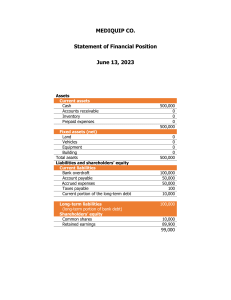
LECTURE 1 Accounting: → “the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information about an entity to a variety of users for decision-making purposes” (textbook) also the PROCESS → “recording and reporting for decision-making” → an information system Not everything is black and white. Some areas of accounting subject to estimation/ judgement/ choices Users of accounting information Resource providers: • Investors • Lenders • Suppliers • Employees • Members • Donors • Government Recipients: • Customers • Beneficiaries e.g. taxpayers, community Parties performing review or oversight function: • Regulatory agencies (ASIC,ASX,ATO) • Advisors • Analysts • Labour unions • Media • Community groups Management and governing bodies • Management: within the organisation, responsible for decision-making • Governing bodies: (NOT government) e.g. trustees, board of directors Information needs of users Investors: risk and return, dividends, potential for capital growth (increases share prices), performance of management Lenders: ability that firm can repay debt, pay interest Suppliers: ability to pay debt Employees: benefits, ongoing employment customers/ beneficiaries: fair & reasonable prices/ fees/ taxes, ongoing supply Regulatory agencies: compliance with reporting regulations, statistical data Advisors and analysts: financial information for analysis Community groups: social/ environmental impact Accounting focuses on PRIMARY USERS (too many users and needs to consider. Satisfying primary likely to meet other users needs) Summary of information needs Financial • Profitability (the rate at which profit is being generated %) • Efficiency (ability of entity to generate cash flow, turning assets into cash flow) • Liquidity (ability to meet short-term debts. Most important debt is the one you need to pay tomorrow) Liquidation: sell off assets, pay off debts • Gearing/ capital structure (the debt/ equity mix) More debt, more highly geared (measure of risk) • Market performance (share-based analysis) Non-financial • Corporate governance/ compliance • Social and environmental impact (sustainability reporting) How accounting provides information: Internal users: those involved in day-to-day decision making and the preparation of financial statements e.g. managers Can access whatever information whenever MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING (internal) External users: stakeholders outside the entity e.g. customer, investor, lenders, employees Only have access to General Purpose Financial Reports (released annually or 6 months) FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING (external) +sustainability reports (aren’t mandatory) CORPORATE AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY REPORTING Components of GPFR: According to Corporations Act, company must prepare GPFR • Statement of financial performance aka statement of profit or loss aka income statement • Profit or loss & other comprehensive income • Statement of financial position aka balance sheet • Statement of cash flows - () means outflow • Statement of changes in equity • AND notes e.g. estimations, judgment, choices Statement of profit or loss Over the year () in income statement means negative → expenses Line items Profit = revenue - expenses Balance sheet at a point in time Assets: → current assets e.g. cash → non-current assets e.g. equipment Liabilities: (debt) → current liabilities e.g. trade, tax → non-current liabilities e.g. borrowings, leases Equity Statement of cash flows () means outflow over period of time Examples of cash flows: receipts from customers, payments to suppliers/ employers, interest received Companies are most common form of business structure in Australia • Because of limited liability • E.g. JB HI-FI Ltd.