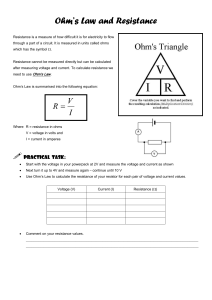
Rizal Technological University College of Engineering, Architecture, and Technology Preliminary Data Report Ohm’s Law Prepared by: Lim, Sheryl M. Manzana, Louie Mer J. Marcaida, Cedrick C. Medina, Aecer S. September 2022 I. Summary of the Experiment Based on the conducted experiment, wherein it involves in Ohm’s law. It can be used to identify the relationship of the three electrical properties such as voltage, current, and resistance in any DC electrical circuit, by using multism simulator. Concurrently, Ohm's Law is one of the most fundamental and important laws governing electrical and electronic circuits. It relates current, voltage, and resistance for a linear device, such that if two are known, the third can be calculated. Meanwhile, Multism is a software that integrates industry standard simulation. Whereas, it provides an interactive schematic environment to instantly visualized and analyze an electronic circuit. In additional, it can be used to easily compute the current, resistance, and voltage. Now, using the Ohm’s Law formula, which is V=IR. You can use the multism simulator, in order to make sure that your calculation is accurate. Thus, you should know first the placing and finding of the components, so that you can able to create a circuit diagram that is suitable in your experiment. Given those values on the table, you should make effort by changing the values stated by the instructor in each circuit diagram needed. In result, as shown in our graph and table we were able to gather information and prove that as soon as the voltage increase the current also increases, meaning the voltage with respect to current is directly proportional, while inversely proportional to resistance. Hence, the theoretical calculations were achieved from the original formula, which is V = IR. II. Data and Results VOLTAGE CURRENT (A) SIMULATIONS CURRENT (A) CALCULATIONS 5V 999.998mA or 1 A I = V/R = 5/5 =1A 10V 2A I = V/R = 10/5 =2 A 15V 3A I = V/R =15/5 =3 A 4A I = V/R = 20/5 =4A 5A I = V/R = 25/5 =5A 20V 25V TABLE NO. 1: For R= 5Ω (constant resistance) RESISTANCE CURRENT (A) SIMULATIONS CURRENT (A) CALCULATIONS 2Ω 30 A I = V/R = 60/2 = 30 A 3Ω 20 A I = V/R = 60/3 = 20 A 5Ω 12 A I = V/R = 60/5 = 12 A 6Ω 10 A I = V/R = 60/6 = 10 A 12Ω 5A I = V/R = 60/12 =5A TABLE NO. 2: For V= 60V (constant Voltage) TABLE NO.1: Fixed Resistance R=5Ω TABLE NO. 2: Fixed Voltage V= 60V 2.1. CIRCUITS DIAGRAMS DIAGRAM: For Fixed Resistance (R=5Ω) DIAGRAM: For Fixed Voltage (V=60V) 2.2 TABLES VOLTAGE 5V 10V 15V 20V 25V CURRENT (A) SIMULATIONS CURRENT (A) CALCULATIONS 999.998mA or 1 A I = V/R = 5/5 =1A 2A I = V/R = 10/5 =2 A 3A I = V/R =15/5 =3 A 4A I = V/R = 20/5 =4A 5A I = V/R = 25/5 =5A TABLE NO.1: For R= 5Ω (constant resistance) CURRENT (A) SIMULATIONS CURRENT (A) CALCULATIONS 2Ω 30 A I = V/R = 60/2 = 30 A 3Ω 20 A I = V/R = 60/3 = 20 A 5Ω 12 A I = V/R = 60/5 = 12 A 6Ω 10 A I = V/R = 60/6 = 10 A 12Ω 5A I = V/R = 60/12 =5A RESISTANCE TABLE NO. 2: For V= 60V (constant Voltage) 2.3 SIMULATIONS SIMULATIONS: For Fixed Resistance (R=5Ω) 5V.) 10V.) 15V.) 20V.) 25V.) SIMULATIONS: FOR FIXED VOLTAGE (V= 60V) 2Ω). 3Ω). 5Ω). 6Ω). 12Ω). 2.4. CALCULATIONS FOR FIXED RESISTANCE (R = 5Ω) 𝑉 FORMULA: V=IR (ohm’s law) 5V). I 𝑉 = 10V). 𝑅 = = I= 5 I=𝑅 𝑉 𝑅 = 5 1A 20V). I = 10 𝑉 𝑅 = 5 =2A 𝑉 𝑅 25V). I = 20 25 =5 5 =4A =5A FOR FIXED VOLTAGE (V = 60V) 𝑽 FORMULA: I = 𝑹 2Ω). I = 𝑽 𝑹 = 𝟔𝟎 𝟐 = 30 A 3Ω). I = = 𝑽 𝑹 𝟔𝟎 𝟑 = 20 A 5Ω). I = 𝑽 𝑹 = 𝟔𝟎 𝟓 = 12 A 6Ω). I = 𝑽 𝑹 = 𝟔𝟎 𝟔 = 10 A 12Ω). I = 𝑽 𝑹 𝟔𝟎 = 𝟏𝟐 =5A REFERENCES: https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/basic_concepts/resistance/what-is-ohms-lawformulaequation.php?fbclid=IwAR3c9gYILDW30SzB8ai2mzOaxW4uj_IzFhrJ5umXwOui XPzfu5f2KuWS5jw https://ohmlaw.com/ohms-law-lab-report/?fbclid=IwAR0sQnLqyRpDPQt59N4LfVU8hKPg6n1jeJDK8eJ6MiuNHMEufEyFveOF0A