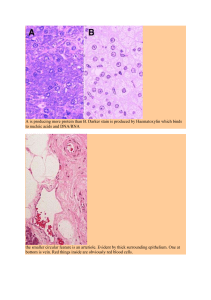
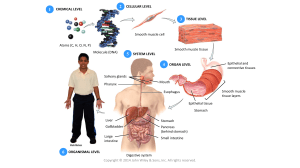
Cell biology •Animal cell types and their classification Animal tissue 4 types •Epithelial tissue •Connective tissue •Muscle tissue •Nervous tissue Epithelial tissue 1. Superface epithelium • Location: skin , mucosal layer of eyes, mouth, stomach, intestine and etc. • Function: protection, secretion, metabolism • Example in human body: protection and absorption of substances in the intestines and kidneys 2. Grandular epithelium • Location- glands(salivary, sweat glands) • Function: biosynthes and release of different substanses(saliva, sweat and etc.) 3.Ciliated epithelium Location: has outgrowths in the form of cilia and can be found in respiratory tract. Cilias remove dust and small particles from respiratory tract Function: protective Connective tissue Can be liquid (blood or lymph) or solid(bones, fat and etc.) Location: blood, lymph, bones, fat and etc. Function: transport,protection •Muscle tissue Skeletal muscle tissue • Location: Skeletal muscle includes the tissue fibers attached to the skeleton or bones and is responsible for all movements. • Function: movement Cardiac muscle tissue • Location: heart • Function: heart contraction • Smooth muscle tissue Location: stomach, urinary bladder, arteries and etc. Function: contraction of stomach, urinary bladder, arteries and etc. Nervous tissue Cells of nervous system are called neurons Location: brain, spinal cord, nerves Function: nervous tissue provides the interaction of tissues, organs and systems of the body and their regulation.