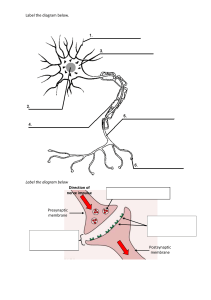
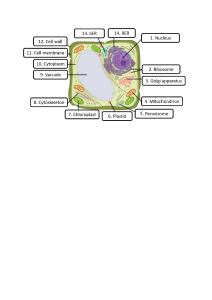
ALLAMA IQBAL OPEN UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE EDUCATION Course: Trends and Issues in Science Education (6771) Assignment-II QUESTION: 1 Describe the importance and scope of performance assessment in science learning. Also develop a mechanism for assessment of performance of learners in science. ANSWER: PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT IN SCIENCE LEARNING: Science, as we all know is about facts and the evidence which proves those facts. In this modern era, the new discoveries and invention are all due to science and its application. It is the fundamental pillar of our society and world. Learning science makes one use his brain to its fullest and the basic of any science evaluation or theory is a "hypothesis". (S Dehaene, 2001) It has been proven that all great scientists first "thought" of something and then worked to achieve their desired results. And throughout history, there have also been cases of accidental discoveries like the famous discovery of gravity by Isaac Newton. His story is worldwide famous for its simplicity and now his rules are the fundamentals of physics which we all study in our secondary school education. These all things are now the part of science. And as students learn something they need to give assessment. These assessments helps in measuring how well a student can apply their knowledge which they've learned, not if, they can recall the topic. ( R Carnap, 1966) IMPORTANCE: Performance assessment in science learning develops a sense of independency in learners. It increases the ability and way of observing, thinking and analyzing problems, and it also helps in developing skills of operating and utilizing the equipment and devices used in science learning. Furthermore, it enhances the emphasization of conceptual based learning. “The content and form of an assessment task must be congruent with what is supposed to be measured”( NL Webb, 1997) It helps to improve the student learning experience and evaluate the effectiveness of lesson plans. The assessment process is a tool for interacting with the expectations of the science education system. Assessment practices and policies gives a proper definition of what is important.( MC Lemos, 2005) For example, what students need to learn, how teachers should teach, and where resources need to be allocated. SCOPE: Scope of performance assessment in science learning is to develop the self-assessment skills in students. It is use to generate the ability to justify their answers beyond guessing them. “Eliciting and analyzing explanations are useful ways of assessing science achievement”.( OL Liu, 2011) Moving onto the assessment of performance in scientific learning is quite crucial. Scientific learning is all about proving your theories which is perfomed and then proved. The performance takes place in the designated labs. The students who are learning and are involved in scientific education, it is compulsory for them to prove and work on their particular research which is assessed by their teachers who have expertise in their field of education.( J Osborne & J Dillon, 2008) MECHANISM: Assessment can be held through different ways or methods like framework matrix, observation form, rubrics to evaluate their ability. There can be a combination of four components in numerous ways. For example, teachers is using students’ data to plan and modify teaching practices, and leaders of business are using per capita educational expenditures to locate their businesses. A number of users, methods and data contributes for importance of assessment process. DATA USE DATA COLLECTION METHODS TO COLLECT DATA USERS OF DATA PLAN TEACHING TO DESCRIBE AND QUANTIFY STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT AND ATTITUDE TEACHER PREPARATION AND QUALITY PROGRAM PAPER AND PENCIL TESTING PERFORMANCE TESTING TEACHERS INTERVIEWS EDUCATIONAL ADMINISTRATORS PORTFOLIOS PARENTS GUIDE LEARNING CALCULATE GRADES MAKE STUDENTS COMPARISIONS CREDENTIAL AND LICENSE DETERMINE ACCESS TO SPECIAL OR ADVANCED EDUCATION DEVELOP EDUCATION THEORY INFORM POLICY FORMULATION CHARACTERISTICS RESOURCE ALLOCATION POLICY INSTRUMENTS PERFORMANCES PUBLIC OBSERVING PROGRAMS, STUDENTS, AND TEACHERS IN CLASROOM TRANSCRIPT ANALYSIS POLICYMAKERS EXPERT REVIEWS OF EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS MONITOR EFFECTS OF POLICIES ALLOCATE RESOURCES EVALUATE QUALITY OF CURRICULA PROGRAMS, AND TEACHING PRACTICES INSTITUTIONS OF HIGHER EDUCATION BUSINESS AND INDUSTRY GOVERNMENT CONCLUSION: The learning is as basic as a child learning, he makes mistakes which is then corrected by their parents, and similarly teachers are a parent to that learning students. It is their responsibility to correct them and show them the right path to make them successful in their lives. Without the expertise and guidance of our teachers students will not be able to get proper guidance and there will be no one to correct us that’s why the assessment is vital in scientific education. QUESTION: 2 Q-2 Identify major online resources for teaching of Mathematics or Biology, develop a lesson plan by using these resources. ANSWER: MAJOR ONLINE RESOURCES FOR TEACHING OF BIOLOGY: 1- Interactive display system (IDS): Interactive teaching is a type of teaching in which the teachers make students actively involved in learning process by way of making regular interaction with teachers, students, student and use of audio-visuals. Every students is encouraged to be an active participants. (I Korytina, 2021) IDS also help teachers in sharing digital images and video clips. 2- Slide share: Slide share is done by teachers in giving online lectures. This slide share can be done on Google meet, zoom or any other application which is used in taking online classes. (AK Jena S Bhattacharjee & 2020) 3- PowerPoint presentation: PowerPoint is use to make lectures and presentations. It help teachers in making Class lectures in outline format, which can then be shown as slides. (RJ Craig & JH Amernic 2006) 4- Simulations & animations: Animation plays a great role in Simulation by making the movement of characters or None Playable Characters. It’s also helps in creating weather effects. For instance, wind is blowing the trees. Simulations promote concept attainment through experiential practice. They assist students for understanding the nuances of an idea. Students often find themselves engaging more deeply in this than other activities, as they get personal experience in activity, instead of hearing about it or seeing it. (J Cioffi, 2001) 5- Websites: Websites can be used as a tool for learning because it has so many resources regarding the subject. 6- YouTube: Teachers usually make videos on YouTube of different topics and share link with students. 7- Scrambled class: Students in a scrambled class start their class online by watching a summarize lecture or reading a course outline, before engaging in an online discussion with classmates and teacher. (JC Bean & D Melzer, 2021) LESSON PLAN GENERAL OBJECTIVE: After teaching this topic student will be able to: 1- Know the importance of cell in human body. 2- Classify difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms. SPECIFIC OBJECTIVE: After going through the topic the student will be able to: 1- Identif which living being’s cell it is. 2- Can explain various types of cells. 3- Give description of all components of cell. TEACHING METHOD: Online teaching method (Using IDS, you tube, websites etc.). AV AIDS: Computer, Digital projector, interactive whiteboard, internet connection. PREVIOUS KNOWLEDGE ASSUMED: Teacher assure the student must know everything about cell. ANNOUNCING THE TOPIC: Cell-A basic unit of life. Scrambled cell: The class shall be divided into two groups. Every group will pick their representative. Scrambled letters will be shown on the screen and students will guess what term it is. 1- SPALAM 2- SMMEOSEO 3- MMNEEARB 4- SUELCUN 5- OOOMMRECSH Answers will be written on the illustration boards. Group which have more points will win. INTRODUCTION: Cell is the basic unit of life. (Ellinger, 2014) Our body is consist of millions or billions of particles called cells. Cell is just like a tiny system which has organelles with different functions inside it. MOTIVATION: There's a picture given which is showing a bank robbery. Students have to answer these questions. 1- Imagine our houses and Schools are permeable to anyone. According to your thinking what will happen to our daily life. 2- just like that do you think there’s a need of guards or barriers for cells to protect their inside material? Using PowerPoint presentation teacher will present the topic. IN DETAIL: CELL: Cell is composed of many organelles like mitochondria, ribosomes, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum etc. But before going deep first we will discuss important parts of cell. (KR Pitts, Y Yoon & EW Krueger, 1999) •Cell wall •Cell membrane CELL WALL: Cell wall was first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. Cell wall is a flexible layer which is rough and surrounds some type of cells. It is present outside the cell membrane and it provides structural support and protection to these cells. (VP Sahi, 2018) Major regions of cell wall: •Middle lamella •Primary wall •Secondary wall Components: •Cellulose •Cross linking glycan •Peptic polysaccharide •Protein •Lignin •Suberin •Wax •Cutin •Water Structure: Cell wall is present only around plant cell. It is made up of cellulose. (UP Agarwal, 2006) Functions: 1- It helps in maintaining shape of the cell. 2- It gives support and mechanical strength. 3- It prevents bursting of cell membrane. 4- It control cell volume and cell growth. 5- It allow water and other liquid substances to pass through it. CELL MEMBRANE: Cell membrane was first described by C. Naegeli and and C. Cramer in 1855. (A Kleinzeller, 1995) Cell membrane is a membrane which separate all the internal parts of cell wall from outside environment. It is permeable in nature and prevent substances coming from in and out of cells. It is also known as plasma membrane. Components: •Lipids •Proteins Structure: The plasma membrane structure is like a mosaic of components. It includes phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates which provides the membrane a character of fluid. (GL Nicolson, 2021) Function: Cell membrane is important to maintain cellular integrity and transportation of molecules inside and outside of the cell. It is selectively permeable. (AA Gurtovenko, J Anwar, 2010) TODAY’S CHALLENGE: • Students will be divides in 2 teams. • Every team will make 5 questions based on today’s lesson • These questions should be of objective type. • Make answers of your own quiz questions. • Quiz questions and answers will be taken. • Your questions will be ask from second team. • Each question will carry 1 point. • Team who got most points win. Cell wall and cell membrane model construction: Class will be divided into six groups. Three groups will construct cell wall model and three will construct cell membrane model. Time will be of 15 minutes. RECAPITULATION: 1- Who discovered cell wall? 2- Give three functions of cell wall. 3- Describe cell membrane as barrier. HOMEWORK: Read locomotion of cell. Write your findings on 1/2 crosswise white paper. CONCLUSION: Since online learning have been introduced the learning process has developed. Online learning has made life easier. It saves time, wealth and energy. Teaching has become easier through these online resources. Online teaching and learning also faced some challenges which are making it difficult but maybe it will resolve after sometime. QUESTION: 3 Q-3 Highlight the quality parameters for science learning. What are the problems in ensuring quality of science teaching in Pakistan? ANSWER: QUALITY PARAMETERS FOR SCIENCE LEARNING: Following are the main quality parameters for the developments of science learning. OBJECTIVE: To provide better understanding and concept of interpreting the natural systems of the era. ( G Walsham, 1993 ) CURRICULUM: The curriculum should be based on observation and building hypothesis, prediction, planning and carrying out solution to the problems, results (based on recording and analyzation) and spread thinking to accommodate sharing and discussing.( DH Clements & J Sarama , 2008 ) EVALUATION/ASSESSMENT: It must be based on learner’s skills either analytical or technical, observance, judging the parameters of science, and how they respond to the nature of science, their critical thinking, and problem solving techniques rather than getting assessed on the basis of their power of memorization. ACTIVITIES : Activities must include practical learning which throughout help in clearing the doubts and concepts of learners. They must be able to learn how to interact with science learning and how to remove basic barriers and come up with alternative solutions of science problems. (M Esteves, B Fonseca & L Morgado, 2011) RESOURCES: Quality of learning enhances when learners are provided with the appropriate resources. Resources includes tool which are valuable resource of learning science and creating tasks. (K Regmi, L Jones , 2020) RESEARCH: Learners must know how to read research paper and how to extract knowledge and information from that particular research. It would probably benefit the learner to figure out more better their skills and how to approach conclusion in a professional manner. ( P Freebody, 2013) PROBLEMS IN ENSURING QUALITY OF SCIENCE TEACHING: LACK OF UNIFORMITY: Quality of teaching isn’t considered as a problem nowadays. The wave of increasing dissidence make a huge gap in uniformity and these are the logical consequences of this system. In result, the current polarized system of education occurred a great difference on grounds on the basis of social, politics and economy.( M Aziz bloom, 2014) EDUCATION WITHOUT DIRECTION: Education without any goal is meaningless, similarly teaching without any motivation is regardless of fruitful result. Every system create its own base of teaching and education on the basis of lusty training and skills on different paths. Pakistan system being a directionless and unable to develop and guide a science teaching and education system causes in lack of students skills and creativity. (JA Piazza, 2006) OUTDATED CURRICULA: The outdated curriculum is the major sector and prove of that we’re living in backward era. This system doesn’t meet the needs of current era modern times. The main purpose of education is to build a psychological, philosophical and sociological foundation of education which can only be possible with the new methods of science teaching. .( A Rehmani, 2006) LACK OF PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT OF TEACHERS: Education system cannot be developed brightly until and unless the development of professional teaching ways made not possible, and there is a lack of training of teachers for professional development due the lack of resources and funding’s. There aren’t such standards and institutes which give teachers a proper training and where there are available the resources and methods are so outdated that are not enough useful for the current time to made a progress. . ( R Esichaikul, 1998) SYSTEM OF EXAMINATION: System of education doesn’t match the requirements of the modern world i.e. its method of assessment and evaluation. It is based on memorizing rather than it should be based on the students’ skills and performance. It doesn’t promote critical thinking, observance, technical and analytical skills among students. LACK OF RESOURCES: The equipment, devices which help in enhancing the skills and ability of students aren’t available. However, outdated books and facilities are available which doesn’t fulfill the requirements and needs of modern era progress. Books, libraries aren’t providing enough information about new technologies that are being used in today’s world. ( J Dunlosky, 2013) POLICY IMPLEMENTATION: The policies which were announced by our government are highly ambitious but could not be implemented in true manners and spirit. Problem related to corruption, lacking of funds and gross inconsistency in various political regimes in Pakistan is rising day by day. Policies for such problems i.e. science teaching and learning hasn’t been made as it is the most neglected problem for the policymakers. LOW BUDGET ALLOCATION: Finance is like the engine of any system. Our so called government is giving less than 2.5 percent budget to the teaching and education sector which is not sufficient for the growing educational needs in the present changing times. The education system of Pakistan has been wiped out mostly due to infrequent financial condition. Developed countries invest a lot in science teaching and education that’s why they made more progress in the world of technology as compare to the developed countries. Although, developing countries like Sri Lanka and Bangladesh have set more budget on science but the budget of Pakistan has got stuck at one point instead of increasing. ( A Qayyum, SZ Lasi, 2013) CONCLUSION: The problems which aren’t even thoroughly considered in the field of teaching causing a damage to the future of Pakistan. These are completely negligible by the education system and the voices which are raised against this problem, system turns a deaf ear onto it. The critical analysis has also been done to provide a path to solve such problems. QUESTION: 4 Q-4 Select two research papers related to science teaching, write critical review of each paper separately. RESEARCH PAPER: 1 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311420835_Science_Teaching_and_Learning_ in_Schools_Theoretical_and_Empirical_Foundations_for_Investigating_ClassroomLevel_Processes CRITICAL VIEW ON SCIENCE TEACHING: INTRODUCTION: The progress and abilities of students depend on the method of teaching. Teachers contributes a major role in the development of science students, the way they think, they observed and analyse the methods, processes of the nature of world. The relationship between the teacher and student plays a dynamic role in the effectiveness of education. (Hugener et al, 2009). Mainly, the latest information and knowledge helps the learners to gain an advantage from teaching. ASPECTS: This study shows five important dimensions of variables which can be identified. CLARITY: Clarity in learning goals and relation to the presented content. STRUCTUREDNESS: Refers to the systematic approach of instruction. COGNITIVE ACTIVATION: The cognitive level of tasks mainly based on attention pacing. PACING: adaptively sequencing and tasks to students’ abilities. CLASROOM MANAGEMENT: the learning environment. (Neumann et al, 2012 ). Classroom environment created by the teachers leads a focus of students towards learning abruptly and to the participation. Supportive teaching pattern i.e. constructive feedbacks, leading conclusions helps more in science field towards activation in knowledge, challenging tasks, activities based on science learning. Several studies shows this pattern and get agreed with it (e.g. Baumert et al, 2010 ; Lipowsky et al,2009 ; Rakoczy et al,2007 ). Studies showed a focus on different variables of science teaching. In respective of components of science TIMSS 1999 video study (Roth et al, 2006 ),shows patterns of teaching of science. The descriptive findings showed two faces. First, that the five countries, varied in their features of organizational instructions, content features, and the ways in which students were involved in actively doing science work (Roth et al, 2006 , p. 179). Secondly, there were common grounds of social, economic, socio-economical among the four relatively high achieving countries. Here, the teachers focus on high expectations for student learning, and always try to share different platforms for the students to engage them in doing science work. TEACHING BASED VARIABLES: Different models on science teaching variables have been implemented across the world after several surveys. Effective science teaching and learning based on the assumption of active participation and hands-on experiments and this thing creates a framework. The domain specifies perspective is being given more attention by this framework following the basic characteristics which are mentioned as, interactive science teaching scale that involves debates and discussion in the classroom on science subjects, conclusions that are being carried out by performing experiments and concluded the result that are coming out by those observation, science teaching and learning aim is to engage the students on broader spectrum their skills of evaluation, performance and investigation on their knowledge on the basis of science they’ve learned, real life applications help them in teaching the concepts more clearly. CONCLUSION: The teacher supports competence of students by providing them with opportunities to regulate learning processes on their own. Autonomy is only supported when students can determine and realize their personal goals and interests. Teacher’s interest clearly be shown in assessing students and the way they teach and feed the concepts and logical importance in the field of science. Several studies have shown positive consequences on students’ cognitive and emotional processes (Ryan and Deci, 2000 ;Kunter, 2005) RESEARCH PAPER: 2 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335927886_The_Role_of_Cooperative_Learning_Met hod_in_Teaching_of_Science_Subject_at_Elementary_School_Level_An_Experimental_Study_ The_Role_of_CLM_in_Teaching_of_Science_Subject_at_ESL_An_Experimental_Study_2 Critical View on Science Teaching INTRODUCTION The crucial purpose for education is to expand the cognitive and comprehensive abilities of students. As the world advances, the awareness of science and nature is necessary to grasp. And one of the foremost aim of science education has been to encourage the mental scientific habits, growth of skills to do scientific analyses and to make students capable of reasoning in scientific context. For this goal the relationship of teachers and students play a dynamic role. Students are dependent on their mentors for their developmental processes, in terms of education and knowledge. Carl sagon quoted that every individual is born with the potential to be a scientist, but we kick it out of them. Only few people do make it across the system with their sense of surprise and excitement for science intact”. The way students behave and interact in classroom is greatly focused on teachers. They should be well trained and must include meaningful interactions, discussions and activities with their students, during the lecture. INCLUSIVE STRATEGIES FOR SCIENCE TEACHERS: As per Walberg, numerous investigations and studies were done to analyze students’ academic achievement, the most effective learning method observed is cooperative learning. (Walberg, 1986). Today’s world teacher must be prepared with all the recommended and necessary tools to progress logical reasoning among students. Rajab and Ibrahim stated that to stimulate interaction between learners and to endorse social skills for thriving conjoint performances, cooperative learning method is the best to address the needs of diverse learners. (Rajab & Ibrahim, 2017). Aronsan and et al. explained that dividing students in minor heterogeneous groups, in a class of various talented learners, it would be fruitful for them as they communicate with each other and most importantly they collectively achieve an academic goal. The collaborative group discussions and activities improve their understanding of scientific content and the theoretical and practical grades in the respective subject. (Aronson; 2014; Çiğdemoğlu, Kapusuz & Kara, 2015; Hosseini, 2017; Rajab & Ibrahim, 2017). A teacher should be welcoming and respecting towards students concepts and ideas. He or she must be a good listener and appreciate even if the student’s response is not accurate. As this will promote the brainstorming and love for scientific learning among students. A teacher should be open minded with sharp judgement, disregarding any gender discrepancies in classroom. Everyone must have their voices being heard by the teacher with proper attention. A classroom with diversity of intellectual students, you can add more colors to it and upgrade the classroom life, by giving an opportunity to students to interact and learn together. Learners appreciate miscellany and esteem each other’s view and idea. (Johnson, Johnson, Stanne, & Garibaldi, 1990; Schwieger, Gros, & Barberan, 2010; Hossain, & Ahmad, 2013). The classroom discussions must be purposeful, authentic and thought provoking with logical reasoning and concept enlightening. The classrooms must be hospitable for all students irrespective of their social identities, cultural values, race, color, language and sexual orientation and gender identities. CONCLUSION: The extent of method of science teaching greatly determines the progress of children’s academic achievement. By providing an inclusive classroom there will be good relationship between teacher and students which will ultimately enhances the level of scientific learning and improve overall literacy rate in country. A teacher’s interest and teaching credibility assess the student’s academic empowerment. A teacher is the one who can make a classroom ecosystem a healthier place for all members. REFERENCES: 1- Berland, L. K., & McNeill, K. L. (2010). A learning progression for scientifi c argumentation: Understanding student work and designing supportive instructional contexts. Science Education, 94 (5), 765–793 2- Chin, C., & Osborne, J. (2008). Students’ questions: A potential resource for teaching and learning science. Studies in Science Education, 44 (1), 1–39. Doi 3- Driver, R., Newton, P., & Osborne, J. (2000). Establishing the norms of scientifi c argumentation in Classrooms. Science Education, 84 , 287–312. 4- James R. Okey ,Journal of Science Education and Technology, March 1995. 5- Barrett, H. (1994). Technology-supported assessment portfolios. 6- Feuer, M., and Fulton, K. (1993). The many faces of performance assessment. 7- Helgeson, S., and Kumar, D. (1993). A review of educational technology in science assessment. 8- Popham, J. (1993). Circumventing the high costs of authentic assessment. 9- Wiggins, G. (1989). A true test: Toward more authentic and equitable assessment. 10- Rehman H. and Khan N., “The flaws in Pakistan’s Education System”, Abasyn Journal of Social Sciences, vol/issue: 4(1), 2011. 11- Government of Pakistan, Ministry of Education. “National Assessment Findings”, Islamabad, National Education System, 2006. 12- Flick, L. B. & Lederman, N. G. (2004). Scientific Inquiry and the Nature of Science: Implications for teaching, learning, and teacher education. Science & Technology Education Library 25. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Press. 13- Barron, B.J.S., Schwartz, D.L., Vye, N.J., Moore, A., Petrosino, A., Zech, L., Bransford, J.D. & The Cognition and Technology Group at Vanderbilt (1998). Doing with understanding: Lessons from research on problem- and project-based learning. Journal of the Learning Sciences, 7(3&4), 271–311 14- The Science Teacher-may/June 2022 (Volume 89, Issue 5), By Ann Haley Mackenzie 15- The Role of CLM in Teaching of Science Subject at ESL: An Experimental Study 2