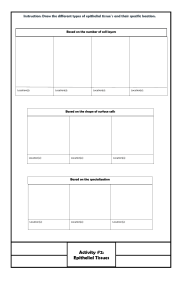
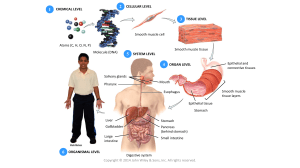
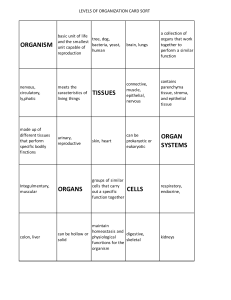
EPITHELIAL TISSUE DEFINITION ❑ Epithelial tissues form the covering of the surfaces of the body located both in internal and external parts. One example is skin found in the uppermost layer of the body which made of epithelial cells. DEFINITION ❑ ❑ Packed tightly (to no intercellular space) Act as a barrier against mechanical injury, microbes, and fluid loss ❑ It has a free surface that is exposed to air or fluid ❑ Cells are attached to a basement membrane. ❑ Avascular – not associate with blood vessel THREE BASIC SHAPES ✓ Flattened, central nucleus ✓ Delicate and thin sheet of cells Location: • Lung alveoli • Blood vessels • Buccal mucosa Functions: • Diffusion • Gas exchange ✓ Cube-shaped, central ✓ Spherical nucleus Locations: • Linings of kidney tubules and ducts • Salivary glands Functions: • Secretion • Absorption ✓ Oval nucleus near at basal end ✓ Apical surface may have cilia or microvilli Locations: • Digestive tract • Upper respiratory tract • Oviducts Functions: • Absorption • Secretion TYPES OF LAYERING TYPES OF LAYERING TYPES OF LAYERING NAMING OF A EPITHELIAL TISSUE First name: Number of layers. ❑ Last name: Shape of its cells. ❑ Example: Simple squamous epithelium. ❑ MUSCULAR TISSUE The muscle tissues are composed of muscle cells that are designed for contraction and movement. These can help us to do the work. The muscle cells are also called muscle fibers.