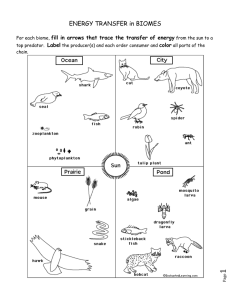
Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem ● Module 2, Lesson 2 Flow of Energy in an Ecosystem This presentation discusses the flow of energy in an ecosystem, including the models of energy flow, autotrophs and heterotrophs, food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids. It also covers the principles of ecology. Energy in an Ecosystem Models of Energy Flow -Autotrophs and heterotrophs are involved in energy flows in ecosystems, which include food chains, food webs, and ecological pyramids. Energy in an Ecosystem ● Autotrophs collect energy from sunight or inorganic substances to produce food. ● Are the foundation of ecosystems because they make energy available for all other organisms ● Green plants and algae that produce their own food are autotrophs. ● Autotrophs are producers. ● ● Heterotrophs consume other organisms for energy. Heterotrophs are consumers. Are predators; make up remaining levels. ● Herbivores eat plants. ● Carnivores prey on other heterotrophs. ● Omnivores eat both plants and animals. ● Detritivores (decomposers) eat fragments of dead matter. -Decomposers break down dead organisms and waste materials, returning nutrients back into the ecosystem. ● Models of Energy Flow 1. Food chains show how energy flows through an ecosystem. -Each step is called a trophic level. -The first trophic level in any ecosystem is autotrophs. -The remaining levels are heterotrophs. Models of Energy Flow 2. Food webs show interconnected food chains; shows pathway of energy flow through a group of organisms. 3. Ecological Pyramids ● ● ● Ecological pyramids show energy flow through an ecosystem from lower to higher trophic levels. Shows relative amount or energy, number of organisms or biomass (mass of living matter) at each level. Only 10% of energy passes from one level to the next. At each higher step, some energy are lost to the environment as heat. Thank you for your time 😊