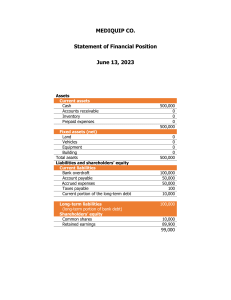
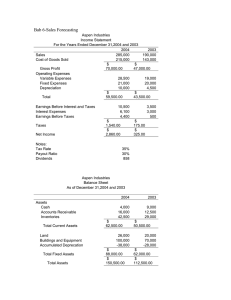
Title: An Introduction to Basic Accounting: Understanding the Language of Business Introduction Accounting is the backbone of any business, serving as the language that communicates financial information to stakeholders. It plays a pivotal role in making sound business decisions, tracking financial performance, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. This essay aims to provide a comprehensive overview of basic accounting principles, processes, and concepts, shedding light on its importance and fundamental role in the business world. 1. The Purpose and Role of Accounting At its core, accounting is a system of recording, summarizing, and interpreting financial transactions. The primary purpose of accounting is to provide accurate and relevant financial information to various users, including business owners, investors, creditors, employees, and government entities. This information allows stakeholders to assess the financial health of a company, make informed decisions, and evaluate its performance over time. 2. Accounting Principles and Concepts To maintain consistency and credibility in financial reporting, accounting relies on a set of principles and concepts. Some of the key principles include: a. Going Concern Principle: Assumes that the company will continue its operations for the foreseeable future, allowing for long-term planning and valuing assets based on their useful life. b. Matching Principle: Matches expenses incurred during a specific accounting period with the revenue generated in that same period, ensuring accurate profit determination. c. Revenue Recognition Principle: Revenue is recognized when it is earned, regardless of when the payment is received, ensuring proper revenue allocation in financial statements. d. Cost Principle: Assets are recorded at their original cost, allowing for reliable valuation and historical comparison. e. Consistency Principle: Requires businesses to use the same accounting methods and principles from one period to another, ensuring comparability between financial statements. 3. The Accounting Equation The foundation of accounting lies in the accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. This equation reflects the fundamental relationship between a company's resources (assets), its obligations (liabilities), and the owners' claims to those resources (equity). It serves as the basis for preparing the balance sheet, which provides a snapshot of a company's financial position at a given point in time. 4. Financial Statements Financial statements are crucial outputs of the accounting process that present the financial performance and position of a business. The three primary financial statements are: a. Income Statement: This statement shows the revenue earned and expenses incurred during a specific period, ultimately revealing the company's net income or net loss. b. Balance Sheet: As mentioned earlier, the balance sheet showcases the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular date. c. Cash Flow Statement: This statement tracks the inflows and outflows of cash over a specified period, helping stakeholders understand how cash is generated and used. 5. Recording Transactions: Double-Entry Accounting Double-entry accounting is the most common method used to record financial transactions. It follows the principle that every transaction affects at least two accounts—one account is debited, and the other is credited. The total debits must always equal the total credits, ensuring accuracy in the recording process. 6. Accrual vs. Cash Basis Accounting In accrual accounting, revenue and expenses are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This method offers a more accurate representation of a company's financial position and performance. On the other hand, cash basis accounting records revenue and expenses only when cash is received or paid, making it simpler but less precise. 7. Importance of Budgeting Budgeting is a critical aspect of accounting and financial management. It involves creating a financial plan for the future, outlining expected income, expenses, and investments. Budgets enable businesses to set financial goals, allocate resources effectively, and measure actual performance against projections, facilitating better decision-making and financial control. Conclusion In conclusion, basic accounting principles are the cornerstone of financial reporting, providing essential information for effective decision-making and business management. By understanding the accounting equation, financial statements, and principles, stakeholders can assess a company's performance and financial health. Accounting's role as the language of business cannot be overstated, as it allows businesses to communicate their financial story to various interested parties, ultimately leading to transparency, credibility, and the long-term success of the organization.