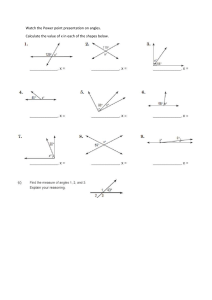
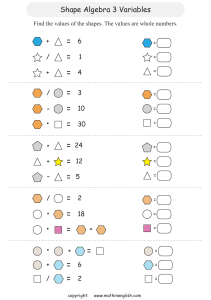
Below is a detailed summary of the expectations by strand in the new 2020 Ontario math curriculum for students from Grades 3 to 8: Grade 3 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and representing whole numbers up to 1000. Developing fluency in addition and subtraction with regrouping. Exploring multiplication and division with single-digit numbers. Solving problems involving money and time. 2. Measurement: Measuring length, mass, capacity, and temperature using standard units. Understanding and solving problems involving perimeter and area of rectangles. Telling time to the minute and solving time-related problems. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Identifying, classifying, and describing 2D shapes (e.g., triangles, quadrilaterals). Describing properties of 2D shapes, including symmetry and angles. Exploring the characteristics of 3D shapes. 4. Patterning and Algebra: Extending, describing, and creating number patterns Identifying and extending patterns in shapes and numbers. Solving problems involving unknowns and simple equations. 5. Data Management and Probability: Collecting, organizing, and representing data using charts and graphs. Interpreting and analyzing data from various graphs. Introducing basic probability concepts. Grade 4 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and representing whole numbers up to 10,000 Developing fluency in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with larger numbers. Identifying prime and composite numbers, factors, and multiples. 2. Measurement: Converting units of measurement (e.g., centimeters to meters). Calculating perimeter and area of rectangles and composite shapes. Estimating and measuring mass and capacity. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Identifying and describing 2D shapes based on properties. Understanding and using a protractor to measure and draw angles. Exploring congruence and symmetry of 2D shapes. 4. Patterning and Algebra: Describing and extending patterns using variables Solving problems involving unknowns and simple equations. Introducing the concept of variables and expressions. 5. Data Management and Probability: Creating and interpreting various graphs (e.g., bar graphs, line plots). Analyzing and organizing data from real-world contexts. Understanding basic probability concepts. Grade 5 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and representing whole numbers and decimals up to hundredths. Developing fluency in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with decimals. Ordering and comparing fractions, decimals, and integers. 2. Measurement: Converting units of measurement within the metric system. Understanding and solving problems involving perimeter, area, and volume. Telling time and calculating elapsed time. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Identifying and describing 3D shapes (e.g., cubes, spheres). Understanding and using the Pythagorean theorem. Exploring transformations (e.g., translations, reflections). 4. Patterning and Algebra: Understanding and extending numerical and geometric patterns. Solving problems involving variables and expressions. Introducing the concept of algebraic equations. 5. Data Management and Probability: Collecting, organizing, and interpreting data using scatterplots and trend lines. Analyzing and drawing conclusions from data distributions. Understanding experimental vs. theoretical probability. Grade 6 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and representing whole numbers, fractions, decimals, and integers. Developing fluency in operations with fractions and decimals. Solving problems involving percentages. 2. Measurement: Converting units of measurement within both the metric and imperial systems. Understanding and solving problems involving volume and surface area. Exploring angles and calculating missing angles in 2D shapes. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Understanding and applying the properties of 2D and 3D shapes. Investigating congruence and similarity of 2D shapes. Describing and comparing transformations. 4. Patterning and Algebra: Representing, describing, and extending linear relationships. Solving problems involving one-step equations. Describing and analyzing patterns and relationships. 5. Data Management and Probability: Organizing, representing, and interpreting data using different graphs. Understanding measures of central tendency and variability. Interpreting and comparing data sets. Grade 7 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and performing operations with integers, fractions, decimals, and percents. Exploring rational numbers, including terminating and repeating decimals. Solving problems involving ratios and proportions. 2. Measurement: Applying the concepts of scale and scale drawings. Understanding and solving problems involving surface area and volume. Exploring angle relationships and properties of 2D shapes. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Describing and analyzing properties of triangles and quadrilaterals. Investigating angle properties in polygons and circles. Understanding and applying the Pythagorean theorem. 4. Patterning and Algebra: Describing and representing linear relationships using equations and graphs. Solving problems involving multi-step equations and inequalities. Exploring patterns and relationships in algebraic expressions. 5. Data Management and Probability: Collecting and organizing bivariate data using scatter plots. Understanding and comparing experimental and theoretical probabilities. Analyzing data to make predictions and draw conclusions. Grade 8 Mathematics Curriculum Summary: 1. Number Sense and Numeration: Understanding and performing operations with integers, fractions, decimals, and radicals. Exploring scientific notation and significant figures. Solving problems involving proportions, ratios, and percentages. 2. Measurement: Applying concepts of scale, surface area, and volume in real-world contexts. Understanding and solving problems involving the properties of 2D and 3D shapes. Applying the Pythagorean theorem to calculate distances. 3. Geometry and Spatial Sense: Investigating properties of 2D shapes, including parallelograms, triangles, and circles. Understanding the relationship between 2D and 3D shapes. Exploring transformations and congruence. 4. Patterning and Algebra: Describing and representing linear relationships using equations and graphs. Solving problems involving systems of linear equations. Analyzing patterns and relationships in algebraic expressions. 5. Data Management and Probability: Collecting, organizing, and representing data using different graphs and charts Analyzing and interpreting data distributions and measures of spread. Understanding compound events and conditional probabilities.