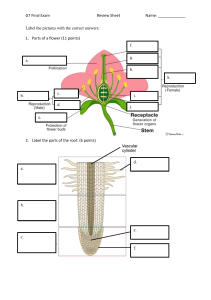
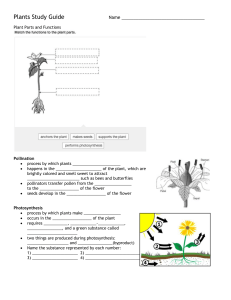
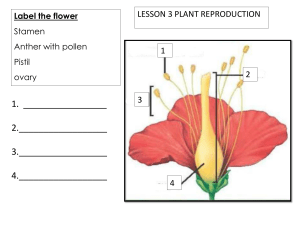
Photosynthesis Unit 1.1 Pages 6 -7 Solar energy is converted to chemical energy Plants make their own food What is Photosynthesis? Forms basis of food chains and food webs Using solar energy to make food in the form of glucose Discovery of Photosynthesis There must be something in the water ! • Partially discovered in 1600 by a Belgian chemist, physiologist and physician. • Performed a 5-year experiment involving a willow tree • Tree was watered for 5 years Concluded that growth of the tree was due to the nutrients it had received from the water and not the soil Although an inaccurate conclusion but proved that water contributes to the plant’s growth Plants, oxygen and light ! • Jan Ingenhousz- proved that plants produced oxygen • Placed submerged plants in sunlight and then in shade • Noticed that small bubbles were produced by the plants when they were in the sunlight but not in the shade • Concluded that plants use light to produce oxygen Discovery of Photosynthesis There must be something in the water There’s also something in the air Plants, oxygen and light Plants need carbon dioxide Plants transform energy Photosynthesis is the process through which plants make their own food using sunlight energy, water and carbon dioxide and convert it into glucose and oxygen Photosynthesis converts solar energy to chemical energy Photosynthesis occurs inside the chloroplasts of a cell The chloroplasts contain the green pigment called chlorophyll which traps the sunlight energy Chloroplasts are found abundantly in the palisade layer of the leaf structure Glucose is a sugar, belonging to a group of chemicals called carbohydrates Glucose is soluble in water which makes it difficult to store inside a cell Excess glucose is converted into starch and then stored inside a cell. Starch is insoluble in water Why do you think photosynthesis is called as a vital process for sustenance of life on Earth? Chloroplasts and Chlorophyll Work in Progress Artificial photosynthesis can produce food without sunshine Scientists are developing artificial photosynthesis to help make food production more energy-efficient here on Earth, and one day possibly on Mars Point to Ponder! Human evolution predictions are impossible to make. But perhaps using modern tools from biotechnology and genetic engineering, we could modify our cells to photosynthesize like plants. What would it take? THINK THINK THINK!! Will We Ever… Photosynthesise Like Plants? Solar-powered humans? What if humans had photosynthetic skin? IS HUMAN PHOTOSYNTHESIS POSSIBLE? Test for Starch Objective: Chemicals/ Apparatus needed: Iodine Solution, ethanol, beaker, leaf, Bunsen burner, forceps, test tube, dropper, white tile, tripod and gauze Procedure: 1. To test a leaf whether it has produced starch Add a leaf to boiling water to breakdown the cell membrane 2. Using forceps, remove the leaf from the water 3. Collect some ethanol in a test tube, stand the test tube in a beaker of very hot water. Put the leaf into ethanol to remove chlorophyll from it 4. Take the leaf out of ethanol and dip it into water to soften it. 5. Spread the leaf on to a white tile and add iodine solution to the leaf. Observation: Leaf turns blue-black in the presence of starch Questions and Answers A1: Explain why the leaf needed to be boiled before testing with iodine solution. To break down the cell membranes around the leaf cells A2: Suggest why it was useful to remove green color from the leaf, before testing it with iodine solution. The green pigment would not give us the accurate results, therefore the leaf’s chlorophyll is bleached out so that it may take up the iodine solution. A3: Describe two things that can be done to reduce the risk of anyone being hurt. Ethanol is highly flammable so Bunsen burner is turned off Wear eye protection A4: Explain why leaves often contain starch. Mineral Salts for the Plants Topic: 1.2 Pages: 8 -9 Fertilizer is a chemical or a natural substance that is added to the soil to provide one or more nutrients essential for the plant growth and optimum yield. It contains a combination of plant nutrients needed for its growth. Minerals needed by the plant: 1. Nitrate: • Needed to make proteins • Proteins are needed to make new cells • Needed to make chlorophyll • Deficiency of nitrate: -leaves turn yellow -plant cannot make enough new cells to grow 2. Magnesium: • Needed to make chlorophyll • Leaves turn yellow due to magnesium deficiency Questions and Answers Page 9 Q1. Give two examples of mineral salts needed by the plants. Q2: Explain why a plant that does not have enough magnesium will not grow? Q3: How do plants absorb mineral salts from the soil? The plants absorb mineral salts through their wide network of roots which are further divided into root hair cells to maximize the absorption of minerals from the soil Plants and Water Topic :1.3 Pages: 10-11 How is water used by the plant? Support - Helps the plant stand upright - Keeps the plant strong, and firm Transport - Water and mineral salts are transported up to the leaves through xylem Cooling - Water evaporating inside a plant leaf helps to keep the plant cool Photosynthesis - Water combines with carbon dioxide inside the chloroplasts Q1: Explain why a plant wilts if it is short of water? Q2: How does water help a plant keep cool? Q3: List the parts of the plant involved as it passes through the soil till it ends up in the air as water vapour Flowers Topic: 1.4 Pages: 12 – 13 Key Terms: 1. Flowers: the reproductive organs of the plants 2. Petals: most colorful part of the flower, which attract insects or birds 3. Nectar: sweet, sugary liquid produced at the base of the petals 4. Pollen: contains the male gametes of the flower 5. Ovules: present inside the ovary, contains the female gamete 6. Pollination: the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma 7. Female part of the flower consists of: 8. Stigma Style Ovary Male part of the flower consists of: Anther Filament Topic: 1.4 Page: 13 Question and Answers Q1. Explain the difference between a plant and flower? Plant is vegetative part of plant. Whereas, Flower is the reproductive part of the plant. Flowers are the most evolved reproductive system in the plant world, with separate male and female organs, however a flower is only part of a plant and does not have an independent life of it's own Q2: Suggest how the scent from the flowers spreads out into the air around them? A flower's fragrance is made up of volatile chemicals produced in sacs in the flower. These chemicals evaporate in the air and produce scent. Each species of flower has its own scent. Within that species, each flower has its own unique scent Pollination Topic: 1.5 Pages 14 - 15 Question and answers Q1: Where are the female gametes present in the flower? Inside the ovules present in the ovary Q2: Where are the male gametes present in the flower? Inside the pollen grains produced by the anther Q3: Explain why plants need help to move their male gametes to the female gametes? The male gametes cannot move by themselves, therefore the flowers make use of insects, birds or the wind to move their pollen grains Q4: Suggest reasons for the differences between the wind pollinated and insect pollinated flowers. The insect pollinated flowers have large brightly colored petals with sweet smelling nectar in order to attract bees and insects. They also have sticky and spiky pollen grains which can easily stick to the bodies of insects. In contrast, the wind pollinated flowers have dull colors and pollen produced is light in weight so that it can easily be blown away by the wind Fertilization Topic: 1.6 Pages: 16 - 17 Key Terms: 1. Fertilization: when the nucleus of male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form a zygote 2. Zygote: a fertilized cell formed by the fusion of male and female gametes 3. Gamete: a reproductive cell 4. Embryo: an initial stage of development of a multicellular organisms. When the zygote starts to divide , it produces a small group of cells called an embryo. 5. Seed: the ovule gradually grows into a seed 6. Testa: tough outer coat of the seed 7. Micropyle: a tiny hole where the pollen tube grew into the ovule 8. Cotyledons: contain the food stores for the embryo to use when it starts to grow Explain the process of fertilization When a flower has been pollinated, there are pollen grains on its stigma. These pollen grains grow out a pollen tube through the stigma downwards the style and into the ovary. Inside the ovary, within the ovule, the nuclei of the male and the female gamete fuse together to form a zygote. Questions and Answers Topic: 1.6 Pages 16 - 17 Q1: What is the name of the male gametes: in humans: in flowers: Q2: What is the name of the female gametes in humans in flowers: Q3: Where does fertilization occur in the humans: flowers: Fruits Topic: 1.7 Pages:18 - 19 Ovule develops into a seed Ovary changes into a fruit Every plant requires water, light and mineral salts in order to grow well The new plants need to be dispersed away from the parent plant so that they do not compete with each other for the essential resources. Fruits have adaptations to help the seeds inside them disperse to new places 1. Wind-dispersed seeds Fruits contain seeds, and usually have a parachute or a wing to help them be carried away from the parent plant by the wind. Examples: dandelion, sycamore The dandelion fruit has a group of fine hairs called a pappus, which catches the wind and acts like a parachute. The fruit counterbalances the pappus. The sycamore has a wing with a large surface area. When the fruit drops off the tree it spins, slowing down in descent. If caught by the wind the seed will be carried away from the parent plant, reducing competition for nutrients, water and light. Animal-dispersed seeds There are 2 main modification of fruits for animal dispersal: succulent fruits and hooked fruits Succulent fruits attract animals because they are brightly coloured, juicy and nutritious. When eaten, the seed pass through animal’s faeces, which may be a long way from the parent plant. The faeces provides nutrients when the seeds germinate. Hooked fruits catch on to an animal’s fur as it brushes past the parent plant. Eventually the seeds drops off, or the animal grooms itself to remove them. This disperses the seeds away from the parent plant. Plant Lifecycle Questions and Answers Q1: Which of these are fruits? orange mango tomato bean pod Q2: a) What is meant by seed dispersal? b) Why is seed dispersal important for plants? c) List three ways in which fruits can help with seed dispersal? potato Practice Questions Complete the flow chart Seed germination Pollination Fertilization State the different methods of dispersal with examples Name the equipment which can be used to measure time Which gas is produced in photosynthesis? Seed Formation Which part of the flower produces pollen grains? How does it reach the ovary? State the function of the following parts of the plant: 1. Flower 2. Leaf 3. Root 4. Stem Differentiate between pollination and fertilization Give two examples of mineral salts that are needed by plants? How is water used in the plant? Practice Questions stigma style ovary fertilization pollination dispersal chlorophyll proteins Plant A is photosynthesizing at a greater rate since it has more chlorophyll There’s also something in the air Joseph Priestly His experiments included placing a lit candle inside a closed jar. The flame quickly went out and Priestley concluded that the air inside the jar had been “injured”. He conducted similar experiments with mice and concluded that the mice had also “injured” the air. Priestley later discovered that plants could be used to restore air that was “injured” by the candle and the mice. In 1774, the results of Priestley’s experiments were published in “Experiments and Observations of Different Kinds of Air, Volume I.” Although Priestley did not know it at the time, his experiments proved that air contains oxygen.