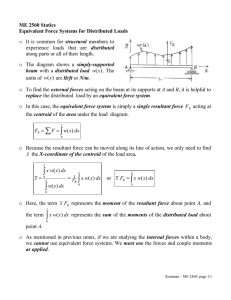
ME350 CHAPTER 1: STRESS (PART-I) Associate Prof. Hussein Zein Mechanical Engineering Department College of Engineering Qassim University Course Schedule: 2 CHAPTER 1: STRESS CHAPTER OBJECTIVES: Review important principles of statics. Use the principles to determine internal resultant loadings (internal reaction forces) in a body. Introduce concepts of normal and shear stress. Discuss applications of analysis and design of members subjected to an axial load or direct shear load. Why do we study Mechanics of Materials? Anyone concerned with the strength and physical performance of natural/man-made structures should study Mechanics of Materials. 4 Introduction to Mechanics of Materials Definition: Mechanics of materials is a branch of applied mechanics that deals with the behaviour of solid bodies subjected to various types of loading. Compression Tension (stretched) Bending Torsion (twisted) Shearing 5 Begin Chapter 1: STATICS REVIEW: EXTERNAL LOADS Small contact area; treat as a point FR is resultant of w(s) = area under curve, acts at centroid Acting on narrow area One body acting on another One body acting on 6 another w/o contact EXTERNAL LOADS: External loads can be Reaction Loads or Applied Loads! Must solve for all unknown external loads (reaction loads) so that internal loads can be solved for! Internal loads produce stress, strain, deformation – SofM concepts! 7 SUPPORT TYPES AND REACTIONS (2D): 8 SUPPORT TYPES AND REACTIONS (2D): 9 Pin connections allow rotation. Reactions at pins are forces and NOT MOMENTS. Degrees of Freedom? 10 STATIC EQUILIBRIUM Vectors: SF = 0 Coplanar (2D) force systems: SFx = 0 SFy = 0 SMz = 0 SM = 0 Perpendicular to the plane containing the forces • Draw a FBD to account for ALL loads acting on the body. 11 Example FBD: Draw a FBD of member ABC, which is supported by a smooth collar at A, roller at B, and link CD. 12 GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING (continued) C A B F.B.D 13 EXAMPLE: FIND THE VERTICAL REACTIONS AT A AND B FOR THE SHAFT SHOWN BELOW. 14 FBD (800 N/m)(0.150 m) = 120 N 225 N A B Ay By F.B.D Comment on dashed line around the distributed load. 15 EQUILIBRIUM EQUATIONS + SMA 0 .400 m (B y ) 120 N (.275 m) 225 N (.500 m) 120 N (.275 m) + 225 N (.500 m) By .400 m B y 363.75N + SFy 0 Ay 120 N 363.75 N 225 N A y 18.75 N A y 18.75N 16 STATICS: YOU NEED TO BE ABLE TO… Draw free-body diagrams, Know support types and their corresponding external reactions, Write and solve equilibrium equations so that unknown forces can be solved for, Solve for appropriate internal loads by taking cuts of inspection, Determine the centroid of an area, Determine the moment of inertia about an 17 axis through the centroid of an area. INTERNAL REACTIONS Internal reactions are necessary to hold body together under loading. Method of sections - make a cut through body to find internal reactions at the point of the cut. 18 FBD AFTER CUT Separate the two parts and draw a FBD of either side. Use equations of equilibrium to relate the external loading to the internal reactions. 19 RESULTANT FORCE AND MOMENT • Point O is taken at the centroid of the section. • If the member (body) is long and slender, like a rod or beam, the section is generally taken perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. • Section is called the cross section. 20 COMPONENTS OF RESULTANT • Components are found perpendicular & parallel to the section plane. • Internal reactions are used to determine stresses. 21 COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEM Start with internal system of forces as shown below to get proper signs for V, N and M. V 22 Summary of Typical Strength of Material Problem: 1. Draw FBD. 2. Calculate unknown external reaction forces first (at supports). 3. Calculate internal forces at point of interest by cutting member if necessary. 4. Calculate area properties (inertia, centroid, area, etc.). 5. Calculate stress!! 23 F.B.D 24 25 Bending Moment, Shear force, and Normal Force Sign convention for bending moment (M): Negative Bending Positive Bending Sign convention for Shear force (V) : Positive Shear Negative Shear Sign convention for Normal force (N) : Positive Normal 26 Negative Normal 27 28 F.B.D F.B.D 29 EXAMPLE: THE 500 KG ENGINE IS SUSPENDED FROM THE BOOM CRANE AS SHOWN. DETERMINE RESULTANT INTERNAL LOADINGS ACTING ON THE CROSS SECTION OF THE BOOM AT POINT E. 30 F.B.D 31 32 Example (Classwork): Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at G of the beam shown in fig. 1-6a. Each joint is pin connected. 33 (Classwork): F.B.D 34 35 QUESTIONS? 36