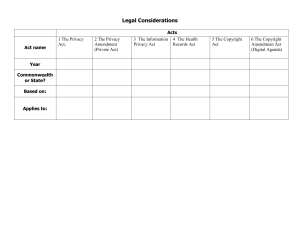
Module 4 The Information Age The Information Age - - Also called o Digital Age: use of digits or numbers o Computer Age: information is read by computers o New Media Age: utilization of digital platforms, unlike the traditional media such as radio, television, and newspapers Digital Platforms Timeline o 1440 ▪ Printing Press • Johannes Gutenberg o 1936 ▪ Modern Computing • Alan Turing o 1970 ▪ Personal Computers o 1973 ▪ Social Media o 1976 ▪ Apple Inc. • Steve Jobs o 1980 ▪ World Wide Web • Tim BernersLee Printing Press - - A device that applies pressure to an inked surface lying on a print medium to transfer ink Johannes Gutenberg Mass Communication: process of creating, sending, receiving, and analyzing messages to large audience via verbal and written media - The development of printing press and mass communication paved way to fast and easy way of disseminating information in print and permanently reformed the structure of the society Computers - - - - - A machine that solve any problem by performing any task from a written program Calculations: it became involved in communication due to rapid developments in the trade sector Computer: people who compiled actuarial tables and engineering calculations Allies Countries o United States of America, Canada, Britain, France, USSR o shortage of human computers for military calculations o Harvard Mark 1 ▪ a general-purpose electromechanical computer that was 50 feet long and capable of doing calculation in seconds that usually took people in hours Axis Powers o Germany, Italy, Japan, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria o German Navy’s Enigma Code ▪ an enciphering machine that the German armed forces used to securely send messages (Enigma: enciphering machine) - - - Alan Turing o an English mathematician hired by British top-secret Government Code and Cipher School o Code-Breaking Methods by Alan Turing ▪ an industrial process having 12,000 people working 24/7 ▪ Nazi made Enigma more complicated having approximate 10r144 ▪ Bombe Machine (Turing): An electromechanical machine that enables the British to decipher the Enigma machine ▪ Turing Machine • a theoretical machine that can solve any problem from simple instructions encoded on a paper tape • On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsp roblem (1937) Universal Machine o the foundation of computer science and the invention of computer Electronic Brains (1970) o The first to be introduced to personal computers (PCs) and witnessed the dawn of computer ages - - Homebrew Computer Club o An early computer hobbyist group, gathered regularly to trade parts of computer hardware and talked about how to make computer more accessible to everyone Steve Wozniak o Co-founder of Apple Inc. o Apple I or Apple Computer I ▪ A fully assembled printed circuit board Information and Communications Technology (ICT) - - - Information Technology o Utilizing technology o Storing, processing, and collecting data Communications Technology o Utilizing technology o Transmitting information thru broadcasting media or audiovisual processing o Transmitting information through wired or wireless network ICT refers to collecting, processing, storing data, and transmitting this data by the use of networks, internet, or telecommunications Diosdado Banatao - Bill Gates of the Philippines Invented two of the fundamental components in every PC today: the first single-chip set and the Windows Graphics Accelerator chip. These allowed data processing to be faster with the use of very little space The Eras of Information - - - Pre-Gutenberg Era o Before the invention of printing press Gutenberg Era o Invention of printing press Post-Gutenberg Era o After the invention of printing press Information Age Accelerated Growth of ICT o Printing Press (1440) ▪ Johannes Gutenberg ▪ A device that mass produced printed information Information Explosion in the Information Age - - - Information Explosion o A situation where there is an overabundance of data due to the rapid increase in the amount of information being published o The influx of information being easily accessible makes the processing of these data difficult for the user leading to information overload Information Overload o Occurs when information users become overwhelmed with the excessive flow of information which usually affects their psychological, social effects, and physical well-being Credible Source o A source of information authored by a person or an organization expert in their field which is free from personal biases and is based on evidence o CRAAP Test ▪ A framework primarily used in evaluating the credibility of information resources ▪ C: Currency – The timeliness of the information • When was the information published or posted? Revised or updated? • Does your topic require current information, or will older sources work as well? ▪ R: Relevance – The importance of the information for your needs • Does the information relate to your topic or answer your question? • Who is the intended audience? / an appropriate level? ▪ A: Authority – The source of the information • Who is the author/publish er/source/spon sor? • What are the author’s credentials or ▪ ▪ organizational affiliations? • Is the author qualified to write on the topic? Contact information? A: Accuracy – The reliability, truthfulness, and correctness of the content • Where does the information come from? / supported by evidence? • Has the information been reviewed or refereed? • Does the language or tone seem unbiased and free of emotion? P: Purpose – The reason the information exists • What is the purpose of the information? Is it to inform, teach, sell, entertain, or persuade? • Does the point of view appear objective and impartial? • Are there political, religious, institutional, or personal biases? Social Media - - Means of interaction among people in which they create, share, and, or exchange information ideas in virtual communities and networks The Universal Declaration of Human Rights o Article 27 ▪ Everyone has the right freely to participate in the cultural life of the community, to enjoy the arts and to share in scientific advancement and its benefits ▪ Everyone has the right to the protection of the moral and material interest resulting from any scientific literary or artistic production of which he is the author ▪ This document affirms everyone’s tight to participate in and benefit from scientific advances and be protected from scientific misuses. The right to the benefits of science comes under the domain of culture, so it is usually examined from a cultural right. ▪ Mukherjee listed some of the most important documents that center on a human rightsbased approach to S&T, and development and their key principles o o As stated by Quinto et.al. (2019), human rights should be integral to the journey toward the ultimate good. They should guide humans not only to flourish as individual members of society, but also to assist each other in flourishing collectively as a society. Human rights are rights to sustainability, as one author puts it. They may function as the “golden mean” particularly the protection the weak, poor, vulnerable from the deficiencies and excesses of S&T. S. Romi Mukherjee ▪ A senior lecturer on Political Theory and History of Religions (Paris Institute of Political Studies) ▪ Human rights-based approach to science, technology, and development ▪ [If] seeks to place a concern for human rights at the heart of how international community engages with urgent global challenges. The UN Development Programme characterizes this approach as one that ‘leads to better and more sustainable outcomes by analyzing and addressing the inequalities, discriminatory practices, and unjust o power relations which are often at the heart of development problems. It puts the international human rights entitlements and claims of the people (rightholders) and the corresponding obligations of the state (duty-bearer) in the center of the national development debate, and it clarifies the purpose of capacity development.” ▪ This approach identifies science as a socially organized human activity which is valueladen and shaped by organization structures and procedures ▪ It requires answer to whether the government and other stakeholders can craft and implement science and technology policies that ensures safety, health, and livelihoods; includes peoples need and priorities in development and environmental strategies; and ensure they participate in decision-making that affects their lives and resources Basic Human Rights ▪ We are born free and equal ▪ Don’t discriminate ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ - The right of life No slavery No torture You have rights no matter where you go ▪ We’re all equal before the law ▪ Your human rights are protected by law ▪ No unfair detainment ▪ The right to trial ▪ We’re always innocent until proven guilty ▪ The right to privacy ▪ Freedom to move ▪ The right to seek a safe place to live ▪ Right to a nationality ▪ Marriage and family ▪ Right to your own things ▪ Freedom of thought ▪ Freedom of expression ▪ Right public assembly ▪ Right to democracy ▪ Social security ▪ Worker’s rights ▪ Right to play ▪ Food and shelter for all ▪ Right to education ▪ Copyright ▪ A fair and free world ▪ Responsibility ▪ No one can take away your human rights UNESCO Recommendation on the Status of Scientific Researchers – 1974 (Article 4) o This document affirms that all advances in scientific and technological knowledge should solely be geared towards the welfare of the global citizens and calls upon members states - - - - to develop necessary protocol and policies to monito and secure this objective. o Countries are asked to show that science and technology are integrated into policies that aim to ensure a more humane and just society UNESCO Declaration of the Use of Scientific Knowledge – 1999 (Article 33) o This document states, “Today more than ever, science and its applications are indispensable for development. All levels of government and the private sector should provide enhanced support for building up an adequate and evenly distributed scientific and technological capacity through appropriate education and research programmes as an indispensable foundation for economic, social, cultural, and environmentally sound development. This is particularly urgent for developing countries. o This declaration encompasses issues such as pollution free production, efficient resource use, biodiversity protections, and brain drains. Human right should guide human not only to flourish as individual members of society, but also to assist each other in flourishing collectively as a society. Human rights in the face of technological development are critical factors in one’s journey toward eudaimonia or the good life. Human rights may function as the golden mean by protecting the weak, - poor, and vulnerable from the deficiencies and excesses of S&T. By imposing upon S&T, the moral and ethical duty to protect and uphold human rights, there can be more effective and sustainable approach to bridging the gap between poor and rich countries on both tangible and intangible aspects. o Artificial Intelligence - - - It is the simulation of human intelligence processes through machines Goals o To create expert systems ▪ Intelligent behavior ▪ Demonstration ▪ Explain ▪ Advice o To implement human intelligence in machines ▪ Understand ▪ Think ▪ Learn ▪ Behave like humans Applications of AI o Health care ▪ AI applications can provide personalized medicine and X-ray readings. Personal health care assistants can act as life coaches, reminding you to take your pills, exercise, or eat healthier. o Retail ▪ AI provides virtual shopping capabilities that offer personalized recommendations and discuss purchase options with the consumer. Stock management and site layout technologies will also be improved with AI. Banking ▪ AI enhances the speed, precision, and effectiveness of human efforts. In financial institutions, AI techniques can be used to identify which transactions are likely to be fraudulent, adopt fast and accurate credit scoring, as well as automate manually intense data management tasks. Impacts of Information Age - - Economic Shift o Explosion of the non-routine jobs ▪ Researchers Ian Stewart, Debapratim De, and Alex Cole found that jobs that require a routine have declined the most because they can be easily substituted by technology o Efficient production ▪ Computerized manufacturing to increase production and save time o Data storage and management ▪ Outsourcing improves data storage and file management Education Shift o o o o o o o - - - Computer-assisted learning Virtual classroom Distance learning Online education Papers to computer Libraries to google There is a shift from the teaching methods, techniques, and contents to concentrate more on critical reasoning skills to be able to take tons of information and synthesize it better. Government and Political Shift o Globalization of knowledge o E-government o Online voting and automated election o Improved national security o Interacting and providing services to the citizens o Controlling the content and flow of information o Managing government supply chains Private Life o Improved entertainment o Online shopping ▪ Lazada, Shopee o Payment and banking ▪ Online banking apps (transfer money without going to the bank) o Better communication o Food delivery services Positive o Improved entertainment and communication o Networking o Interactivity o Globalization: capacity of the internet to expand the user’s social world to faraway people - Negative o Increase cyber crime o Invasion of privacy o Online pornography o Threat to security o Plagiarism o Fake news o Digital divide Advantages of Technology (Adil, 2021) - - - - Medical o Helps physically challenged persons o Aids in the diagnosis of patients’ diseases Transportation o We can go to places easier and faster Communication o Before we used paper and pens to communicate but now, we can communicate through email, messenger, etc. Agriculture Banking Access to Information Education Entertainment Disadvantages of Technology - - Wastes our time o We spend too much time using technology, instead of sleeping already, we are browsing, playing, etc. Distracts us from work and study Reduces creativity Causes social isolation o We are busy using social media and we get addicted to it. We get isolated. o Instead of spending time eating with your family, you use your phone instead. - - - Causes environmental problems o Air, noise, and water pollution. Factories and vehicles are the main contributors of pollution Addiction Dependency on technology o If we depend on technology, then the value of human workers decrease Security issues o Spying, information mishandling Right to Privacy in Digital Environments - Data Protection o Data Privacy Act (DPA) of 2021 ▪ Monitor and ensure compliance of the country with international standards set of data protection ▪ Stronger privacy and cyber security policies ▪ Prevent hacking incidents ▪ Government agencies collect and process information but they are unregulated and unsecured that’s why DPA was created. ▪ In March 2016, 2 groups hacked the website of COMELEC and personal information belonging to 55 million registered Filipino voters was compromised o Digital Surveillance ▪ The Philippines generally prohibits wiretapping and other violations of the privacy of communication, but o it allows lawful interception when such activity is authorized by a written court order in relation to cases involving specific crimes. • Crimes such as treason, espionage, provoking war, and disloyalty in case of war, mutiny, rebellion, sedition, and kidnapping ▪ Cases of wire-tapping are not uncommon in the Philippines • In 2004, the controversial “Hello Garci” scandal, which wiretapped a conversation between the President Gloria Arroyo and an election officer from the COMELEC prior to the May 2004 elections, illustrated the shortcoming of safeguards that need to be in place. Privacy and Social Media ▪ Developments in technology have brought about more challenges to ▪ ▪ ▪ informational privacy – the person’s right to control information about himself/herself Protection of Filipinos against unreasonable searches and seizures Privacy of their communication and correspondence In the Philippines as in the rest of the world, several violations of privacy in social media using multiple platforms have been reported. These include the circulation of private images and videos without a person’s consent. Women and girls are mostly the victims of such online violations, that include the identity theft, unauthorized posting of images and videos, etc.