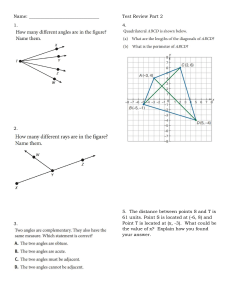
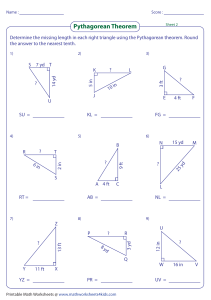
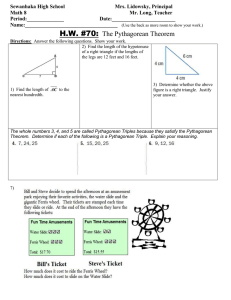
What we want to show: ||v|| = 2 2 2 𝑣1 + 𝑣2 + 𝑣3 Proof: Assume v = (v1, v2, v3), with v1, v2, v3 ϵ R Then (v1, v2, 0) is v1 away from the origin on the x-axis and v2 away from the origin on the y-axis by definition of cartesian coordinate system So we can construct a triangle with perpendicular legs of lengths v1 and v2, with a hypotenuse we will call A by definition of cartesian coordinate system And A2 = v12 + v22 A = Then cartesian And 2 by Pythagorean Theorem 2 𝑣1 + 𝑣2 We can define a line B, perpendicular to A, that extends by definition of from (v1, v2, 0) to (v1, v2, v3) the length of B is v3, because the endpoints differ in the Z-axis only, by v3 coordinate system Then And So We can define a line C extending from the origin to (v1, v2, v3) C, B, and A form a right triangle C2 = B2 + A2 by Pythagorean Theorem 2 2 2 2 C = v3 + (v1 + v2 ) by substitution And C= 2 2 2 𝑣1 + 𝑣2 + 𝑣3 Therefore ||v|| = 2 2 2 𝑣1 + 𝑣2 + 𝑣3 by the definition of norm