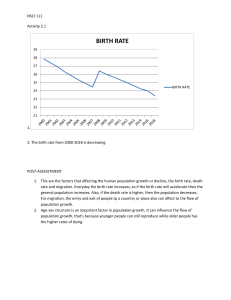
Lesson 2: Applied Economics Price and Basic Commodities Price • Price is only one of the factors that affects a buyer’s purchasing decision • It is important indictor of quality and image and provides customers with a way of making a judgement about value for money • Importance of price can vary tremendously depending on the product • Price is the only part of the marketing mix that will make a producer money - Product, Place and Distribution all cost a firm. COMMODITY • Commodity is a marketable item produced to satisfy wants and needs. • Refers to a basic, marketable good or service that is produced to meet a demand, whether that be a want or a need. Soft commodities are agricultural products such as wheat, coffee, cocoa and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil.. Labor Supply, Population Growth, and Wages Labor • Is the amount of physical, mental and social effort used to produced goods and services in an economy. • It is one of the four factors of production that drive supply. • Labor supplies the expertise, manpower and service needed to turn raw materials into finished products and services. Supply • Is a fundamental economic concept that describes the total amount of a specific good or service that is available to consumers. Supply can relate to the amount available at a specific price or the amount available across a range of prices is displayed on a graph. Population Growth • An increase in the number of people that reside in a country, state, country, or city. To determine whether there has been population growth. ( birth rate+ immigration) – (death rate + emigration) How Supply and Demand affects the population Salary structure affects prices, and prices affect supply and demand, which affect consumption. In a market-oriented economic system, the impact of population size on market demand affects supply and demand and prices. Population changes are slow, and consumption changes are slow. Wages • Money that is paid or received for work or services, as by the hour, day, or week. Labor migration and the Overseas Filipino Worker (OFW) phenomenon What is migration? • Refers to the movement of people from one place to another. 2 types of Migration: a. Internal Migration- refers to the movement of people within one country i.e. rural to urban migration. b. International Migration – refers to the movement of people from one country to another. Effects of Migration Positive Effects - Increase labor supply - Cheap labor Negative Effects - Overcrowding - Lack of housing facilities - Traffic congestion - Heavy pollution in air, water , noise - Unemployment - Occurrence of squatter areas What is Labor Migration? • Labor migration – is the process of shifting a labor force from one physical location to another • Labor migration takes place with the support of labor force Causes of labor migration 1. The desire of job seekers to increase income and improve the standard of living 2. The emergence of new industries 3. The relocation of production facilities of a given business to a new area. The OFW Phenomenon What are OFWs? • Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs) – are Filipinos who are presently and temporarily working outside the country. They may be land-based or sea-based workers. Ex. Domestic Helpers, Teachers, Seamen, Nurses Reasons behind the OFW Phenomenon 1. High Unemployment Rate - Newly graduates join the labor force that increases the competition in the labor market. Instead of waiting for them to be hired locally, Filipinos seek employment overseas. 2. Low Salary offered by employers in the Philippines - Filipinos are willing to work abroad due to low salary. Even professionals like nurses, engineers and teachers would prefer to work abroad ad household help or office workers because of the higher salary offered overseas. • 3. Discrimination in job hiring in the Philippines - Local employers tend to hire candidates even if they’re not the most qualified for jobs. The qualified and overage applicants who were not able to find jobs decide to work abroad. 4. High Withholding Tax - The Philippines has a high income tax rates for workers. Workers’ take home pay decreases after deducting the withholding tax, GSIS/SSS premium, Pag-ibig and Philhealth and other mandatory deductions. The Philippine and Foreign Currencies Determine the value of Peso Exchange rate • What is Exchange Rate? • Importance? • How does it change? Dollar as International Currency • What is the history behind? What is Exchange Rate? The exchange rate is the price of a unit of foreign currency in terms of the domestic currency. Importance 1. It serves as the basic link between the local and the overseas market for various services and financial assets. 2. Exchange rate movements can affect actual inflation as well as expectations about future price movements. 3. Exchange rate movements can affect the country’s external sector through its impact on foreign trade. 4. The exchange rate affects the cost of servicing principal and interest payments on the country’s foreign debt. How does it changes? Types of exchange rate: 1. Fixed rates the value of the currency is determined by the nation’s central bank and held in place by central bank actions, mainly the purchase and sale of the currency. 2. Floating rates- market forces : Supply and demand 3. Managed rates- a mix of both fixed and floating rates Dollar as International Currency. Why? • 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement • Fall of Bretton Woods Agreement • Options: Floating Rates or Revaluation of Gold •The Philippine housing shortage and the real estate boom: Rent and Price structure Housing Shortage • A deficiency or lack in the number of houses needed to accommodate the population of an area present when there is insufficient housing to accommodate the population in an area the supply cannot meet the demand Factors that affect housing needs 1. Location – the specific placing of home 2. Cost- the crucial factor in housing needs for almost everyone 3. Lifestyle- when selecting a home, one needs to consider the lifestyle of all the family members. Why does housing shortage occur? 1. Rapid population growth- leads to rapid increase in demand for housing (demand > Supply= Housing Shortage) 2. Migration – movement of people from one place to another stay at least a year 3. High Birth Rates- leads to the increase in the population (Housing Shortage when the supply of houses cannot meet the increased housing demand) 4. Land is used for many purposes. What are the Consequences of housing Shortage in Cities? 1. Homelessness- lack of shelter in which to sleep 7 carry out basic activities. ( Poor Health and Illnesses) 2. Slums and Squatter settlement- shanty towns (Favela in Brazil, Barong-barong in Philippines) 3. Lack of waste disposal facilities 4. Absence of proper sanitation facilities 5. Lack of clean water supply 6. Absence of proper sewage Real Estate • Is a property compromised by land and the buildings on it . Also, the business of real estate is the profession of buying, selling or renting land, building or housing. Three broad Categories 1. Residential – includes undeveloped land, houses, condominiums and town houses 2. Commercial – includes office buildings, warehouse and retail store building (rentals) 3. Industrial – includes factories, mines and farm Thank you!!!