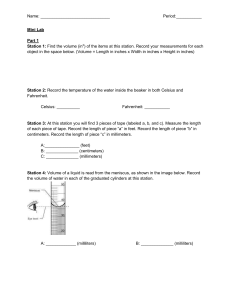
Key Terms Meter (m): The unit of length, used for measuring distances. Kilogram (kg): The unit of mass, used for measuring the amount of matter in an object. Second (s): The unit of time, used for measuring the duration of events or processes. Ampere (A): The unit of electric current, used for measuring the flow of electric charge. Kelvin (K): The unit of temperature, used for measuring temperature on an absolute scale. Mole (mol): The unit of amount of substance, used for measuring the number of atoms, molecules, or other entities in a sample. Candela (cd): The unit of luminous intensity, used for measuring the brightness of light. Accuracy: The degree of closeness between a measured or calculated value and the true value of a quantity. Ampere: The SI unit of electric current. Constant: A fixed value that does not change in an equation or experiment. Conversion Factor: A ratio used to convert one unit of measurement to another. Dependent Variable: A variable in an experiment that is observed or measured and depends on the independent variable. Derived Units: Units that are combinations of base units and are used to measure various physical quantities. English Units: The traditional system of units used in the United States, which includes units like inches, feet, and pounds. Exponential Relationship: A mathematical relationship in which one variable is raised to a power. Fundamental Physical Units: The base units in the SI system, such as meter, kilogram, and second. Independent Variable: A variable in an experiment that is deliberately changed or manipulated. Inverse Relationship: A mathematical relationship where one variable increases as the other decreases. Inversely Proportional: A relationship in which the product of two variables is constant. Kilogram: The SI unit of mass. Linear Relationship: A mathematical relationship in which two variables are directly proportional and form a straight line when graphed. Meter: The SI unit of length. Method of Adding Percents: A method used to calculate the combined uncertainty of measurements. Order of Magnitude: A rough estimate of the size or scale of a quantity. Precision: The degree to which repeated measurements under the same conditions show the same result. Scientific Notation: A way of expressing numbers as a coefficient multiplied by a power of 10. Second: The SI unit of time. SI Units: The International System of Units, a standardized system of measurement. Significant Figures: The meaningful digits in a measured or calculated quantity. Slope: The steepness of a line on a graph. Uncertainty: The range within which the true value of a measurement is likely to fall. Variable: A factor that can change in an experiment or equation. Y-Intercept: The point where a line crosses the y-axis on a graph. Physical Quantities and Measurements Vocabulary Worksheet Instructions Fill in the blanks with the appropriate vocabulary term from the list provided. 1. _______________: The degree of closeness between a measured or calculated value and the true value of a quantity. 2. _______________: The SI unit of electric current. 3. _______________: A fixed value that does not change in an equation or experiment. 4. _______________: A ratio used to convert one unit of measurement to another. 5. _______________: A variable in an experiment that is observed or measured and depends on the independent variable. 6. _______________: Units that are combinations of base units and are used to measure various physical quantities. 7. _______________: The traditional system of units used in the United States, which includes units like inches, feet, and pounds. 8. _______________: A mathematical relationship in which one variable is raised to a power. 9. _______________: The base units in the SI system, such as meter, kilogram, and second. 10. _______________: A variable in an experiment that is deliberately changed or manipulated. 11. _______________: A mathematical relationship where one variable increases as the other decreases. 12. _______________: A relationship in which the product of two variables is constant. 13. _______________: The SI unit of mass. 14. _______________: A mathematical relationship in which two variables are directly proportional and form a straight line when graphed. 15. _______________: The SI unit of length **Answer Key:** 1. Accuracy 2. Ampere 3. Constant 4. Conversion Factor 5. Dependent Variable 6. Derived Units 7. English Units 8. Exponential Relationship 9. Fundamental Physical Units 10. Independent Variable 11. Inverse Relationship 12. Inversely Proportional 13. Kilogram 14. Linear Relationship 15. Meter Worksheet 1 Unit Conversions Instructions: Convert the following quantities from one unit to another using the appropriate conversion factors. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth, if necessary. 1. Convert 500 millimeters to meters. 2. Convert 2.5 kilometers to meters. 3. Convert 750 grams to kilograms. 4. Convert 3.2 liters to milliliters. 5. Convert 150 centimeters to meters. 6. Convert 0.045 kilograms to grams. 7. Convert 8000 milligrams to grams. 8. Convert 5.75 meters to centimeters. 9. Convert 0.006 kilometers to millimeters. 10. Convert 2.3 liters to liters. The step-by-step procedure to convert each of the quantities from one unit to another: 1. Convert 500 millimeters to meters: To convert from millimeters (mm) to meters (m), you need to divide by 1000 (since there are 1000 millimeters in a meter). 500 mm ÷ 1000 = 0.5 meters So, 500 millimeters is equal to 0.5 meters. 2. Convert 2.5 kilometers to meters: To convert from kilometers (km) to meters (m), you need to multiply by 1000 (since there are 1000 meters in a kilometer). 2.5 km × 1000 = 2500 meters So, 2.5 kilometers is equal to 2500 meters. 3. Convert 750 grams to kilograms: To convert from grams (g) to kilograms (kg), you need to divide by 1000 (since there are 1000 grams in a kilogram). 750 g ÷ 1000 = 0.75 kilograms So, 750 grams is equal to 0.75 kilograms. 4. Convert 3.2 liters to milliliters: To convert from liters (L) to milliliters (mL), you need to multiply by 1000 (since there are 1000 milliliters in a liter). 3.2 L × 1000 = 3200 milliliters So, 3.2 liters is equal to 3200 milliliters. 5. Convert 150 centimeters to meters: To convert from centimeters (cm) to meters (m), you need to divide by 100 (since there are 100 centimeters in a meter). 150 cm ÷ 100 = 1.5 meters So, 150 centimeters is equal to 1.5 meters. 6. Convert 0.045 kilograms to grams: To convert from kilograms (kg) to grams (g), you need to multiply by 1000 (since there are 1000 grams in a kilogram). 0.045 kg × 1000 = 45 grams So, 0.045 kilograms is equal to 45 grams. 7. Convert 8000 milligrams to grams: To convert from milligrams (mg) to grams (g), you need to divide by 1000 (since there are 1000 milligrams in a gram). 8000 mg ÷ 1000 = 8 grams So, 8000 milligrams is equal to 8 grams. 8. Convert 5.75 meters to centimeters: To convert from meters (m) to centimeters (cm), you need to multiply by 100 (since there are 100 centimeters in a meter). 5.75 m × 100 = 575 centimeters So, 5.75 meters is equal to 575 centimeters. 9. Convert 0.006 kilometers to millimeters: To convert from kilometers (km) to millimeters (mm), you need to multiply by 1,000,000 (since there are 1,000,000 millimeters in a kilometer). 0.006 km × 1,000,000 = 6000 millimeters So, 0.006 kilometers is equal to 6000 millimeters. 10. Convert 2.3 liters to liters: No conversion is needed in this case since you're converting from liters to liters. The answer is 2.3 liters.