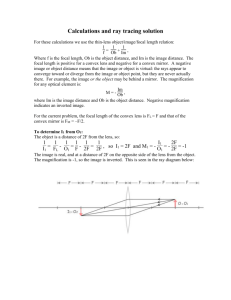
MAGNIFICATION EQUATION Magnification The magnification M of an image is the ratio of the height of the image the height of the object: This number is a dimensionless ratio (a length over a length) and does not have any units. To calculate M for virtual images, consider the diagram below: From similar triangles: Remember! ✔ +di = real image located in front of the mirror ✔ -di = virtual image located behind the mirror ✔ +hi = upright virtual image located behind the mirror ✔ -hi = inverted real image located in front of the mirror ✔ +f = Concave lens ✔ -f = Convex lens ✔ +M = Upright image ✔ -M = Inverted Image ✔ M greater than 1 = Image is LARGER than Object ✔ M between 0 & 1 = Image is SMALLER than Object Magnification: Magnification This result also holds for real images: Rule: The magnification factor M of a lens is always positive and given by: From the diagram, using similar triangles: Sample Problems A concave mirror produces an inverted image that is magnified 2.5 fold. Determine the image distance if the original object was placed 4.0 cm in front of the mirror. Given: Equation: M = (-2.5) do = 4.0 cm Asked: Image distance ? Derive: Substitute: di = -(M x do) di = - ( (-2.5) x 4.5 cm ) = 10 cm Therefore, the image is 10 cm from the mirror. Sample Problems Determine the image height for a 5.00 cm tall object placed 45.0 cm from the concave mirror if the image is real and is 22.5 cm from the mirror. Given: ho = 5.00 cm do = 45.0 cm Equation: Derive: Substitute: hi = -(di x ho)/do hi = -(22.5 cm x 5.00 cm)/45.0 cm = -2.50 cm di = 5.00 cm Therefore, the height of the Asked: Image height ? inverted image is 2.50 cm