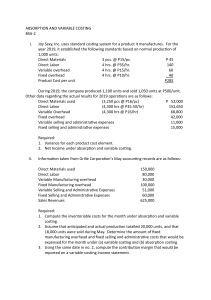
1. Trio Company reports the following information for its first year of operations. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Units produced Units sold Ending finished goods inventory $ 15 $ 16 $4 $ 160,000 20,000 14,000 6,000 per unit per unit per unit per year units units units a. Compute the product cost per unit using absorption costing. b. Determine the cost of ending finished goods inventory using absorption costing. c. Determine the cost of goods sold using absorption costing. 1 2. Trio Company reports the following information for its first year of operations. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Units produced Units sold Ending finished goods inventory $ 15 $ 16 $4 $ 160,000 20,000 14,000 6,000 per unit per unit per unit per year units units units Assume instead that Trio Company uses variable costing. a. Compute the product cost per unit using variable costing. b. Determine the cost of ending finished goods inventory using variable costing. c. Determine the cost of goods sold using variable costing. 2 3. Aces Incorporated, a manufacturer of tennis rackets, began operations this year. The company produced 6,000 rackets and sold 4,900. Each racket was sold at a price of $90. Fixed overhead costs are $78,000 per year, and fixed selling and administrative costs are $65,200 per year. The company also reports the following per unit variable costs for the year. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 12 8 5 2 a. Prepare an income statement under variable costing. b. Compute the cost of ending finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet using variable costing. c. Prepare an income statement under absorption costing. d. Compute the cost of ending finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet using absorption costing. 3 4. D’Souza Company sold 10,000 units of its product for $80 per unit. Cost of goods sold is $55 per unit. Each unit had $40 in variable cost of goods sold and variable selling and administrative expenses are $10 per unit. a. Compute gross profit under absorption costing. b. Compute contribution margin for this company. 4 5. Cool Sky reports the following for its first year of operations. The company produced 44,000 units and sold 36,000 units at a price of $140 per unit. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses $ 60 $ 22 $8 $ 528,000 $ 11 $ 105,000 per unit per unit per unit per year per unit per year a. Assume the company uses absorption costing. Determine its total product cost per unit. b. Assume the company uses absorption costing. Prepare its income statement for the year under absorption costing. c. Assume the company uses variable costing. Determine its total product cost per unit. d. Assume the company uses variable costing. Prepare its income statement for the year under variable costing. 5 6. Sims Company began operations on January 1. Its cost and sales information for this year follow. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses Units produced Units sold Sales price $ 40 $ 60 $ 30 $ 7,000,000 $ 11 $ 4,250,000 100,000 70,000 $ 350 per unit per unit per unit per year per unit per year units units per unit a. Prepare an income statement for the year using variable costing. b. Prepare an income statement for the year using absorption costing. 6 7. Jax Incorporated reports the following data for its only product. The company had no beginning finished goods inventory and it uses absorption costing. Sales price Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead $ 56.00 $ 9.00 $ 6.50 $ 11.00 $ 720,000 per unit per unit per unit per unit per year a. Compute gross profit assuming (a) 60,000 units are produced and 60,000 units are sold and (b) 80,000 units are produced and 60,000 units are sold. b. By how much would the company’s gross profit increase or decrease from producing 20,000 more units than it sells? 7 8. Huds Incorporated reports the information below on its product. The company uses absorption costing and has a target markup of 40% of absorption cost per unit. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Variable selling and administrative expenses Fixed selling and administrative expenses Units produced Units sold $ 100 $ 30 $8 $ 600,000 $3 $ 120,000 50,000 50,000 per unit per unit per unit per year per unit per year units per year units per year Compute the target selling price per unit under absorption costing. 8