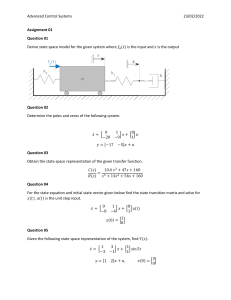
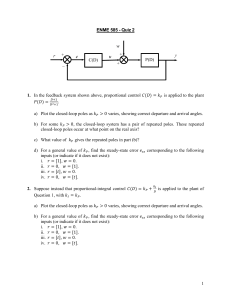
ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Thursday, Jan. 26, 2012 Solution to Quiz #1 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Question 1: Which of the following statements is FALSE? A system is stable, [C] (A) then all output signals are bounded (B) then all errors are bounded (C) then most output signals are bounded (D) then all subsystems are stable Question 2: For a dynamic system, its present outputs are the result of [B] (A) its present inputs only (B) its previous and present inputs (C) its previous, present and future inputs (D) none of the above Question 3: Which of the following statements is FALSE? The closed-loop control system will be able to [A] (A) reduce the cost of the system (B) reject the disturbance (C) reduce the steady-state error (D) improve the sensitivity to system parameter variations Question 4: Which of the following statements is FALSE? For an open-loop control system, [A] (A) it requires sensors to measure the system outputs (B) it is simpler than a closed-loop system (C) it can be calibrated if it does not perform satisfactorily (D) its control signals do not depend on the system performance Question 5: The input and output of a system are X(s) and Y(s), respectively. Then the system transfer function is given by [C] (C) Y(s)/X(s); (D) X(s)/Y(s) (A) Y(s)-X(s); (B) X(s)-Y(s); ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Thursday, Feb. 2, 2012 Solution to Quiz #2 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Question 1: For block diagram models of a system, a block represents (A) a variable of the system; (B) the transfer function of a component; (C) the direction of a signal; (D) the sign of a variable Question 2: For signal-flow graph models of a system, a node represents (B) the transfer function of a component; (A) a variable of the system; (C) the direction of a signal; (D) the sign of variable Question 3: Which of the following statements are TRUE? For a given system, (A) its state variable model and transfer function are unique (B) its state variable model and transfer function are NOT unique (C) its state variable model is unique, but its transfer function is NOT unique (D) its state variable model is NOT unique, but its transfer function is unique Question 4: An n-th order system has m input variables and l output variables, then the number of state variables for its state variable model is (A) m; (B) n; (C) l; (D) unknown Question 5: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ) , its stability depends on (A) A, B and C; (B) A and B only; (C) A and C only; (D) A only [B] [A] [D] [B] [D] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Thursday, Feb. 9, 2012 Solution to Quiz #3 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ) , which parameters depend on the selection of state variables? [A] (A) A, B and C; (B) A and B only; (C) A and C only; (D) A only Q2: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ) , its system matrix is (A) A; (B) B; (C) C; (D) unknown [A] Q3: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ) , its transfer function is a function of [A] (B) A and B only; (C) A and C only; (D) A only (A) A, B and C; Q4: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ) , its fundamental matrix a function of (A) A, B and C; (B) A and B only; (C) A and C only; (D) A only is [D] Q5: For a system X (t ) AX (t ) Bu (t ); y(t ) CX (t ); X (0) X 0 , its system response Y(s) depends [C] (A) on X 0 only; (B) on U(s) only; (C) linearly on U(s) and X 0 ; (D) nonlinearly on U(s) and X 0 ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Thursday, Feb. 16, 2012 Solution to Quiz #4 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Question 1: The poles of an under-damped 2nd order system are on the left half of the s-plane. The time constant of the system is determined by [B] (A) the distance from a pole to the Origin (B) only the real part of the poles (C) only the imaginary part of the poles (D) both the real and imaginary parts of the poles Question 2: The poles of an under-damped 2nd order system are on the left half of the s-plane. The natural frequency of the system is equal to [A] (A) the distance from a pole to the Origin (B) only the real part of the poles (C) only the imaginary part of the poles (D) both the real and imaginary parts of the poles Question 3: The poles of an under-damped 2nd order system are on the left half of the s-plane. The damped frequency of the system is equal to [C] (A) the distance from a pole to the Origin (B) only the real part of the poles (C) only the imaginary part of the poles (D) both the real and imaginary parts of the poles Question 4: For the response of an under-damped 2nd order system, the swiftness is represented by [B] (A) the time constant and the percentage overshoot (B) the rise time and the peak time (C) the settling time and the steady state error (D) the rise time and settling time Question 5: For a 2nd order system G( s) (A) undamped (C) critically damped n2 , if 2 , then it is s 2 2 n s n2 (B) under damped (D) over damped [D] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Tuesday, March 6, 2012 Solution to Quiz #5 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: For a control system below (input: R(s); output: Y(s)), the closed-loop transfer function is (A) (B) (C) (D) GcG GcGH GcG/(1+GH) GcG/(1+GcGH) Q2: For a control system in Q1, output: Y(s) resulted from the disturbance Td(s) is (A) TdG (C) TdGcG/(1+GcGH) T G G Gc (B) T Gc Gc T [D] (B) TdGcG/(1+GH) (D) TdG/(1+GcGH) Q3: For a control system in Q1, the sensitivity of closed-loop transfer function T to the controller Gc is given by (A) [D] (C) T Gc G H (D) [B] T H H Gc Q4: Which of the statement is FALSE? With a feedback control, (A) the system is more sensitive to parameter variation (B) the system can have a faster transient response (C) the system can reject disturbance better (D) the system can have smaller steady state error Q5: For the response of an under-damped 2nd order system, the closesness is represented by (A) the settling time and the percentage overshoot (B) the percentage overshoot and the steady state error (C) the time constant and the steady state error (D) the overshoot and the settling time [A] [A] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Tuesday, March 13, 2012 Solution to Quiz #6 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: The type number N of a unity feedback system is defined as (A) (B) (C) (D) [C] the number of poles at Origin of the closed-loop transfer function T(s). the number of zeros at Origin of the closed-loop transfer function T(s). the number of poles at Origin of the plant transfer function G(s). the number of zeros at Origin of the plant transfer function G(s). Q2: If NOT ALL the poles of the closed-loop transfer function of a system are on the left half of s-plane, then this system is (A) stable (C) not stable [C] (B) marginally stable (D) unstable Q3: In the optimal control design of a system, if the performance index is chosen T as I te 2 (t )dt , then which of the statements about the design is TRUE? [B] 0 (A) (B) (C) (D) it only consider the total square of errors it emphasizes errors occurring later in the response it does not consider the actual system output it does not consider the desired system output Q4: The characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system is Q(s)=a4s4+…+ a1s +a0. If a0, a1, a2, a3 and a4 are positive, then [D] (A) the system is stable (C) the system is not stable (B) the system is unstable (D) the stability cannot be determined Q5: The characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system is Q(s)=a4s4+…+ a1s +a0. If a1=0, and a0, a2, a3 and a4 are positive, then [C] (B) the system is stable (C) the system is not stable (B) the system is unstable (D) the stability cannot be determined ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Tuesday, March 20, 2012 Quiz #7 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: The characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system is Q(s)=a4s4+…+ a1s +a0. If a1<0, and a0, a2, a3 and a4 are positive, then (A) the system is stable (B) the system is unstable (C) the system is not stable (D) the stability cannot be determined Q2: In the Routh-Hurwitz criterion, the number of sign changes in the first column of the Routh array is equal to (A) the number of poles on the imaginary axis (B) the number of poles on the real axis (C) the number of poles on the right half s-plane (D) the number of poles on the left half s-plane Q3: If the closed-loop transfer function of a system has no poles on the left half of s-plane, then this system is (A) stable (B) marginally stable (D) not unstable (C) not stable Q4: The characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system is Q(s)=a4s4+…+ a1s +a0. If a0, a1, a2, a3 and a4 are positive, then (A) the system is stable (B) the system is unstable (C) the system is not stable (D) the stability cannot be determined Q5: For the Routh Array of the characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system, if one row has all zero elements, then (A) this system is unstable (B) this system is stable (C) this system has an auxiliary polynomial (D) this system has poles on the imaginary axis [B] [C] [C] [D] [C] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Tuesday, March 27, 2012 Quiz #8 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: The root locus originates on (A) the poles of the loop transfer function (B) the zeros of the loop transfer function (C) the poles and zeroes of the loop transfer function (D) the poles, zeroes and Origin of the loop transfer function Q2: In the root locus method, a root locus is a plot of the roots as (A) the time t varies from 0 to infinity (B) the input signal r(t) varies from 0 to infinity (C) the frequency varies from 0 to infinity (D) the control gain K varies from 0 to infinity Q3: The critical frequencies in the root locus method are defined as the frequencies at (A) the zeros only (B) the poles only (C) the poles and zeros (D) the poles, zeros and origin Q4: The root locus is a plot of the roots of (A) the plant transfer function (B) the loop transfer function (C) the closed-loop transfer function (D) the open-loop transfer function Q5: In the Routh-Hurwitz criterion, the number of sign changes in the first column of the Routh array is equal to (A) the number of poles on the imaginary axis (B) the number of poles on the real axis (C) the number of poles on the right half s-plane (D) the number of poles on the left half s-plane [A] [D] [C] [C] [C] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Tuesday, April 3, 2012 Quiz #9 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: The frequency response method studies a system’s (A) the steady-state responses to any input signals (B) the steady-state responses to sinusoidal signals (C) the transient and steady-state responses to any input signals (D) the transient and steady-state responses to sinusoidal signals Q2: The breaking frequencies in frequency response method (Bode plot) are defined as the frequencies at (A) the zeros only (B) the poles only (C) the poles and zeros (D) the poles, zeros and origin Q3: The bandwidth is defined as the frequency at which the gain is equal to _____ times the gain at the low frequency (A) 1/4; (B) 1 / 2 ; (C) 1/2; (D) 2 Q4: In the frequency response method, for the magnitude diagram (dB) of a Pole at Origin, which statement is TRUE: (A) It is a straight line with slope at 20 and passes the axis at =0 (B) It is a straight line with slope at 20 and passes the axis at =1 (C) It is a straight line with slope at -20 and passes the axis at =0 (D) It is a straight line with slope at -20 and passes the axis at =1 Q5: In the frequency response method, for the phase diagram of a positive gain, which statement is TRUE: (A) Its phase is a constant 0 degree (B) Its phase is a constant 90 degree (C) Its phase is a constant -90 degree (D) Its phase is a constant 180 degree [B] [C] [B] [D] [A] ENGG*3410 Systems and Control Theory (Winter 2012) Thursday, April 5, 2012 Solution to Quiz #10 Multiple Choice Questions: Select only ONE choice. Q1: For a 2nd order system G( s) (A) undamped (C) critically damped n2 , if 1 , then it is s 2 2 n s n2 [C] (B) under damped (D) over damped Q2: The characteristic polynomial of a closed-loop transfer function of a system is [D] Q(s)=a4s4+…+ a1s +a0. If a0, a1, a2, a3 and a4 are positive, then (A) the system is stable (B) the system is unstable (C) the system is not stable (D) the stability cannot be determined Q3: The frequency response method studies a system’s [B] (A) the steady-state responses to any input signals (B) the steady-state responses to sinusoidal signals (C) the transient and steady-state responses to any input signals (D) the transient and steady-state responses to sinusoidal signals Q4: In the root locus method, a root locus is a plot of the roots as [D] (A) the time t varies from 0 to infinity (B) the input signal r(t) varies from 0 to infinity (C) the frequency varies from 0 to infinity (D) the control gain K varies from 0 to infinity Q5: In the Routh-Hurwitz criterion, the number of sign changes in the first column of the Routh array is equal to [C] (A) the number of poles on the imaginary axis (B) the number of poles on the real axis (C) the number of poles on the right half s-plane (D) the number of poles on the left half s-plane