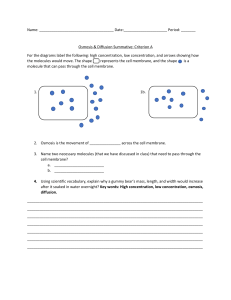
Biology Osmosis movement of H O across a membrane so there’s the same amount of H O on both sides of the membrane/movement of water across a membrane from high to low concentration until evenly distributed. Diffusion movement of molecules from high to low concentration. E.g. if someone sprays perfume at one end of the room, the molecules will spread until they are evenly distributed through the room. Facilitated osmosis (type of passive transport) An enzyme called permease binds to the membrane opening so that molecules that were too big to fit through now can fit through. E.g. when glucose is moved into the liver Bulk transport the movement of large quantities of materials into or out of the cell. Passive transport movement of molecules across a cell membrane along a concentration gradient. Cell uses no energy since it’s going for high to low concentration e.g. diffusion, osmosis Active transport movement of molecules across a cell membrane against the concentration gradient. Uses energy since going from low to high concentration. Exocytosis materials in cell are expelled e.g. waste Endocytosis (type of active transport) process to bring substances into cell. (2 types) 1. pinocytosis – brings in very small substances (fluids, dissolved materials) 2. phagocytosis – brings in larger substances e.g. bacteria ● material attaches to cell membrane causing it to bulge in thereby producing a vacuole enclosing the material. The vacuole is released into the cytoplasm. Lysosomes fuse to the vacuole and release enzymes to break down inner contents.