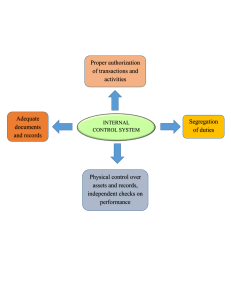
Typical Fraud Schemes and Related Controls Function/Activity Procurement/ Purchasing Indicators Controls to Prevent or Detect Significant internal control weaknesses. Corporate code of ethics prohibiting the acceptance of kickbacks. Cost of purchases is higher than prior years. Corporate policy prohibiting the acceptance of anything of value. Cost of purchases is higher than budget. Establishing and approving longterm contracts with major vendors. Purchases from particular vendors are higher than normal. Cost of purchases is higher than market values. Require that only approved vendors are paid for purchases, and only based on production activity. Requiring mandatory vacations Purchasing agent’s standard of living has increased. Kiting (which refers to the recording of a deposit from an interbank transfer in this period, while failing to record the related disbursement until the next period) Lapping (which refers to the concealment of the first customer’s payments, then allocating the second customer’s payment to the account of the first, and the third to the account of the second, etc.) Unjustified buildup of inventory or an increase in inventory turnover in days. Buyer is not taking any vacations and refused a promotion. Buyer accompanies a vendor on regular excursions. Significant deposits in a bank account towards the end of a period. Requiring frequent rotation of duties. Maintaining proper segregation of duties between the ordering, receiving, payable, and accounting functions. Typically, the auditor would examine a schedule of bank transfers for the week before and week after period end searching for checks that should have been listed as outstanding in the prior period but were not. Mandatory vacations and/or rotations of duties. Segregation of duties between sales, collections, and book keeping. Regular confirmations of customers’ balances and immediately investigating differences. Management’s pre-occupation with increased financial performance. An otherwise poor cash or current assets position. Several discrepancies between the books and customers’ confirmations. Lack of adequate segregation of incompatible duties. Employees failing to take vacations and/or refusing promotions. Unexplained lifestyle Senior Management Sales Inventory Managers regularly assume subordinates’ duties Managers subject to formal performance reviews. Managers dealing in matters outside their normal scope of responsibility. Strong Board and Audit Committee oversight Managers failing to comply with corporate directives and procedures. Ethical management Management’s pre-occupation with increased financial performance. A domineering management Generous performance-based reward systems. Compensation is significantly dependent on sales and/or profitability. Strong controls Significant returns after period end. No shipping documents available for sales invoices. An increase in bad debts. Poor controls over the warehousing. Strong controls <Accidental= fires or other forms of <environmental= damages