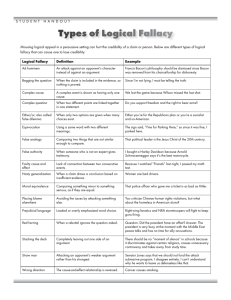
Disagreement in attitude- Disagreement about preferences Knowledge by acquaintance- Knowledge of familiar places or people Propositional knowledge- Knowledge of something that is true or false Observation- Used to check the truth of an empirical statement Mystical experience- Usually a spiritual or religious experience Merely verbal disagreement- Disagreement brought about by misunderstanding Reasoning- Truth is being a part of a coherent system of belief Practical knowledge- Knowledge of skills Correspondence Theory- Truth is reference to a fact Theories of truth- Ways of explaining the truth Pragmatic Theory- Truth is what is beneficial to believe Coherence theory- Used to check the coherence of the statements Opinion- An unjustified claim that something is true Methods of Truth- Ways of knowing the truth Knowledge- Justified true belief Intuition- A direct grasping of the truth Disagreement in belief- Disagreement about facts. A priori truth- Can be known before any relevant experience A posteriori truth- Can be known only after some relevant experience Empirical truth- Established by sense of experience. Fallacies Sound Deductive Argument Informal fallacies Reasoning Formal fallacies Premise Weak Inductive Argument Deductive Argument Conclusion Inductive Argument Strong Inductive Argument Valid Deductive Argument Invalid Deductive Argument Unsound Deductive Argument Cogent Inductive Argument Uncogent Inductive Argument THE KINDS OF SOUL ACCORING TO ARISTOTLE 1. SOUL OF PLANTS- VEGETATIVE OR NUTRITIVE SOUL - it enables plants to perform activities necessary for nourishment, growth, and reproduction. 2. SOUL OF ANIMALS- SENSITIVE SOUL - enables animals to perform the activities necessary for nourishment, growth, reproduction, sensation, and locomotion. 3. SOUL OF HUMANS- RATIONAL SOUL - enables animals to perform the activities necessary for nourishment, growth, reproduction, sensation, locomotion, intelligence or rational thinking, and freedom or free will. TWO ARGUMENTS OF PLATO FOR THE IMMORTALITY OF THE SOUL 1. THE SOUL MUST BE IMMORTAL OTHERWISE WE CAN NEVER EXPLAIN THE NATURE OF KNOWLEDGE AS RECOLLECTION. 2. SOULS ARE IMMATERIAL (NONPHYSICAL) THEN THEY ARE NOT COMPOSED OF PARTS. TWO KINDS OF FALLACIES 1. FORMAL FALLACIES 2. INFORMAL FALLACIES THREE KINDS OF INFORMAL FALLACIES 1. FALLCY OF AMBIGUITY 2. FALLACY OF RELEVANCE 3. FALLACY OF PRESUMPTION 14 SPECIFIC TYPES OF FALLACIES FALLCY OF AMBIGUITY- (1) Fallacy of Equivocation (2) Fallacy of Composition (3) Fallacy of Division FALLACY OF RELEVANCE- (1) Fallacy of Argument from Ignorance (2) Fallacy of Appeal to inappropriate Authority (3) Fallacy of Appeal to the Person (4) Fallacy of Appeal to Pity (5) Fallacy of Appeal to Popular Will (6) Fallacy of Appeal to Force FALLACY OF PRESUMPTIONS FALLACY OF PRESUMPTION- (1) Fallacy of Complex Question (2) Fallacy of False Cause (3) Fallacy of Begging the Question (4) Fallacy of Accident (5) Fallacy of Hasty Generalization