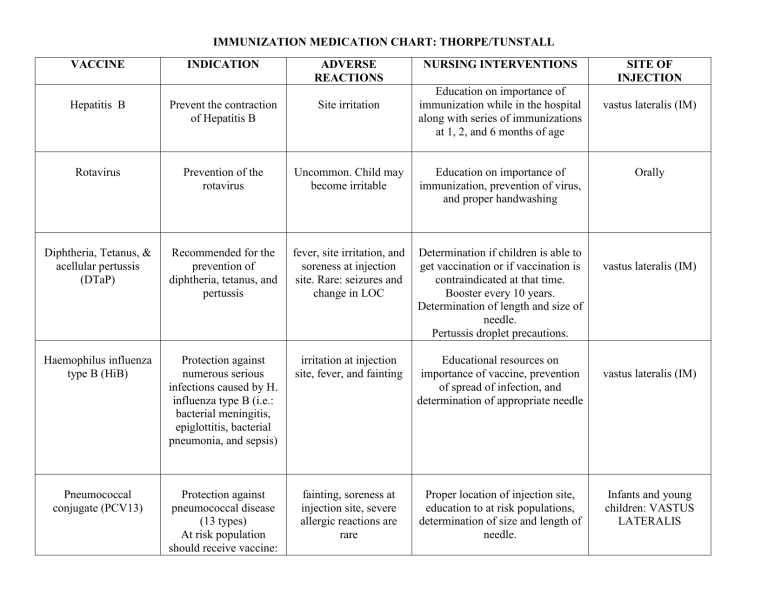
IMMUNIZATION MEDICATION CHART: THORPE/TUNSTALL VACCINE INDICATION ADVERSE REACTIONS NURSING INTERVENTIONS Education on importance of immunization while in the hospital along with series of immunizations at 1, 2, and 6 months of age Hepatitis B Prevent the contraction of Hepatitis B Site irritation Rotavirus Prevention of the rotavirus Uncommon. Child may become irritable Education on importance of immunization, prevention of virus, and proper handwashing Diphtheria, Tetanus, & acellular pertussis (DTaP) Recommended for the prevention of diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis fever, site irritation, and soreness at injection site. Rare: seizures and change in LOC Determination if children is able to get vaccination or if vaccination is contraindicated at that time. Booster every 10 years. Determination of length and size of needle. Pertussis droplet precautions. Haemophilus influenza type B (HiB) Protection against numerous serious infections caused by H. influenza type B (i.e.: bacterial meningitis, epiglottitis, bacterial pneumonia, and sepsis) irritation at injection site, fever, and fainting Educational resources on importance of vaccine, prevention of spread of infection, and determination of appropriate needle Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) Protection against pneumococcal disease (13 types) At risk population should receive vaccine: fainting, soreness at injection site, severe allergic reactions are rare Proper location of injection site, education to at risk populations, determination of size and length of needle. SITE OF INJECTION vastus lateralis (IM) Orally vastus lateralis (IM) vastus lateralis (IM) Infants and young children: VASTUS LATERALIS sickle cell, nephrotic syndrome, CRF, DM, HIV, immunosuppression, CHF, Cystic Fibrosis, Asthma, liver disease, cardiomyopathy Older children and adults: DELTOID Inactivated poliovirus Protects individuals from polio Uncommon. Site irritation may occur Education. Evaluate if the patient is sick (may need to reschedule vaccination). Assess allergy to neomycin Influenza Reduce the risk of contracting the “flu” mild – same as all other vaccines. More severe: Guillian-Barre Syndrome (nerve cell damage- paralysis) Education during peak season. Correct site location, needle size, and needle length. Watch for adverse side effects. Assess allergy to eggs IM or SQ (depends on age and doctor order) Children: vastus lateralis (IM) Older children and adults: deltoid (IM) Nasally live virus Subcutaneously Measles, Mumps, rubella (MMR) Prevention against the viral diseases: Measles, Mumps, and Rubella. Not given to pregnant women. Soreness, swelling, seizures, low platelet count, rash, and deafness (rare). Educate women not to receive while pregnant or 28days after receiving vaccination. Correct site of administration, needle length, and size. Children: smallanterolateral aspect of thigh. Older childrenposterior triceps Adults: posterior triceps (may require one more dose) Varicella Prevent against contracting “chickenpox” if patient has not had the infection soreness and irritation. Uncommon: rash, seizure, meningitis, and pneumonia. Obtain adequate history on patient’s exposure or vaccination history. Provide education to patient/family. Administer SUBCUTANEOUS. Posterior tricep or is not a reliable historian. Hepatitis A Prevention of Hepatitis A injection in appropriate site with appropriate needle. Soreness at site lasting 1-2 days Provide proper education on importance of vaccine. Ensure patient is not sick at time of administration. Administer vaccination via appropriate needle and location site. IM Children: vastus lateralis Older children and adolescents: deltoid Adults: deltoid Reminders: *General contraindication for ALL immunization is a severe febrile illness, because increases the risk for a serious adverse reactions. The presence of MINOR ILLNESS, like the common cold is not a contraindication for immunizations. *Do NOT give live virus to immunocompromised, presence of acquired passive immunity through blood transfusions/immunoglobulin or allergic response to a previously administered vaccine or substance in vaccine. Must wait 3 months to receive vaccine after any treatment that causes acquired passive immunity. *Documentation of Vaccines: date given, vaccine manufacturer name, vaccine lot number, expiration date, person administering, location (clinic), parent consent, vaccine information sheet (VIS) provided to parent, Route and Site of vaccine administer and any adverse reactions if apply