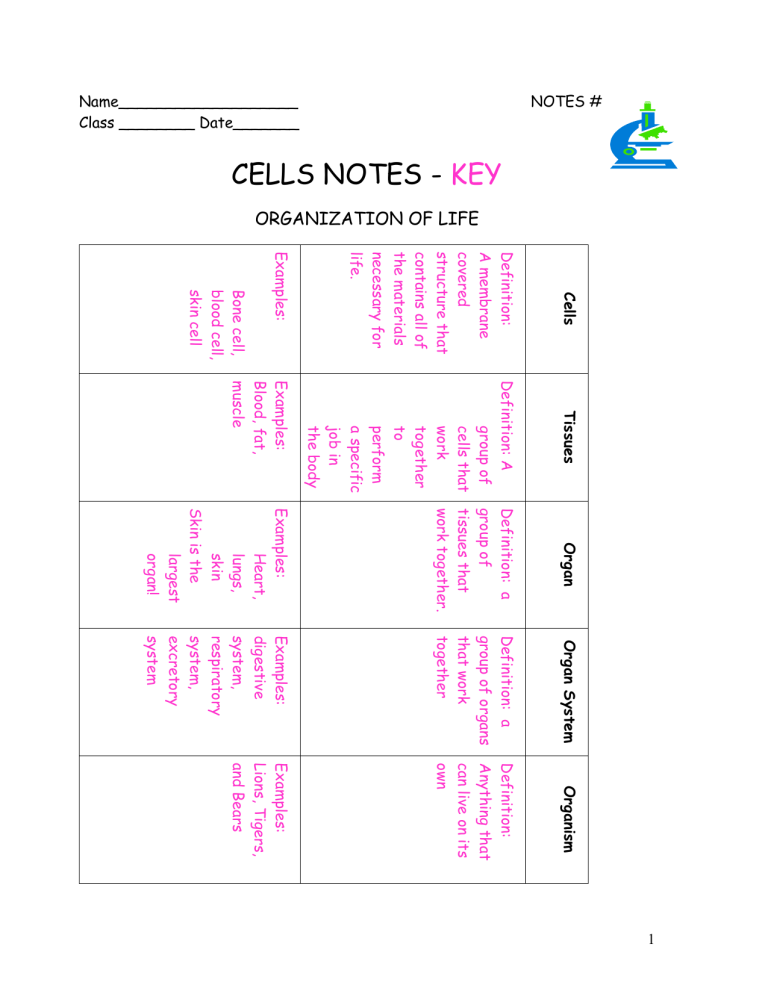
NOTES # Name___________________ Class ________ Date_______ CELLS NOTES - KEY ORGANIZATION OF LIFE Examples: Definition: A membrane covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. Cells Examples: Blood, fat, muscle Definition: A group of cells that work together to perform a specific job in the body Tissues Definition: a group of tissues that work together. Organ Examples: digestive system, respiratory system, excretory system Definition: a group of organs that work together Organ System Examples: Lions, Tigers, and Bears Definition: Anything that can live on its own Organism Bone cell, blood cell, skin cell Examples: Heart, lungs, skin Skin is the largest organ! 1 Two Types of Cells: Prokaryotic Cell— Does NOT have a nucleus or any other membrane covered organelles, example bacteria. Eukaryotic Cell— Describes a cell that DOES have nucleus. Multi-cellular organisms have eukaryotic cells. Two Types of Organisms: Unicellular Organism — single celled organism Multicellular Organism—more then one celled organism How do the cells of unicellular organisms differ from the cells of multicellular organisms? The cells of unicellular organisms can survive on their own, but the cells of multi-cellular organisms must remain a part of an organisms body to survive. 2 The Discovery of Cells Directions: Using pages 60-66 in your textbook, answer the following questions. 1. Robert Hooke saw the first ____________ using a _______________ ________________. 2. What are the three parts of the Cell Theory? 1. 2. 3. 3. What do ALL cells have in common? 4. What are two advantages of being multicellular? 5. What are organelles? 6. What is the cytoplasm? 3 7. What is the function of the cell membrane? 8. What is DNA? 9. Why do all cells need DNA? 10. What organelle is DNA enclosed inside of? 11. How are Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells different? Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells 4 Organelle Function Cell wall Provides strength and support. Found in Animals Found in Plants ☺ Controls what enters and leaves a cell Controls cell activities Controls what enters and leaves the nucleus. X shaped organelle made of DNA. Holds the code that controls the cell. Endoplasmic Makes lipids. Transports proteins reticulum & other materials through the cell Ribosomes Makes protein Mitochondria Supply the cell with energy. Respiration occurs here. Vacuoles Stores food, water, and waste ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ Lysosomes Chloroplasts ☺ Cell membrane Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Chromosomes Cytoplasm Golgi Complex Contain enzymes that digest food Contain the chlorophyll need to carry on photosynthesis (produce food) Liquid portion of the cell containing all the organelles Processes and transports materials out of the cell ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ ☺ 5 6 7 Movement of Particles Into and Out of the Cell DIFFUSION is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration (crowded) to an area of low concentration (less crowded) Occurs with and between cells Do NOT need energy (ATP) In the body: 8 OSMOSIS - diffusion of water through the semi-permeable cell membrane. Semi-permeable-only certain substances can pass through NO energy required Can also occur in plant cells SMALL PARTICLE MOVEMENT *PASSIVE TRANSPORT-movement across the cell membrane without the use of energy -movement is from an area of high to low concentration -does NOT require energy -Osmosis is an example 9 *ACTIVE TRANSPORT-usually movement of particles from an area of low to high concentration *requires energy! LARGE PARTICLE MOVEMENT *Endocytosis - bringing particles within the cell *Exocytosis-releasing particles (exit) 10 CELLULAR REPRODUCTION How did I grow taller? How are my worn-out cells replaced? How do I heal from injuries? The answer is….Cellular Reproduction or Mitosis MITOSIS 1. Type of cell division when chromosomes are duplicated and then separate into two identical and complete sets to be passed to each of the two daughter cells. For example in humans, body cells have 46 chromosomes. After mitosis, each of the two new identical daughter cells will have 46 chromosomes. 2. In this type of cell division, the hereditary information is identical in all the cells that result. 3. Responsible for growth, maintenance and repair. 4. In some one-celled organisms, asexual reproduction is achieved through mitosis. 5. Cancers are a result of abnormal cell division. MEIOSIS 1. Responsible for producing egg and sperm 2. The resulting daughter cells contain one-half the hereditary information. For example, in humans, each sperm or egg would contain 23 chromosomes. 11





