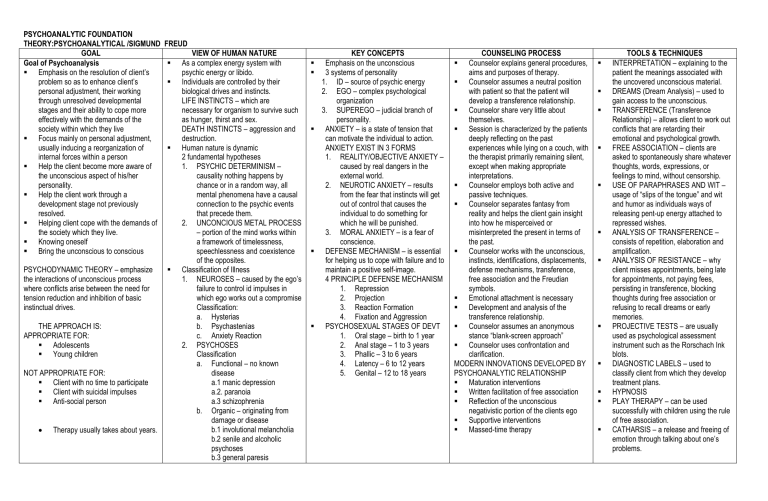
PSYCHOANALYTIC FOUNDATION THEORY:PSYCHOANALYTICAL /SIGMUND GOAL Goal of Psychoanalysis Emphasis on the resolution of client’s problem so as to enhance client’s personal adjustment, their working through unresolved developmental stages and their ability to cope more effectively with the demands of the society within which they live Focus mainly on personal adjustment, usually inducing a reorganization of internal forces within a person Help the client become more aware of the unconscious aspect of his/her personality. Help the client work through a development stage not previously resolved. Helping client cope with the demands of the society which they live. Knowing oneself Bring the unconscious to conscious PSYCHODYNAMIC THEORY – emphasize the interactions of unconscious process where conflicts arise between the need for tension reduction and inhibition of basic instinctual drives. THE APPROACH IS: APPROPRIATE FOR: Adolescents Young children NOT APPROPRIATE FOR: Client with no time to participate Client with suicidal impulses Anti-social person Therapy usually takes about years. FREUD VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE As a complex energy system with psychic energy or libido. Individuals are controlled by their biological drives and instincts. LIFE INSTINCTS – which are necessary for organism to survive such as hunger, thirst and sex. DEATH INSTINCTS – aggression and destruction. Human nature is dynamic 2 fundamental hypotheses 1. PSYCHIC DETERMINISM – causality nothing happens by chance or in a random way, all mental phenomena have a causal connection to the psychic events that precede them. 2. UNCONCIOUS METAL PROCESS – portion of the mind works within a framework of timelessness, speechlessness and coexistence of the opposites. Classification of Illness 1. NEUROSES – caused by the ego’s failure to control id impulses in which ego works out a compromise Classification: a. Hysterias b. Psychastenias c. Anxiety Reaction 2. PSYCHOSES Classification a. Functional – no known disease a.1 manic depression a.2. paranoia a.3 schizophrenia b. Organic – originating from damage or disease b.1 involutional melancholia b.2 senile and alcoholic psychoses b.3 general paresis KEY CONCEPTS Emphasis on the unconscious 3 systems of personality 1. ID – source of psychic energy 2. EGO – complex psychological organization 3. SUPEREGO – judicial branch of personality. ANXIETY – is a state of tension that can motivate the individual to action. ANXIETY EXIST IN 3 FORMS 1. REALITY/OBJECTIVE ANXIETY – caused by real dangers in the external world. 2. NEUROTIC ANXIETY – results from the fear that instincts will get out of control that causes the individual to do something for which he will be punished. 3. MORAL ANXIETY – is a fear of conscience. DEFENSE MECHANISM – is essential for helping us to cope with failure and to maintain a positive self-image. 4 PRINCIPLE DEFENSE MECHANISM 1. Repression 2. Projection 3. Reaction Formation 4. Fixation and Aggression PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGES OF DEVT 1. Oral stage – birth to 1 year 2. Anal stage – 1 to 3 years 3. Phallic – 3 to 6 years 4. Latency – 6 to 12 years 5. Genital – 12 to 18 years COUNSELING PROCESS Counselor explains general procedures, aims and purposes of therapy. Counselor assumes a neutral position with patient so that the patient will develop a transference relationship. Counselor share very little about themselves. Session is characterized by the patients deeply reflecting on the past experiences while lying on a couch, with the therapist primarily remaining silent, except when making appropriate interpretations. Counselor employs both active and passive techniques. Counselor separates fantasy from reality and helps the client gain insight into how he misperceived or misinterpreted the present in terms of the past. Counselor works with the unconscious, instincts, identifications, displacements, defense mechanisms, transference, free association and the Freudian symbols. Emotional attachment is necessary Development and analysis of the transference relationship. Counselor assumes an anonymous stance “blank-screen approach” Counselor uses confrontation and clarification. MODERN INNOVATIONS DEVELOPED BY PSYCHOANALYTIC RELATIONSHIP Maturation interventions Written facilitation of free association Reflection of the unconscious negativistic portion of the clients ego Supportive interventions Massed-time therapy TOOLS & TECHNIQUES INTERPRETATION – explaining to the patient the meanings associated with the uncovered unconscious material. DREAMS (Dream Analysis) – used to gain access to the unconscious. TRANSFERENCE (Transference Relationship) – allows client to work out conflicts that are retarding their emotional and psychological growth. FREE ASSOCIATION – clients are asked to spontaneously share whatever thoughts, words, expressions, or feelings to mind, without censorship. USE OF PARAPHRASES AND WIT – usage of “slips of the tongue” and wit and humor as individuals ways of releasing pent-up energy attached to repressed wishes. ANALYSIS OF TRANSFERENCE – consists of repetition, elaboration and amplification. ANALYSIS OF RESISTANCE – why client misses appointments, being late for appointments, not paying fees, persisting in transference, blocking thoughts during free association or refusing to recall dreams or early memories. PROJECTIVE TESTS – are usually used as psychological assessment instrument such as the Rorschach Ink blots. DIAGNOSTIC LABELS – used to classify client from which they develop treatment plans. HYPNOSIS PLAY THERAPY – can be used successfully with children using the rule of free association. CATHARSIS – a release and freeing of emotion through talking about one’s problems. PSYCHOANALYTIC FOUNDATION / NEO-FREUDIAN THEORY:ADLERIAN COUNSELING / AFLRED ADLER GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE Focuses on human wellness, individual Humans were motivated by social, growth and expansion and social interpersonal factors. interest Saw people as having control over their It is aimed at helping the client lead to a lives with each individual developing socially useful life by encouraging the unique life style. re-alignment of the individual interest The attempt to master feelings of with that of society. inferiority provides the motivation for Main goal of the counseling process is striving for perfection and creativity. to aid the client to realize his priorities Humans are pushed by feelings of and to decide whether or not it is worth inferiority and pulled by feelings of paying the price behaviorally to change superiority, and tend to compensate for his present life style. the areas of weakness or desirability by Behavioral goal is directed and developing a lifestyle that allows him to purposive and that life goals motivate be successful. human behavior. No two individuals develop the same Life goals involve overcoming feelings style of life. of inferiority and striving for security. Lifestyle is a result of judgments the All human beings have “striving for individual makes about the status of the superiority” as their life goal. self. Judgment of self in relation to one’s Drive toward superiority is similar perception of status in the world begins to the concept of self-actualization. to form patterns of behavior that “The great upward drive” – pulls become one’s lifestyle. the individual through the By the age of 4 or 5 the style of life has developmental stages. been formed, and future experiences ------------are merely integrated into it. Adler introduced terms (individual psych): BASIC MOTIVATION Inferiority complex Striving for perfection – “drive” or Masculine protest motivating force behind all or Organ inferiority behavior and experience. It is the desire, we all have to fulfill our Psychological Types = 4 Humors potentials, to come closer and 1. Ruling type Choleric closer to our ideals 2. Leaning type Phlegmatic Aggressive Drive – referring to the 3. Avoiding type Melancholic action we have when other drives 4. Socially useful type Sanguine such as our need to eat are frustrated. Compensation – striving to overcome. KEY CONCEPTS Emphasis is on conscious rather than unconscious. Process with individuals assuming responsibility for their life decisions. Human/individual Striving for superiority Feeling of inferiority and compensation. Life style Family constellation / birth order/ sibling rivalry Social determinant of personality and life style. Birth order was an important determinant of the child’s perception of the world outside the family. Earliest recollections to help understand style of life. Counselor believes that clients could overcome feelings of inadequacy and weakness. Core of Adlerian counseling is the psychology of use – all behavior has use or payoff that is usually unconscious disorder (eg. Conversion disorder – losing bodily function due to psychological reason. The process aggressively fosters autonomy for self-identity in society while holding on to the belief in the possible perfectibility of humankind. Adlerian counseling is humanistic, holistic, phenomenological, teleological, fieldtheoretical and socially oriented. Teleology – we are drawn towards our goals, our purposes, our ideals. Fictional Finalism – as if we are sure what good and bad are all abort, as if everything we see is as we see it. The fiction lies in the future, and yet influences our behavior today. Social interest/Social Feeling COUNSELING PROCESS 1. 2. 3. 4. Counselor should feel warm and accepting toward the clients; empathy was considered to be an important factor in the establishment of the therapeutic climate. Collaborative relationship – in which equal partners work out and agree upon specific goals. Assessment phase – counselor works to assess the clients style of life through an understanding of the clients beliefs, feelings, goals and motives. Empathy enables the counselor not only to develop the relationship but also to understand the beliefs underlying the feelings. Counselor probes the clients early childhood to assess siblings relationship and the clients perception of his place in the family. Early recollections are used to further the life style investigation, Counselor identifies the clients “basic mistakes” and interpretation they are presently influencing the client. Counselor emphasizes the development of insight into problems through an awareness of mistaken goals and selfdefeating behaviors. Counselor is confrontive in pointing out hidden purposes during interpretation to facilitate insight. Counselor interprets the clients lifestyle, it is hoped that they will come to understand their role in creating their problems, so that they can see how to improve their present situation Counselor orients the client toward action. Clients are encouraged to take risks and try out new behaviors, to take responsibility for their lives and how to make new decisions that will enable them to reach their goals. TOOLS & TECHNIQUES FAMILY CONSTELLATION – information by means of questionnaires. EARLY RECOLLECTIONS – single incident from childhood. NARRATIVE SUMMARY – all the data required. ESTABLISHING RELATIONSHIP thru: use of listening, respect and encouragement. PERFORMING ANALYSIS AND ASSESSMENT PROMOTING INSIGHT REORIENTATION PROGRAMS STEP – Systematic Training for Effective Parenting DUSO-R – Developing Understanding of Self and Others. HEURISTIC DEVICE – useful fictions. CARL RANSOM ROGERS THEORY:CLIENT CENTERED THERAPY/ PERSON CENTERED/ HUMANISTIC APPROACH/RELATIONSHIP ORIENTED APPROACH/NON-DIRECTIVE COUNSELING/EXPERIENTIAL COUNSELING/SELF THEORY COUNSELING GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE KEY CONCEPTS COUNSELING PROCESS TOOLS & TECHNIQUES To establish the proper therapeutic conditions to allow the normal development pattern of the individual to be brought back into play. To help the clients become more mature and reinstitute the movement towards selfactualization by removing the obstacles. The objective, then, is to free individuals from anxiety and doubts that prevent them from developing their own resources and potential. TERMS FORCE OF LIFE /actualizing tendency – defines as built in motivation present in every life – form to develop its potentials to the fullest extent possible. ORGANISMIC VALUING – organism know what is good for them. POSITIVE REGARD – umbrella term for things like love, affection, attention, nurturance, & so on. POSITIVE SELF-REGARD – self -esteem, selfworth, a positive self-image. CONDITIONS OF WORTH – society gives us what we need when we show that we are "worthy" CONDITIONAL POSITIVE REGARD – getting positive regard “on condition”. CONDITIONAL POSITIVE SELF-REGARD: REAL SELF – (I am) “you” that if all does well IDEAL SELF – (I should) something not real/out of reach/standard we can’t meet INCONGRUITY – (neurosis) gap between the real self & ideal self. Threatening Situation – when you are in a situation where there is an incongruity between your image of yourself. ANXIETY – is a signal indicating that there is trouble ahead, & you should avoid the situation. DEFENSES – one way to avoid situation DENIAL – blocking out the threatening situation altogether PERCEPTUAL DISTORTION – it is a matter of reinterpreting the situation so that it appears less threatening PSYCHOSIS – occurs when a person’s defenses are overwhelmed, & their sense become “shattered” into little disconnected pieces. 1. 2. 3. 4. The individual can “guide, regulate & control himself” Rogers view in 4 basic areas Belief in the dignity & worth of each individual. A perceptual view of behavior One’s experience are either Organized into self-structure Ignored because they are inconsistent with the sense of self Perceive distortedly because they are not harmonious with self-perception A tendency towards self-actualization A belief that people are good & trustworthy Human beings are seen as possessing positive goodness & desire to become “fully functioning” – that is to live effectively as possible. Based on self-theory (theory of personality) – wherein an individual’s view of self within the context of environment influences his/her actions & personal satisfactions Belief that a person’s perceptions of self & environment are reality for that person Faith in & respect for the client is the philosophical orientation of the non-directive counselor 9 formal propositions All individuals exist in a continually changing world of experience which they are the center (phenomenal field) 2. Individuals react to their phenomenal field as they experience & perceive it. (reality) 3. Behavior is basically the goal-directed attempt of individuals to satisfy their needs as experienced, in their phenomenal field as perceived. 4. The best vantage point for understanding behavior the internal frame of reference of the individual. 5. Most ways of behaving adopted by the individual are consistent with the individuals concept of self 6. The incongruence that often occurs between an individuals’ conscious wishes & his behavior is the result of a split between the individuals self-concept & his experiences 7. When the incongruence between the individuals self-picture & the individuals experience is very wide, a state of anxiety exists. 8. To lower an individual’s anxiety, the selfconcept must become more congruent with the individuals actual experiences 9. The fully functioning individual is completely open to all experiences, exhibiting no defensiveness MAJOR CONCEPTS ARE: Self-actualization Self-direction Counselor is fully involved in the client’s world of values. Characteristics of Healthy person/fully functioning 1. Openness to change 2. Existential living 3. Organismic trusting 4. Experiential freedom 5. Creativity Special Qualities of Client-centered counselor 1. Congruence – genuineness, honesty with client 2. Empathy – the ability to feel the client feel 3. Respect – acceptance, unconditional positive regards towards the client. 1. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. “if, then” approach – if certain conditions exist, then a definable process is set in motion. Conditions that are both necessary & sufficient for counseling CONDITIONS FOR GROWTH Psychological contact – 2 persons be in contact Minimum state anxiety – client be in a state of incongruence, feeling vulnerable or anxious Counselor Congruence – counselor must be congruent or genuine in the relationship Unconditional positive regard – counselor must experience emphatic understanding of the client’s internal frame of reference Client perception – client must perceive at least to a minimal degree, the counselor’s unconditional positive regard & emphatic understanding OUTCOMES – counselor must allow the client to set the goals. Emphasis on the here-and-now of the individual’s existence, both inside & outside of the counseling relationship The focus is on the current state of the individual Silence, acceptance, restatement, empathy & immediacy responses occur most frequently, with the client taking the lead on what is discussed & being responsible for outcomes. Counselors encourage careful self-exploration, but they tend to avoid confrontation & interpretation as tools of hastening insight. Shifted focus from “what” the therapist does, to “who” the therapist is Ability of the counselor to establish a relationship Counselor must be expert listener One who fully accepts each individual by offering an atmosphere of unconditional positive regard and emphatic understanding Counselor attempts to help the client develop insight by encouraging free expression & then reflecting these feelings. 2 PHASES OF EFFECTIVE CC Relationship FIRST PHASE – dynamics that Rogers traditionally identified: 1. Empathy 2. Acceptance 3. Genuineness 4. Liberality 5. Involvement 6. Sensitive listening 7. Equalizing SECOND PHASE – depends on the effectiveness of the relationship built in the first phase, centers on the needs of the client *Developmental of CC Approach over years; change include a more active, direct &confrontational role of the counselor COUNSELING STRATEGIES 1. Listening 2. Emphatic understanding 3. Caring COUNSELOR ENCOURAGES Ages inquiry Hypothesis testing Investigation of results COUNSELOR USES 1. Reflection of attitudes & feelings *Reflection – is the mirroring of emotional communication 2. Self-disclosure 3. Kind confrontation AFFECTIVE APPROACH – GESTALT THERAPY FREDERIC “fritz” PERLS GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE Views of people as essentially Gestalt = whole Gestalt Therapy – is a therapeutic approach which the therapist assists the client toward self-integration & toward learning to utilize his energy in appropriate ways to grow, develop &actualize Purpose of GT is to increase the clients selfawareness, since awareness is, itself, therapeutic Perls, believe that, with awareness, the most important unfinished business would emerge to be dealt with Attainment of awareness as it relates to the present Seeks to assist clients in discovering that they need not to be dependent upon others, but they can become independent beings Helping individuals assume responsibility for themselves, rather than carrying out duties to another’s expectations. Aim is to challenge the client to move from “environmental support” to “self-support” Achieving integration -----SAFE EMERGENCY – the client can feel safer in working toward self-support IMPASSE – client is stuck, unable to experience his feelings because of the threat involved. 5 defenses that result in impasses 1. Introjection 2. Projection 3. Retroflection 4. Deflection 5. Confluence 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. phenomenological Passon’s assumption that form the framework of G Approach A person is composite whole made up of interrelated parts. A person is also a part of his own environment and cannot be understood apart from it. A person chooses how to respond to external and internal stimuli, is an actor on his world, not a reactor. A person has potential to be fully aware of all sensations, thoughts, emotions & perceptions A person is capable of making choices because of this awareness People have the capacity to govern their own lives effectively People cannot experience the past and the future; they can only experience themselves in the present People are neither basically good nor bad. All other needs were viewed as stemming from & grounded in the basic need to actualize oneself Striving for self-actualization is present centered Gestaltist believe that a healthy personality exists when a person’s experiences form a meaningful whole (gestalt), where there is smooth transition between those sets of experiences that are immediately in the focus of awareness & those sets that are in the background. One has the capacity to know one’s own balance & to attend to one’s own needs as these needs emerge 5 Layers of Perls’ Onion Phony layer – reacting to others in stereotypical & inauthentic ways Phobic layer – avoiding the emotional pain associated with seeing ourselves the way we really are. Impassive layer – the point where we are struck in our own maturation Implosive layer – exposing our defenses & beginning to make contact with authentic selves. Explosive layer – releasing an enormous amount of energy as we let go of phony roles and pretenses KEY CONCEPTS NOW (here-and-now) Provides basis for an I-thou relationship, which includes emphasis on addressing someone directly (even if absent) instead of talking about that person to be counselor Anxiety – is the gap between the now & the later Awareness per se-by & itself – can be curative Emphasizes the need to relive or reexperience situations from the past about which clients have unexpressed feelings such as anger, pain, anxiety, grief, guilt, resentment, alienation & so on Growth or maturation – the transcendence from environmental support or self-support Focuses on experience, not on intellect The approach is phenomenological, it is existential BASIC PRINCIPLE 1. The holistic principle which state that persons are organized wholes 2. The didactic principle of opposites which also includes the principles of homeostasis Kinds of problems that individual experiences 1. Lack of awareness 2. Lack of responsibility 3. A loss of contact with environment 4. Inability to complete gestalts 5. Disowning of needs 6. Dichotomizing dimensions of self (topdog, underdog) COUNSELING PROCESS Therapist attempt to presentize the past by using fantasy to bring the past into present (done through relating past events as if they were occurring at the moment) Counselors must be able to pick out discrepancies between verbal and nonverbal expressions back to clients Counseling is a confrontative& active approach stressing the what & how of behavior & leading to the acceptance of personal responsibility for behavior Counselor maximizes actual experiencing of the existential meaning of the problem Works with the clients dream but does not interpret them, instead let the client discover the meaning of the dream. Dream is seen as projection of self. Establishment of “continuum awareness” Counselor is deliberately playing provocative games with client, games intended to force the client to confront & acknowledge feelings that have been so ardrously avoided “you can & must be responsible for yourself” (counselor to client) Questions like: What is your right hand doing now? How does your voice sound now? *use of how & what questions focus attention on current functioning Counselor should have experience, patience & emotional presence because GT often leads to intense emotional experiences TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Use of experiential games Specific techniques 1. Use of personal pronouns 2. Converting questions to statements 3. Assuming responsibility 4. Playing the projection 5. The empty chair Techniques (Passons) 1. Enhancing awareness 2. Personalizing pronouns 3. Changing questions to statements 4. Assuming responsibility 5. Asking how & what 6. Sharing hunches 7. Bringing the past into now 8. Expressing resentments & appreciation 9. Using body expressions Other technique 1. The dialogue exercise 2. Sharing hunches 3. Substitute phrase 4. Exaggeration 5. Making rounds 6. Guided fantasy 7. Playing the projection INTERVENTIONS 1. Body awareness 2. Experimentation 3. Role playing 4. Empty-chair technique 5. Psychodrama AFFECTIVE APPROACH – EXISTENTIAL THERAPY/ LOGOTHERAPY ROLLO MAY, ADRIAN VAN KAAM, VICTOR E. FRANKL GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE Aim is to enable individuals to accept responsibility for themselves Help the client find & develop meanings in life as a way of reducing anxiety associated with the threat of nonbeing. STAGES 1. Client must recognize his freedom of choice, being capable of choosing both that which is right for him & that which is not 2. The client learns to accept responsibility for his decisions by recognizing his need to see how the consequences of his choices make a profound impact on his existence COUNSELOR GOAL Bring the clients to the point where they cease to flee from or to fight their symptoms, & instead exaggerate them. Logotherahy – (Victor Frankl) provides the answer a person that do not have a meaningful purpose in life Challenges the client to become more fully involved in life with less complaints Addresses spiritual conflict more than psychological conflict It is a mix of concepts, attitudes & personal challenges Terms Sunday Neurosis (arises from an existential vacuum) referring to a form of depression resulting from an awareness in some people of the emptiness of their lives once the working week is over existential vacuum - or, as he sometimes terms it, "existential frustration" - is a common phenomenon and is characterized by the subjective state of boredom, apathy, and emptiness. -------Applied to persons suffering from physical & psychological trauma of all kinds Helps them understand their pain Helps them build attitude for constructive behavior Helps them deal with pain Directs them to focus on the future Encourage them to use their human capacity for self-determinant of self-transcendence May (1961) six existential characteristics that constitute the nature of an existing person 1. Humans are centered in themselves. 2. Humans have the character of self-affirmation 3. Humans have the possibility of moving from centeredness to participation with other beings 4. Awareness lies on the subjective side of centeredness 5. Humans have a unique form of awareness called self-consciousness 6. Humans have the characteristic of anxiety, the feeling of one in a struggle against that which would destroy one’s being. 7. (Frankl(1959) added) The primary force in one’s life is one’s search for meaning May "stages" of development: *Innocence – the pre-egoic, pre-self-conscious stage of the infant. An innocent is only doing what he or she must do. However, an innocent does have a degree of will in the sense of a drive to fulfill needs. *Rebellion – the rebellious person wants freedom, but does not yet have a good understanding of the responsibility that goes with it. *Decision – The person is in a transition stage in their life such that they need to be more independent from their parents and settle into the "ordinary stage". In this stage they must decide what to do with their life, and fulfilling rebellious needs from the rebellious stage. *Ordinary – the normal adult ego learned responsibility, but finds it too demanding, and so seeks refuge in conformity and traditional values. *Creative – the authentic adult, the existential stage, self-actualizing and transcending simple egocentrism. man expresses the freedom to take a stand, expressed in attitude & in action man possesses a spiritual or existential dimension that allows him to go beyond physical, psychological & other limitations human capacity for self-detachment – the ability to see oneself at a distance & assume selfless attitude toward demand SELF TRANSCENDENCE – ability to move beyond one’s needs and priorities to help others the will to meaning directs behavior seeking pleasure for its own sake leads to disillusionment KEY CONCEPTS Existential counselor recognizes that psychological forces take their meaning from the existential situation of the client’s immediate life. Emphasize the philosophical concerns of what it means to become fully human Focuses on the human condition An attitude that stresses the understanding of persons One is responsible for one’s existence & one’s destiny; they are not result of deterministic forces of conditioning Awareness of freedom & responsibility is a basic human attribute EXISTENTIAL ANXIETY results from the awareness of being finite & from facing the inevitable prospect of death EXISTENTIAL GUILT result of failing to become what one is fully able to become EXISTENTIALISM – a philosophical movement stressing individual responsibility for creating one’s way of thinking, feeling &behaving EXISTENTIAL NEUROSIS – feelings of despair & anxiety that result from inauthentic living, a failure to make choices, & an avoidance of responsibility EXISTENTIAL VACUUM – a condition of emptiness & hollowness that result from meaninglessness in life FREEDOM – an inescapable aspect of the human condition, implying that we are author of our lives COUNSELING PROCESS Counselor must understand the client’s unique world Counselor helps the client experience his existence as fully as possible Counselors expose their true selves Counselor takes time to help his client determine sources of meaning & encourages him to look at these meaning in relation to his lifestyle Client -Counselor relationship – client is guided to assume responsibility for meaning in life Counselor accepts the value system of the client unless the client’s values are unfounded or the client believes that existence is senseless & useless, & he denies moral truth Counselor is accepting & challenging Opens o discussions of values of beliefs TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Honesty, authenticity, spirituality knowledge & insight are presumed to follow commitment Emphasis is on flexibility & versatility Futuristic (future rather than past or present) Confrontation Borrowed Techniques 1. Imagery Exercises 2. Awareness Exercises 3. Goal setting activities TERMS ARISEN IN THE PRACTICE EXISTENTIAL THERAPY DEREFLECTION – diversion of client’s attention away from their problems towards accessible meaning outside the problematic self PARADOXICAL INTENTION – intentional exaggeration of problematic behaviors, which breaks the compulsion to do them DISIDENTIFICATION – one of the results of avoiding death is an over-identification with one’s world DESCRIPTION – the initial verbal expressions of the clients’ experience are best understood when they are descriptive EMPATHY – empathy is expressed when the counselor provides agree of understanding that rows out of listening to client’s experience as from the client’s point of view PRESENCE – therapeutic presence means being there, being authentically one’s self, openly & truly with the client, & encountering the client as a human being NEO-FREUDIAN KAREN HORNEY VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE TEN NEUROTIC NEEDS The neurotic need for 1. Affection & approval 2. A partner who will take over one’s life 3. To restrict one’s life within the narrow boarders 4. For power 5. To exploit others 6. Prestige 7. Personal admiration 8. Personal achievement 9. Self-sufficiency & independence 10. Protection & unassailability The need simply cannot be satisfied because of the deep inner conflict that lies at its source 3 BASIC ORIENTATIONS Moving toward people – need for love Moving away from people – need for independence Moving against people – need for power KEY CONCEPTS The concept of anxiety that grew out of the child’s feelings of isolation & helplessness. The root of anxiety lies in the parent-child relationship with anxiety being produced by anything that disturbs the child’s fundamental security The insecure children handle their feelings by developing irrational (neurotic) solution to problem Conflicts are avoidable if the child is reared in loving, accepting home in which warmth trust, &affection characterize the parentchild relationship NEO-FREUDIAN HARRY STACK SULIVAN KEY CONCEPT Role of interpersonal relationship The importance both of interpersonal relationships &the role of the therapist as involved participant in the interview Personality exists only through the individual’s interactions with others. Processes such as thinking, perceiving, & even dreaming are considered to be interpersonal The self-system develops out of the anxiety experienced in interpersonal relationships, which originally stems from the motherinfant relationship Individuals learn that The good-me self – If they please their parents, they will be praised The bad-me self – if they misbehave they will be punished the self protects from anxiety & guards security if the individual experiences much anxiety, the self-system will become inflated & will prevent the individual from growing & interacting with others in healthy relationships Sullivan was first to change the role of the therapist from a removed observer and interpreter of the patients experience, to an active, involved participant in an interpersonal relationship COUNSELING PCOUNSELING P COGNITIVE PROCESSING PROTOTAXIC - involves experiences that have no connection or meaning for the experiencing individual. Infants undergo this kind of experiencing PARATAXIC – involves seeing a relationship between events that occur simultaneously, but have no actual relationship. Superstitions are examples of parataxic thought processes SYNTAXIC – involves the use of language in which commonly agreed-upon verbal symbols enable communication Stages of development 1. Infancy 2. Childhood 3. Juvenile era 4. Preadolescence 5. Early adolescence 6. Late adolescence Therapeutic interview – the therapist focus on the communication between the therapist & patient. Therapist influence the interaction in the interview through his attitudes, feelings, doubts, or personal difficulties. STAGES OF PSYCHIATRIC INTERVIEW 1. He formal inception 2. Reconnaissance 3. The detailed inquiry 4. The termination COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL APPROACH – TRAIT FACTOR COUNSELING/DIRECTIVE COUNSELING/COUNSELOR-CENTERED THEORY EDWARD G. WILLIAMSON/FRANK PARSONS GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE KEY CONCEPTS Attempt to apply a scientific approach to Human behavior can be ordered & Is the only counseling approach that counseling by the use of measurement measured along continua of defined originated from an essential vocational & prediction utilizes a process of traits & factors counseling use. gathering data, synthesizing it, forming Man is rational being with potentialities TFA is essentially a rational-problem a diagnosis, & planning a program for which may be developed in either solving approach. the client positive or negative directions Explain personality as a system of Goals of counseling typically include interdependent traits & factors such as Is capable of developing autonomously self-understanding, choosing but needs assistance of others to abilities, interests, attitudes & appropriate goals for living, & striving achieve full potentiality temperament for the good life. Assumption that man seeks to use self- TFT – jobs & workers should match Williamson Opinion – the purpose of understanding & knowledge of his (Parsons) counseling is to facilitate the abilities as means of developing Today career satisfaction involves not development of excellence in all potentialities only matching person a person to a aspects of human life. work environment but also taking other He asserts that “the task of TF type of vital factors into consideration that Counseling is to aid the individual in includes interests, skills, personality & successive approximations of selfvalues, family influences, sociounderstanding & self-management by economic status & physical health. means of helping to assess his assets & liabilities in relation to the requirements of progressively changing life goals & his vocational career 1. 2. 3. COUNSELING PROCESS Parsons’ 3 step model Develop knowledge about self: aptitudes, interests, resources Develop knowledge about the world of work: advantages & disadvantages opportunities & requirements associated with occupations Find a suitable match between the individual & the world of work. Counselor influences the development of the client Counselor with TF viewpoint is active in the learning situation represented by counseling Counselor involved in diagnosis, presenting information, clarifying issues & the like. Counselor collects data & evaluates the individual understand himself. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Techniques used Establishing rapport Cultivating self-understanding Advising Checking on the client to see how the client carried out the advise Use of psychological test Williamson placed the counselors techniques in 5 General Categories: Forcing conformity Changing the environment Selecting the appropriate environment Learning needed skills Changing attitudes Williamson 5 stages of counseling Establishing rapport Cultivating self-understanding Advising or planning program of action Carrying out the plan Where appropriate, making referral’s to other personnel workers COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL APPROACH – TRANSACTIONAL ANALYSIS ERIC BERNE GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Particularly effective in group counseling Basic goal is to help client achieve autonomy Autonomy is characterized by: Awareness – a realistic understanding of one’s world Spontaneity – ability to express emotion in an uninhibited, game free fashion Intimacy – the capacity to share love & closeness with others Attempt to enable a client to free his adult from the confluence of the child & the parent so that the adult is in control of decision making TA evolved from the discovery of the ego states re-experienced by the persons under direct stimulation of the brain INJUNCTION – when the parents are threatened by a child’s behavior Injunctions & some possible decisions that could be made in response to them Don’t make mistake Don’t be Don’t be close Don’t be important Don’t be a child Don’t grow Don’t succeed Don’t be you Don’t be the sane & don’t be well Don’t belong *Anything that has been learned can be unlearned Counterinjuctions – when parents observe their child not succeeding or being comfortable with who they are, they attempt to “counter” the effect of earlier messages *Be perfect, try hard, hurry up, be strong, please me Berne stresses the interaction between individual as both a symptom & a cause of psychological difficulties Berne described an ontology of games origination from 3 positions 1. Prosecutor 2. Rescuer 3. Victim 4 basic life positions 1. I’m okay, you’re okay 2. I’m okay, you’re not okay 3. I’m not okay, you’re okay 4. I’m not okay, you’re not okay TA emphasized the human need for emotional & physical strokes Strokes – is any act of recognition or source of stimulation Strokes come in form of physical, verbal & psychological; they can be positive or negative, unconditional or conditional. Berne believed that individuals need to learn how to ask for the strokes they want 2 KINDS OF ANALYSIS STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS – involves the analysis & recognition of the influence of the individuals ego states on thinking or behaving TRANSACTIONAL ANALYSIS – identifying which ego state is in the power at any given time, the individual is better be able to understand the nature of her behavior & the behavior of the others within a social context - Concerned with the diagnosis of the ego states from which a social interchange is emanating for two persons involved & within the clarification of that exchange Transactional Stimulus – when one person encounters another & speaks Transactional response – reply to TS Complementary Transaction – occur when both parties speak from their Adults or when the vectors are parallel, as when parent speaks to child, & child responds to parent Crossed Transaction – occur when the vectors are not parallel, & communication is broken off Ulterior Transaction – occur when more than two ego states are in operation simultaneously Permission – when parents are excited by a child’s behavior KEY CONCEPTS COUNSELING PROCESS TA focuses on the games people play to avoid intimacy in transactions with others TA is based on a personality theory utilizing 3 distinct patterns of behavior or ego states PARENT – filled with values, injunctions, “should” &oughts” ADULT – data processing, probability estimation & decision making Regulate the activities of the child & the parent Deal with presenting situations in an organized, adaptable& intelligent way – that is reality testing CHILD – childlikeness, fun loving part of most individuals Function in 2 distinct form 1. Neutral child – strives for total freedom to do what it wants whenever it wants, that includes natural impulses for love, affection, creativity, aggression, rebellion & spontaneity 2. Adapted child – influenced by the parent & has discovered ways usually compliance or procrastination, to deal with feelings in a way that will prevent parent reprimand Duplicates the original reactions individual have towards their parents during childhood including feeling like guilt, fear, anger & frustration The emerging adult in the child is called the little professor & it’s the source of intuition, creativity & manipulation; it serves as the negotiator between the neutral child & adapted child. TA is learning to analyze one’s relationships with other TA Counselor acts very much like teacher, trainer & resource person with heavy emphasis on involvement TA Counselor attempts to help clients make full & effective use of all three ego states & to live game-free lives with intimate rewarding relationships TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Use of Contract – includes a statement about what the client hopes to achieve in counseling Use of Learning Tools – diagrams by drawing lines, circles, & grids on available blackboard & whiteboard Techniques 1. Clients early memories 2. Helping clients free themselves from constraints of those early decision 4 Kinds of rational analyses 1. Structural A – analysis of individual personality *Family modeling *complementary T, Crossed T, Ulterior T *analysis of rituals & past times *analysis of games & rackets Racket – consist of the calling up & collection of feelings that one uses to justify one’s life script & ultimately one’s decision Involves collection of stamps 2. Transactional A –analysis of what people say & do to another 3. Game A – identification of games & resulting racket feelings 4. Script A – analysis of overall life plans Life script – determine action COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL APPROACH – REALITY THERAPY WILLIAM GLASSER GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE Responsible behavior is its ultimate Measures behavior against an objective goal standard which calls reality Sees individual as functioning in consonance or dissonance with the reality All human behavior is motivated by striving to meet basic needs – physiological & psychological that are the same for all individuals 2 basic psychological need 1. Need to love & be Loved 2. Need to feel that we are worthwhile to ourselves & to others IDENTITY – 2 needs that have been incorporated into one need. Glasser believes that identity is a person’s most important psychological need, built into the biological system from birth Delinquency & withdrawal – resolved from failure of identity Philosophical base of reality is that people are determining, autonomous & responsible RT Views a person as 1. An adjusted person is classified “success”. He is happy, confident, rational & responsible 2. A maladjusted person is classified as “failure”. He is lonely self-critical, irrational & irresponsible KEY CONCEPTS Focus is on what the person does, not feels Emphasizes the idea of client’s making value judgments’ about their own behavior Glasser believes that certain generally accepted moral principles should be encouraged by the therapist Once clients are able to make value judgments about their own behavior & to the reality squarely, they are ready to assume personal responsibilities for their behavior Responsibility – the ability to fulfill one’s needs & to do so in a way that does not deprive others of the ability to fulfill their needs. Change is impossible until individuals stops using conditions in the past, factors in the present or the behavior of the others as excuses for their own actions & start accepting responsibility for their own lives The more responsible people the healthier they are; the less responsible, the less healthy RT is known as an action system which focuses on involvement & motivation RT is problem centered & success oriented. It is more of a teaching process 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. COUNSELING PROCESS Behavior change involves helping the client to do what is right, responsible & realistic Reality therapist attempts to teach clients on approach to life that involves living responsibly 8 STEPS PROCEDURE Be involved Focus on behavior, not feelings Focus on the present Making value judgments Making a plan Getting a commitment Accept no excuses Eliminate punishment Counselor teaches client that happiness is a quality that grows within self & only client can work for it himself Counselor concentrates on the clients’ conscious thoughts TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Verbal system is direct, frank & realistic Humor is used that will allow for both counselor & client to be sensitive to laughable conditions Confront client in a non-punitive way toward a responsible behavior Verbal shock confrontation – may be necessary to guide client to responsible action & behavior COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL APPROACH – BEHAVIORAL COUNSELING WOLPE, LAZARUS, BANDURA, KRUMBOLTZ & THORESEN GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE People are neither good nor bad; they are Concerned with behavior change essentially neutral at birth with equal potential for Behavioral counselors have begun to good or evil. Dustin and George assumptions emphasize processes that are more 1. Man is viewed as being neither intrinsically cognitive in nature, recognizing for good nor bad, but as an experiencing instance that there is a cognitive organism who has potential for all kinds of behavior element operating whenever behavior 2. Man is able to conceptualize and control his changes as the result of its own behavior consequences 3. Man is able to acquire new behaviors 6 steps employed: 4. Man is able to influence others’ behavior as 1. Identify & state the behavior to be well as to be influenced by others in his own behavior changed in operational terms Behaviorist sees maladaptive behaviors as being 2. Obtain a base line of the desired target learned behaviors; their development & behavior maintenance are the same as that of any other 3. Arrange the situation so that the target behavior. behavior will occur 4. Identify potential reinforcing stimuli & Implication of this views: events That no behaviors are maladaptive in & of themselves; rather a behavior becomes 5. Reinforce the desired target behavior of inappropriate because someone cleans it so. successive approximations of it Maladaptive behaviors as learned is the idea 6. Evaluate the effects of the treatment that only behavior that brings a pleasant result procedure by maintaining records of or that helps to reduce unpleasant result is likely change in the target behavior increased. General goals KEY CONCEPTS Behaviorist generally considers the stimulus-response. Paradigm the basic pattern of all human learning. Behavior is a function of the stimulus. Conditioning Classical Conditioning (Ivan Pavlov) – respondent is controlled by its antecedents. “Systematic sensitizing and desensitizing”. Operant Conditioning (B.F. Skinner) – openinstrumental is controlled by its consequences that strengthen behavior. “behavior modification” Reinforcer (Operant) – the consequences that strengthen behavior. Extinction – the process of eliminating an undesirable behavior. Shaping – a procedure that reinforces successively closer approximations of the desired behavior. Strategy: 1. Counterconditioning – a new desirable behavior is substituted for the undesirable behavior. 2. Withdrawing the reinforcement that has previously followed a behavior. Feelings of client are secondary to clients’ behaviors. Behavior therapy is characterized by: 1. Focus on specific overt behavior. 2. Very precise therapeutic goals 3. The development if a treatment procedure appropriate to the client’s problem. 4. An objective assessment as of whether the therapeutic goals were accomplished. COUNSELING PROCESS TOOLS & TECHNIQUES Specification of concrete reachable goals provides greater opportunity for clients to see progress, which is a motivating force in itself. SYSTEMATIC DESENSITIZATION Desensitization – refers to the process of anxiety reduction. Counter conditioning – process of learning an incomparative behavior & is carried out on a step-bystep basis. ASSERTION TRAINING - emphasized teaching clients to stand up for their own rights without violating the rights of others ASSERTIVE BEHAVIOR – consists of expressing one’s thoughts & feelings in direct, honest & appropriate ways Procedure (Wolpe) Relaxation training (30 mins training) Identifying anxiety-producing situations. Working through the anxiety hierarchy. Behavior therapy attempts to help clients: 1. Alter maladaptive behavior. 2. Learn the decision making process Prevent problems by strengthening desirable behaviors. Behavior contract – is based on the idea that it is helpful to the client to specify the kind of behavior desired & the reinforcement contingencies Contract enables individuals to anticipate changing their behavior on the basis of a promise or agreement that some positive consequences will be forthcoming Helps the client “what to do” without nagging Aspect of contract; reality, specificity, freedom from threat; & flexibility SOCIAL MODELING – a person will initiate behavior of others; is used to help the client progressively modify his behavior toward that of observed model. Counselor uses audio models, filmed models, & live models COGNITIVE BEHAVIORAL APPROACH – RATIONAL EMOTIVE THERAPY(RET), RATIONAL THERAPY, SEMANTIC THERAPY, COGNITIVE THERAPY, COGNITIVE-BEHAVIOR, RATIONAL BEHAVIOR TRAINING/RATIONAL EMOTIVE BEHAVIOR THERAPY(REBT), ABC THEORY, ABCDE THEORY – ALBERT ELLIS GOAL VIEW OF HUMAN NATURE KEY CONCEPTS COUNSELING PROCESS TOOLS & TECHNIQUES RET Attempt to help people discriminate between appropriate & inappropriate feelings, as well as to intensify, the appropriate while reducing or eliminating the inappropriate 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. View of people is dominated by the principle that emotion & reason-thinking & feeling-are intricately entwined in the psyche RET stresses that all normal humans think, feel & act & that they do so simultaneously Their thoughts affect, & often create, their feelings & behaviors Their acts affect their thoughts & feelings Assumptions about the nature of humanity The individual is uniquely rational & irrational Emotional or psychological disturbance is the result of irrational & illogical thinking Irrational thinking originates in the early illogical learning that the individual is biologically disposed toward & more specifically acquire from parents & culture Human beings are verbal animals, & thinking usually occurs through the use of symbols or language Continuing states of emotional disturbance, being a result of self-verbalizations, are thus determined not by external circumstances or events but by the perception & attitudes toward these events that are incorporated in the internalized sentences about them Individuals are vast untapped resources of actualizing their potentials & can change their personal & social destinies Negative & self-defeating thoughts & emotions must therefore be attacked by reorganizing perceptions & thinking so that thinking becomes logical & rational, rather than illogical & irrational People’s emotions are a result of their beliefs, philosophies, interpretations & evaluation about events happening to them & not from the events as they are Emotional disturbance includes cognitive behavioral & emotive elements & that he has his own human frailties which incite him to irrational beliefs & behaviors but with great determination & effort, he can think & behave rationally Ellis stresses thinking, judging, deciding & analyzing & doing RET emphasizes that emotions, feelings of emotional disturbance are largely products of peoples thought, ideas & constructs Ellis major illogical ideas 1. It is absolutely essential for an individual to be loved or approved of by every significant person in his environment 2. It is necessary that each individual be completely competent, adequate, & achieving in all areas if the individual is to be worthwhile 3. Some people are bad, wicked, or villainous, & these people should be blamed & punished 4. It is terrible & catastrophic when things are not the way an individual wants them to be 5. Unhappiness is a function of events outside the control of the individual 6. If something may be dangerous or harmful, an individual should constantly be concerned & think about it 7. It is easier to run away from difficulties & self-responsibility that it is to face them 8. Individuals need to be dependent on others & have someone stronger than themselves to lean on 9. Past events in an individual’s life determine present behavior & cannot be changed 10. An individual should be very concerned & upset by others’ problems 11. There is always a correct & precise answer to every problem &its catastrophic if it is not found. ABC theory/ ABCDE Theory principle of emotional disturbance which emphasizes the importance of cognitive control over emotional states It is consistent with the phenomenological position that one’s perception of an event determines one’s behavioral response to that event Counseling is active & confrontive Counselor concerned with detection, pinpointing, & contesting the irrational beliefs & behaviors fundamental to the emotional disturbance of the client RET Major contribution is its emphasis on the close relationship of one’s thinking to one’s emotions & behavior & the belief in an individuals capability for self-actualization System is therapeutic, educative & preventive People are self-talking, self-evaluating & self-sustaining who create problems when they perceive simple preferences & desires as being essential he ends. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. STEPS Show the clients that they are illogical, to help them to understand how & why they became so & to demonstrate the relationship of their irrational ideas to their unhappiness & emotional disturbance This instant leads clients to understand the relationship between their values & attitudes & the should, oughts& must they have incorporated into their lives Help clients believe that thoughts can be challenged & changed This is accompanied by direct disputing of clients beliefs by the therapist Disputing consists of questioning &challenging the validity of ideas clients hold about themselves, others & the world The therapist persistently & forcefully repeats this process, using the most direct, persuasive, & logical techniques available Therapist attempts to teach clients to dispute themselves in such a way that they reach the goal of thinking rationally on their own Helping the client go beyond disputing irrational/inappropriate ideas by encouraging them to continue their efforts toward more rational thinking by rational reindoctrination RET COUNSELOR Is active & directive with most clients, doing a great deal of talking & explaining especially in the early stages Confronts clients directly with their problems so as not to waste unnecessary time Takes a vigorous approach in getting clients first to think & then to get them to reeducate themselves Is persistent and repetitive in hammering away at the irrational ideas underlying clients emotional disturbances Appeals to clients’ reasoning powers, rather than their emotions Is didactic & philosophical in his approach Uses humor & shame exercises as a way of confronting the client’s irrational thinking. Counselor seeks for specific information & offers specific procedures Cures unreason by reason Ellis utilizes a variety of teaching devicespamphlets, books, tape recordings, film & filmstrips – as part of the process through which clients learn to recognize the irrational thoughts which are bringing about the disturbances that are upsetting their lives. RET Technique: active, directive teaching, establishing rapport Counselor-client relationship & expressive emotive, supportive, insight methods Counselor assumes an active teaching role to reeducate the client Counselor demonstrates the illogical origin of the clients disturbances & the self-verablizations that perpetuate the disturbances in the client’s life Clients are shown that their internalized sentences are quite illogical & unrealistic Effective counselor continually unmasks the clients past & especially, their present illogical thinking or self-defeating verbalizations Counselor teaches the client to re think, challenge &reverbalize these sentences to make their internalized thoughts more logical & efficient Uses of homework assignment – giving clients specific assignments to try out behaviors that he fears, encouraging them to take risks, or having them intentionally fail at the same effort to learn that (1) that fail is not catastrophic & (2) how to cope with feeling of failure Also include a great deal of cognitive work: reading specific materials, or commonly using selfhelp forms to analyze their ABCs & to act toward disputing their irrational belief. RET Counselor counters their logic & reason, teaching, suggestion, persuasion, confrontation, deindoctrination, indoctrination, & prescription of behavior to show the clients the irrational philosophies to demonstrate how these lead to emotionally disturbed behavior, to change thinking thus to change the clients emotions Counselor instructs the client in the major irrational ideal of our culture & provides more effective rational ones thus offering protection from future disturbances

