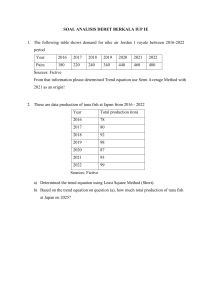
CCT112 Introduction to Management in the Networked Information Economy Introduction and Course Overview Module 1: Managers and You in the Workplace Professor: Sarah Cherki El Idrissi 2 A Little about Me • 2nd year at UTM • Professor at the Digital Enterprise Management (DEM) program • PhD in Management Information systems • Consultant/Project Management of Information Systems projects • Research: Green Information Systems Persuasive Systems Responsible Innovation Pedagogical Innovation Sustainability Course Objectives • Define the main management's functions. • Use a systemic approach to examine the impact of external and internal factors on organizations • Assess the impact of technological innovation on management practices • Critique management practices and trends • Identify and apply specific strategies for collaborating with peers • Reflect on personal development and skills over the duration of the course. Assessments • Individual assessments: Test 1 (30%) – 26 May Test 2 (30%) – 16 June Weekly Quizzes (15%) • Group assessments: Weekly tutorials (25%) Office Hours • Wednesdays from 1h30 pm to 2 pm by appointment. Teaching Assistants Ahmad Tahir Ahmad.tahir@mail.utoronto.ca Nofel Wasey Nofel.wasey@utoronto.ca Management Fifteenth Edition Chapter 1 Managers and You in the Workplace Copyright © 2021. 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objectives 1 Tell who managers are and where they work. 2 Explain why managers are essential to organizations. 3 Describe the functions, roles, and skills of managers. 4 Describe the factors that are reshaping and redefining the manager’s job. 5 Explain the value of studying management. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objective 1 • Tell who managers are and where they work. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Who Is a Manager? Manager: someone who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplished Where do we find managers? Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.1 Levels of Management Exhibit 1.1 shows that in traditionally structured organizations, managers can be classified as first-line, middle, or top. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Classifying Managers • First-Line Managers: manage the work of non-managerial employees. Ex: shift managers, district managers, department managers, or office managers. • Middle Managers: manage the work of first-line managers. Ex: regional manager, project leader, store manager, or division manager • Top Managers: responsible for making organization-wide decisions and establishing plans and goals that affect the entire organization. Ex: executive vice president, president, managing director, chief operating officer, or chief executive. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Where Do Managers Work? • Organization: a deliberate arrangement of people to accomplish some specific purpose. Ex: – Colleges, universities, fraternities, sororities. – Government departments – Religious organizations – Neighborhood grocery store – Sports teams – Clinics Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.2 Characteristics of Organizations Exhibit 1.2 shows the three common characteristics of organizations: distinct purpose, deliberate structure, and people. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objective 2 • Explain why managers are important to organizations. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Why Are Managers Important? • Organizations need their managerial skills and abilities now more than ever • Managers are critical to getting things done. – Normalization of remote work – Acceleration in the use of technology to manage employees – Employees’ changing expectations Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objective 3 • Describe the functions, roles, and skills of managers. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved What Do Managers Do? • Management involves coordinating and overseeing the work activities of others so that their activities are completed efficiently and effectively. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved https://hbr.org/2021/04/what-does-it-mean-to-be-a-manager-today Efficiency and Effectiveness • Efficiency: doing things right – getting the most output from the least amount of input • Effectiveness: doing the right things – attaining organizational goals Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.4 Efficiency and Effectiveness in Management Exhibit 1.4 shows that whereas efficiency is concerned with the means of getting things done, effectiveness is concerned with the ends, or attainment of organizational goals. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Management Functions • Planning: Defining goals, establishing strategies to achieve goals, and developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities • Organizing: Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational goals • Leading: Working with and through people to accomplish goals • Controlling: Monitoring, comparing, and correcting work Henry Fayol Source: Wikipedia Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.5 Four Functions of Management Exhibit 1.5 shows the four functions used to describe a manager’s work: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles and a Contemporary Model of Managing • Roles: specific actions or behaviors expected of and exhibited by a manager • Mintzberg identified 10 roles grouped around interpersonal relationships, the transfer of information, and decision making Henry Mintzberg John Cleghorn Professor of Management Studies (Strategy & Organization); Faculty Director (International Masters for Health Leadership) Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.6 Mintzberg’s Managerial Roles Exhibit 1.6 shows the managerial roles identified by Mintzberg. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Types of Roles • Interpersonal – Figurehead, leader, liaison • Informational – Monitor, disseminator, spokesperson • Decisional – Entrepreneur, disturbance handler, resource allocator, negotiator Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Management Skills • Technical skills – Knowledge and proficiency in a specific field • Human skills – The ability to work well with other people • Conceptual skills – The ability to think and conceptualize about abstract and complex situations concerning the organization Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.7 Skills Needed at Different Managerial Levels Exhibit 1.7 shows the relationships of conceptual, human, and technical skills to managerial levels. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Interactive Session: • If you’ve worked for a manager, played for a coach, or been part of a group that had a leader, you’ve probably noticed management skills that those individuals could have improved. Discuss your experience with both good and bad managers: 1. Make a list of both good and bad management behaviors 2. Relate the behaviors you selected to functions of management and which management skills you think it falls under. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Interactive Session: Good Experiences Bad Experiences Functions Skills Functions What could have been done differently Skills Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objective 4 • Describe the factors that are reshaping and redefining the manager’s job. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved In the Near Future… • Cell-based management app showing: • Status of projects • Percentage benefits • Key performance indicators • Moral level • Buy-in of stakeholders level AI-generated: https://www.fotor.com https://hbr.org/2023/02/how-ai-will-transform-project-management Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved In the Near Future…(2) • Self-adjustments based on parameters chosen by the project manager and the project team • Prioritization based on potential risks • Recommendations to speed up project streams • Plan updates sent automatically to project stakeholders AI-generated: https://www.fotor.com https://hbr.org/2023/02/how-ai-will-transform-project-management Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Challenges Facing Managers Today and into the Future • Focus on technology • Focus on disruptive innovation • Focus on social media • Focus on ethics • Focus on political uncertainty • Focus on the customer Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Technology • Managers must get employees on board with new technology • Managers must oversee the social interactions and challenges involved in using collaborative technologies “The job of a manager is to help people cross the bridge—to get them comfortable with the technology, to get them using it, and to help them understand how it makes their lives better.” Didier Bonnet, coauthor of Leading Challenge Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Technology: AI How can AI be used to enhance management? Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Technology: AI (2) • Decision-making: • IBM's Watson platform is being used by businesses to provide data-driven insights and analytics to help them make better decisions. • Netflix uses AI algorithms to recommend movies and TV shows to its users. The algorithms analyze user data to identify their preferences and recommend content that they are likely to enjoy. • Efficiency: • UPS is using AI technologies to optimize its delivery routes and reduce the amount of time and fuel required to make deliveries. • Amazon is using AI-powered robots in its warehouses to improve efficiency and reduce the time it takes to process orders. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Technology: AI (2) • Resource allocation: • Procter & Gamble uses AI technologies to optimize its marketing campaigns and create more targeted and effective advertisements. • Customer service: • AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide customers with 24/7 support, reducing the burden on human customer service representatives. • AI-powered sentiment analysis can help managers understand customer feedback and improve their products and services accordingly. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Technology: AI (3) • Workplace automation: • UiPath, a global software company that provides a platform for robotic process automation (RPA). With the help of AI, managers can automate many tasks and processes, reducing the need for human intervention. This can lead to increased productivity and cost savings for businesses. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Disruptive Innovation • One of the most critical challenges facing managers today is dealing with disruptive innovation • Disruptive innovation involves new products, processes, or services that radically change the rules of the game Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Social Media • Social media: forms of electronic communication through which users create online communities to share ideas, information, personal messages, and other content How can social media be used in the workplace? Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Ethics • We commonly see unethical business practices in the news • Examples include pharmaceutical firms raising drug prices by 500% or someone turning in fake receipts for expenses • Organizational survival depends on building trust with customers, clients, suppliers, employees, and other stakeholders Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on Political Uncertainty • In the past, major democratic nations like the US, Canada, and the UK have been relatively stable politically • In the last 10 years these countries have shifted to greater political uncertainty • Brexit and the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) are examples of that shift Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Focus on the Customer • Without customers, most organizations would cease to exist • Managing customer relationships is the responsibility of all managers and employees • Consistent, high-quality customer service is essential • Demographics has a significant impact on how managers manage and include such factors as age, income, sex, race, education level, ethnic makeup, employment status, geographic location, and more Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Learning Objective 5 • Explain the value of studying management. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved The Universality of Management • The reality that management is needed in all types and sizes of organizations, at all organizational levels, in all organizational areas, and in organizations no matter where located Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Exhibit 1.8 Universal Need for Management Exhibit 1.8 shows that management is universally needed in all types of, and throughout all areas of, organizations. Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved The Reality of Work • When you begin your career, you will either manage or be managed • Students need to understand management principles regardless of career choice Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Rewards of Being a Manager • Responsible for creating a productive work environment • Recognition and status in your organization and in the community • Attractive compensation in the form of salaries, bonuses, and stock options Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Next Session…. • MyLab activities Copyright © 2021, 2018, 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved