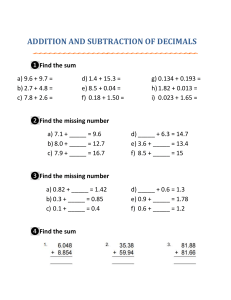
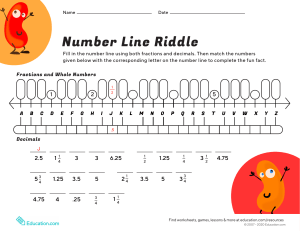
Term Mathematics department Year 9 – Scheme of work (Long term plan) Academic year 2023/2024 Subject Teacher: Ms Zayneb Unit 1 Integers Autumn 1 2 Expressions, formulae and equations Page numbers in the book 9-28 29-64 Topics Factors, multiples and primes. Multiplying and dividing integers. Square roots and cube roots. Indices. Constructing expressions. Using expressions and formulae. Expanding brackets. Core Objectives Understand factors, multiples, prime factors, highest common factors and lowest common multiples. Understand that brackets and operation follow a particular order. Estimate, multiply and divide integers, recognizing generalisations. Recognise square of negative and positive numbers, and corresponding square roots. Recognise positive and negative cube numbers, and the corresponding cube roots. Understand the hierarchy of natural numbers, integers and rational numbers. 3 Place value and rounding 66-79 Multiplying and dividing by 0.1 and 0.01. Rounding. Prepared by: Mr Mahamed Strand of mathematics Number Understand that letters have different meaning in expressions, formulae and equations. Understand that the order of operation (BIDMAS) rules applies to algebraic terms and expressions. Understand that a situation can be represented either in words or as a formula. Understand how to change the subject of a formula by using knowledge of inverse operation. Understand how to expand a bracket with a single term. Algebra Use knowledge of place value to multiply and divide integers by 0.1 and 0.01. Round numbers to a given number of significant figures. Number 4 Decimals 80-103 Ordering decimals. Multiplying. decimals Dividing by decimals. Making decimals calculations easier. Autumn 2 5 Angles and constructions 105-125 Parallel lines. The exterior angle of a triangle. Constructions. 6 Collecting data 7 Fractions Spring 1 126-136 137-170 Data collection. Sampling. Fractions and recurring decimals. Ordering fractions. Subtracting mixed numbers. Multiplying an integer by a mixed number. Dividing an integer by a fraction Making fraction calculations easier. Understand the relative size of quantities to order and compare decimals (positive and negative) using the symbols =, ≠, >, <, ≥, ≤. Estimate and multiply decimals by integers and decimals. Estimate and divide decimals by numbers with one decimal place. Use knowledge of the laws of arithmetic and order of operations (including brackets) to simplify calculations containing decimals. Number Recognise and describe the properties of angles on parallel and intersecting lines, using geometric vocabulary such as alternate, corresponding and vertically opposite. Derive and use the fact that the exterior angle or a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles. Construct triangles, midpoint and perpendicular bisector of a line segment, and the bisector of an angle. Geometry and measure Choose and justify appropriate methods to collect data and choose a sample. Know different sampling methods and their advantages and disadvantages. Statistics Recognise fractions that are equivalent to recurring decimals. Understand how to order and compare decimals and fractions. Subtract mixed numbers, writing the answer as a mixed number in its simplest form, and estimate the answer. Multiply an integer by a mixed number and estimate the answer. Multiply an integer by a proper fraction and estimate the answer. Use the laws of arithmetic and order of operations to simplify calculations containing fractions. Number 8 Shapes and symmetry 171-196 Quadrilaterals and polygons. The circumference of a circle. 3D Shapes 9 Sequences and functions 198-223 Generating sequences. Finding rules for sequences. Using the nth term. Representing simple functions. Identify and describe the hierarchy of quadrilaterals. Understand that the number of sides of a regular polygon is equal to the number of lines of symmetry and the order of rotation. 𝐶𝑖𝑟𝑐𝑢𝑚𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑒 Know that 𝜋 = 𝐷𝑖𝑎𝑚𝑒𝑡𝑒𝑟 Know and use 𝐶 = 𝜋𝑑 Understand and use Euler’s formula: F+V=E+2. Represent front, side and top view of 3D shapes to scale. Extend knowledge of term-to-term rules and generate more complex numerical sequences. Use knowledge of term-to-term rules and generate sequences from spatial patterns. Extend knowledge of nth term rules. Extend knowledge of function machines. 10 Percentages 224-234 Percentage increases and decreases. Using a multiplier. Write change in value as a percentage. Increase or decrease a value by a given percentage. Use a multiplier to increase or decrease a value by a given percentage. 11 Graphs 235-255 Functions. Plotting graphs. Gradient and intercept. Interpreting graphs. Representing situation in words with functions of the form y=mx+c. Constructing table of values for a function and using it to plot a graph. Plotting graphs of y=mx+c. Interpreting the values of m and c. Interpreting real-life graphs with several components. Simplifying ratios. Sharing in a ratio. Ratio and proportion. Spring 2 12 Ratio and proportion 257-274 Geometry measures Use equivalence to simplify and compare ratios. Share an amount into a given ratio with two or more parts. Understand and use the relationship between ratio and direct proportion. Algebra Number Algebra; statistics and probability Number 13 Probability Summer 1 14 Position and transformation 15 Distance, area and volume 275-288 290-330 331-351 Summer 2 16 Interpreting and discussing results 353-387 Calculating probabilities. Experimental and theoretical probabilities. Bearings The midpoint of a line segment. Translating 2D shapes. Reflecting shapes. Rotating shapes Converting between miles and kilometres. The area of a parallelogram and trapezium. Calculating the volume of triangular prisms. Calculating the surface area of triangular prisms and pyramids. Interpreting and drawing frequency diagrams. Time series graphs. Stem-and-leaf diagrams. Pie charts. Representing data. Calculate the probability of an event by first finding the probability of the complementary event, or by listing all the possible outcomes in a systematic way. Compare the results of an experiment to estimate probabilities obtained from equally likely outcomes. Statistics and probability Understand and use bearings. Use coordinates to find the midpoint of a line segment. Translate points and 2D shapes using vectors. Reflect 2D shapes and points in a given mirror line. Identify a reflection and its mirror line. To be able to relate shapes and describe rotations on a coordinate grid. Statistics and probability Know that distance cane be measured in miles or kilometres, and that 1 mile = 1.6 kilometres. Derive and use the formulae for the area of parallelograms and trapezia. Derive and use the formula for the volume of a triangular prism. Calculate the surface area of cubes, cuboids, triangular prisms and pyramids. Geometry and measure Record, organise and represent categorical, discrete and continuous data. Use time series graphs to record, organise and represent discrete and continuous data. Use stem-and-leaf diagrams to record, organise and represent discrete and continuous data. Record, organise and represent categorical, discrete and continuous data. Choose and explain which representation to use in a given situation. Statistics and probability