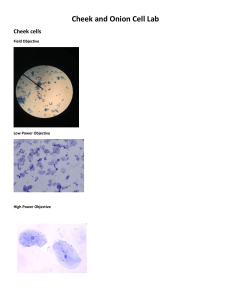
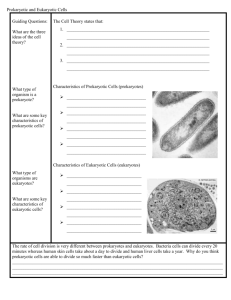
NAME: _________________________ GROUP NO.: ____________________ SECTION: ______________________ DATE PERFORMED: _______________ DATE SUBMITTED: ________________ RATING: _________________________ GENERAL BIOLOGY 1 LABORATORY WORKSHEET 2 OBSERVING EUKARYOTIC AND PROKARYOTIC CELL I. Introduction: The cell is the basic unit of structure of all living organisms, that performs the delicate internal biochemical processes of the body. All cells share common characteristics and are based on a fundamental design, although they show differences in their form and function. Cells are either prokaryotic (mostly unicellular) and eukaryotic (unicellular and multicellular). They are basically differentiated by the presence (in eukaryotes) or absence (in prokaryotes) of a true nucleus. PROKARYOTIC CELL Example: Cyanobacteria, Staphylococcus, etc. EUKARYOTIC CELL Example: Plant cell, Animal cell, Fungi etc. _________________________________________________________________________ In 1665, Robert Hooke published Micrographia, a book filled with drawings and descriptions of the organisms he viewed under the recently invented microscope. The invention of the microscope led to the discovery of the cell by Hooke. While looking at cork, Hooke observed box-shaped structures, which he called “cells” as they reminded him of the cells, or rooms, in monasteries. This discovery led to the development of classical cell theory. Drawing by Hooke Cork Cambium 2 The classical cell theory was proposed by Theodor Schwann in 1839. There are three parts to this theory. 1. All organisms are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of life. These parts were based on a conclusion made by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden in 1838, after comparing their observations of plant and animal cells. The third part, which asserts: 3. Cells come from preexisting cells that have multiplied 3 Was described by Rudolf Virchow in 1858, when he stated omnis cellula e cellula (all cells come from cells). Biogenesisrefers to the process wherein life arises from similar life forms. The principle of biogenesis is opposite to that of abiogenesis/spontaneous generation. The person who first came up with the term biogenesis was Henry Charlton Bastian 1837–1915. Abiogenesis or Spontaneous Generation- the idea that life arose from non-life more than 3.5 billion years ago on Earth. 4 II. Objectives: The learners will be able to: -Describe through observation the onion cell (plant), cheek cell (animal cell) and bacteria under a microscope. -Relate the cell theories to their observations. -Draw the specimens’ cell under various microscope objectives III. Materials: microscope glass slides cover slips pig’s meat toothpick onion skin cheek cells pig’s liver iodine solution methylene blue solution dropper tweezer grapes lab gown IV. Procedure: PLANT CELL (Onion) 1. Ready the microscope. 2. Arrange the materials needed. 3. Peel a thin layer of onion and use a tweezer to pick it, this will serve as your specimen. 4. Put the specimen on the glass slide. Apply a few drops of iodine solution. 5. Place the coverslip (45-degree angle). 6. Put the specimen on the stage. 7. Adjust the stage, make sure that it is at the center, and adjust the objective lens according to the specific magnification required. 8. Gather all the observations. PLANT CELL (Grapes) 1. Prepare a grape, use a scalpel to cut it half-way, and get a small portion of the outer layer. 2. Place it on the glass slide, add a drop of water and cover it with coverslip. 3. Observe. ANIMAL CELL (Cheek Cell) 1. Ready the microscope. 2. Arrange the materials needed. 3. Using a dropper, put few drops of methylene blue solution on the glass slide 5 4. Using a toothpick, scrape a sample of cheek cells 12 times from the mouth of any member. 5. Then, combine the sample cheek cell on the dye and get them all spread out. 6. Place the coverslip (45-degree angle) 7. Put the specimen on the stage. 7. Adjust the stage, make sure that it is at the center, and adjust the objective lens according to the specific magnification required. 8. Lastly, gather all the observations. ANIMAL CELL (Pig’s Meat) 1. Prepare a small amount of meat, use a scalpel to cut to get a sample. 2. Place it on the glass slide and cover it with coverslip. 3. Observe. ANIMAL CELL (Pig’s Liver) 1. Prepare a small amount of meat, use a scalpel to cut to get a sample. 2. Place it on the glass slide, add a drop of water and cover it with coverslip. 3. Observe BACTERIA CELL 1. Use a separate dropper, and get a small amount of cultured bacteria from the petri dish. 2. Place it on the glass slide, add a drop of water and cover it with coverslip. 3. Observe. V. Observation: Plant Cell Draw the onion cell inside the circles according to its specific magnification. 6 Draw the grapes cells inside the circles according to its specific magnification. Animal Cell Draw the cheek cell inside the circles according to its specific magnification 7 Draw the pig’s meat cell inside the circles according to its sp ecific magnification Draw the pig’s liver cell inside the circles according to its specific magnification 8 Bacteria Draw the bacteria specimen inside the circles according to its specific magnification 9 V. Guide Questions: 1. What was the shape of the onion cell and why? 2. What was the shape of the cheek cell? Why is it different compared to the onion cell shape? 3. In general, the surface of a dog has a softer feel compared to a tree that has a harder surface. What do you think is the explanation of this? 4. What do you think are the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? Provide statements that will justify your answer. (You may refer to the pictures on the first page) 5. The cells are able to divide through mitosis and provide 2 daughter cells. The statement corresponds to what principle of cell theory? Explain and justify your answer. 10 6. How would you describe the features and functions of each of the following cell structures? (You may refer to the pictures on the first page and your own research) Eukaryotic: a. cell membrane b. cell wall (include and specify the type of cell wall of plants) c. cytoplasm d. nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pores e. lysosome f. mitochondria g. ribosome h. endoplasmic reticulum (give the 2 types) i. golgi apparatus 11 Prokaryotic: a. cell wall (include and specify the type of cell wall of bacteria) b. cell membrane c. nucleoid region d. plasmid 7. Is the eukaryotic’s nucleus visible through the microscope? How about the prokaryotic? 8. Since an organism is made out of an organ system, and the organ system is made out of organs, then organs are made out of tissue and tissue are made out of cells. Since all of those things end with the “cell”, what theory/ies that corresponds to the statement above? Explain your answer. 9. From the gentlemen/scientist mentioned in the “introduction” part, state their names and their contributions to biology. 12 VII. RUBRICS CATEGORY MATERIALS (20%) DRAWING OF CELL (30%) QUESTION AND ANSWER (50%) EXEMPLARY (4) PROFICIENT (3) PARTIALLY PROFICIENT (2) SCORE NEEDS IMPROVEMENT (1) The learners were able to bring all the materials. The learners were able to bring but lacked 1 material. The learners were able to bring but lacks 2 materials. The learners were able to bring but lacked 3 or more materials. The learners were able to draw the cells/tissue with the right elements: 1. Shape 2. Position of organelles (if any are found) 3. Correct colors were used in the drawing. And adding another element that made the drawing special. The learners were able to draw the cells/tissue with the right elements: 1. Shape 2. Position of organelles (if any are found) 3. Correct colors were used in the drawing. The learners were able to draw the cells/tissue and following only 2 elements below: 1. Shape 2. Position of organelles (if any are found) 3. Correct colors were used in the drawing. The learners were able to draw the cells/tissue and follow only 1 element below: 1. Shape 2. Position of organelles (if any are found) 3. Correct colors were used in the drawing. The learners were able to answer the questions following the correct elements below: 1. Content 2. Emphasis 3. Correct choice of words. And adding another element that made the answer more elaborated. The learners were able to answer the questions following the correct elements below: 1. Content 2. Emphasis 3. Correct choice of words. The learners were able to answer the questions following only 2 elements below: 1. Content 2. Emphasis 3. Correct choice of words. The learners were able to answer the questions following only 1 element below: 1. Content 2. Emphasis 3. Correct choice of words. TOTAL 13 14