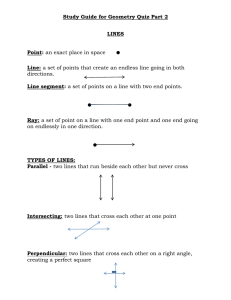
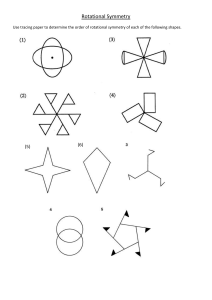
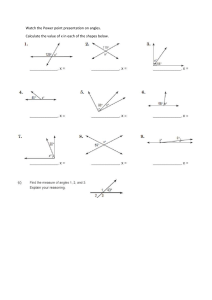
Chapter 8: Shapes and Symmetry SHAPES: Shapes are all around us! They're the forms of things we see every day. The pizza you eat is a circle. The door you walk through is a rectangle. The soccer ball you kick is a sphere. The pyramids in Egypt? They're called pyramids in geometry too. In math, there are two types of shapes we usually talk about: 2D shapes and 3D shapes. 2D shapes are flat, like drawings on paper, and they have two dimensions – length and width. Think about shapes like squares, circles, triangles, and rectangles. 3D shapes are not flat, but like the objects we can pick up and hold. They have three dimensions – length, width, and height. Examples include cubes, spheres (like a ball), cylinders (like a soda can), and cones (like an ice cream cone). SYMMETRY: Have you ever noticed how some things look exactly the same if you cut them down the middle or fold them in half? That's symmetry. Think about a butterfly. If you imagine drawing a line down the middle of a butterfly, both sides would look the same, wouldn't they? That's what we call 'symmetrical'. Symmetry is when something is the same on both sides of a line or point. There are a few types of symmetry too. The butterfly kind is called line symmetry or reflection symmetry, because each side is a reflection of the other across a line. But there's also rotational symmetry, where you can turn a shape around a point (like spinning a top) and it still looks the same. REAL-WORLD EXAMPLES AND USES: In the real world, understanding shapes and symmetry is super important. Architects use shapes and symmetry when designing buildings, bridges, and parks. Knowing about different shapes helps them understand how strong their designs will be. For instance, triangles are used in bridges because they are very stable shapes. Symmetry is used in art and design all the time too. Ever noticed how many logos, flags, or designs are symmetrical? It often makes things look balanced and pleasing to our eyes. Engineers and scientists use shapes and symmetry when designing cars, planes, and space rockets. Symmetry helps things move smoothly and reduces air resistance. Even in nature, many things are symmetrical. Human faces, flowers, snowflakes – symmetry is everywhere once you start to look for it! Understanding shapes and symmetry can also help you in everyday tasks. For example, if you're wrapping a present and you know the box is a cube, you can work out how much wrapping paper you'll need. Or if you're baking and you want to cut a pie evenly for your friends, understanding symmetry can help you make equal pieces. In summary, shapes and symmetry are fundamental concepts in maths and they're used in so many ways in the world around us. Isn't that cool?