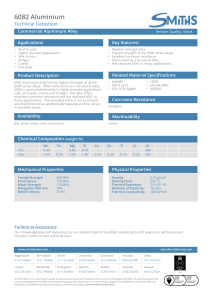
AAB2092 Phase Transformations in Metallic Materials Ts Dr Norlin Nosbi Copyrighted Materials via ULearn “Students are reminded that any file or attachment shared with you by your course lecturer is SOLELY for educational purposes and/or your personal and private study ONLY, and therefore cannot be shared with or disseminated to anyone else or uploaded on any website without the permission or authorisation of the copyright owner”. COURSE OUTCOMES (CO): At the end of this course, students should be able to: CO1 CO2 CO3 Analyze the classes of material, distinguishing and phases in metal alloys, stable and metal stable phases Explain thermodynamic and Kinetic of transformation, transformation type and mechanism (e.g., diffusional and solid state transformation) and their influence on mechanical properties Design a heat treatment for various metal alloys for transformation new microstructure and their influence of mechanical properties. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES (PO): At the end of this course, students should be able to: PLO1 Acquire and apply engineering fundamentals to complex Materials Engineering problems. PLO2 Identify, formulate and solve complex Materials Engineering problems using creativity and innovativeness. PLO3 Design and develop solutions for complex Materials Engineering problems. Aluminium alloy TODAY’S OUTCOME THE STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO UNDERSTAND: -INTRODUCTION ON ALUMINIUM ALLOY, CHEMISTRY, FABRICATION, HEAT-TREATMENT AND APPLICATIONS Aluminium Alloy ISSUE TO ADDRESS... What types of aluminium alloy? What is the applications for this aluminium? Advantages using Aluminium alloy? Active Learning: Think pair share (15 minutes) Show all the issue that need to be address above. Contents Introduction Chemistry Course outline Classification Applications Manufacturing Heat treatment Common Defects Conclusions 7 Introduction Abundance All Others Iron Oxygen Silicon Aluminum Oxide / Bauxite 8 Advantages Introduction High strength to weight ratio High electrical and thermal conductivity High reflectivity and resistance to corrosion Non-toxic (ideal for packaging and cooking material) Ductility-easy to cold work and fabricate 9 History • Aluminum Production • The first commercial batch of Aluminum was produced in 1888 • Production Capabilities Lower the Price – Between 1888 and 1893 Aluminum dropped from $4.86/lb to $.78/lb 10 Application • Early uses for Aluminum • Cooking utensils • Electrical wire and cable • Foil • Auto bodies • Engine parts used by the Wright Brothers’ 11 Chemistry Alloying Elements Principal Alloying Elements Cu, Mn, Mg, Si, Zn, Fe Additional Alloying Elements Ti, B, Zr, Cr, Ni, Bi, Pb 12 Role of Alloying Elements Al 1. Increases strength and hardness 2.If >12% makes the alloy brittle 3. Hot cracking tendency 4. Decreases corrosion Cu resistance 13 Role of Alloying Elements Al 1.Increases yield and tensile strength 2. Improves ductility 3.Good resistance to corrosion Mn 4. Decrease resistivity Manganese 14 Role of Alloying Elements Al 1.Increases tensile strength and hardness uptil 13% wt. 2.Decrease the hot cracking 3. Good resistance to corrosion Si Silicon 15 Role of Alloying Elements Al 1.Increases strength and hardness 2.Good resistance to corrosion Mg 3.Increase weldability and machinability Magnesium 16 Role of Alloying Elements Al Zn 1.Gives heat treatable alloys when combined with Mg 2. Increase strength and hardness 3.Increased toughness but susceptible to stress corrosion cracking 17 Classification Alloy Designation System typically contain low percentages of alloying elements, specifically silicon, which is usually less than 1% Al same elements as wrought, but in greater amounts; and silicon content, generally in the range 1-12%, may exceed in some alloys. 18 Classification Alloy Designation System Standardize by Applications 1XXX 20 Applications 2XXX 21 Applications 3XXX 22 Applications 4XXX 23 Applications 5XXX 24 Applications 6XXX 25 Applications 7XXX 26 Production Wrought Al Alloys 27 Extrusion Process Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= baM5hNnBcT8 28 Heat Treatment Al Alloys • Annealing Treatment • Solution heat treatment • Precipitation (Hardening) treatment 29 Aluminium alloy Forming Processes (Microstructure effects) Heat Treatment Before Solution Heat Treatment After Solution Heat Treatment 31 Heat Treatment 25 Al-Cu phase diagram showing three steps in precipitation hardening Aluminium alloy Forming Processes (Defects) Common Defects Casting Defects Heat Treatment Defects Defect Extrusion Defects Forging Defects 34 Casting Defects Cracks Porosity Inclusions Segregation 35 Cracks Types Centric Radial Loop Transverse 36 Cracks 7075 37 Cracks 2024 38 Inclusions Optical Images 39 Inclusions SEM Images 40 Inclusions SEM Analysis 41 Inclusions Fracture surface 42 Inclusions Fracture surface 43 Extrusion Defects Extrusion tears/ cracks Scratches Fish scaling Un-even wall thickness Layer Formation Coarse grain ring 44 Drawing Defects Scratch Bumped ring Un-uniformity of wall thickness Crack Wrinkle End break 45 Cracks in Extrusion Unetched form 46 Cracks in Extrusion T6 etched form 47 Heat treatment Defects Unqualified mechanical properties Over firing Coarse grain Quenching cracks 48 Grain Coarsening 49 Control of Grain Coarsening 50 The student should be able to understand: Today’s outcome COMPLETED Introduction on Aluminium alloy, chemistry, fabrication, heat-treatment and applications