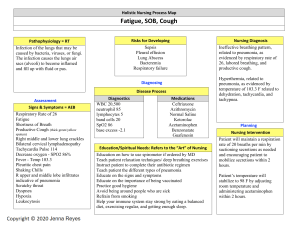
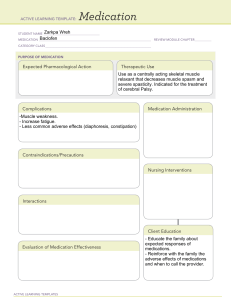
Understanding Benzonatate and Drug Interactions: What You Need to Know Benzonatate is a prescription medication commonly prescribed to relieve cough associated with respiratory tract infections and other conditions. As with any medication, it is essential to be aware of potential drug interactions to ensure your safety and the effectiveness of the treatment. In this article, we will explore what drugs should not be taken with benzonatate and the reasons behind these precautions. Potential Drug Interactions with Benzonatate: While benzonatate is generally well-tolerated, certain drugs can interact with it, leading to adverse effects or reducing its efficacy. Here are some categories of medications that should be used with caution or avoided altogether when taking benzonatate: 1. Other Cough Medications: Combining benzonatate with other cough suppressants or medications containing antitussive agents can lead to excessive suppression of the cough reflex, causing respiratory complications. It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about any other cough medications you may be using to avoid potential interactions. 2. Narcotics and Opioids: Using benzonatate along with narcotics or opioids can increase the risk of central nervous system (CNS) depression. Both benzonatate and opioids have sedative effects, and combining them can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired coordination. In severe cases, this interaction can lead to respiratory depression, which can be life-threatening. 3. Alcohol: Consuming alcohol while taking benzonatate can enhance its sedative effects, leading to increased drowsiness and impairment. It is advisable to avoid alcohol during the course of benzonatate treatment to prevent potential complications. 4. Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants: CNS depressants such as certain antihistamines, sedatives, tranquillisers, and sleep aids can interact with benzonatate and potentiate its sedative effects. The combination can cause excessive drowsiness, impaired cognitive function, and slowed reaction times. 5. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Taking benzonatate with MAOIs, a type of antidepressant, can lead to increased serotonin levels in the brain, causing a potentially life-threatening condition known as serotonin syndrome. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include agitation, hallucinations, rapid heart rate, and fluctuations in blood pressure. 6. Local Anaesthetics: Benzonatate is chemically related to certain local anaesthetics. Using benzonatate with these agents can lead to an increased risk of adverse effects and overdose. 7. Muscle Relaxants: The combination of benzonatate with muscle relaxants can intensify the sedative effects and may lead to excessive muscle weakness and impaired motor function. Important Considerations and Precautions: To ensure your safety while taking benzonatate, consider the following precautions: 1. Always Inform Your Healthcare Provider: Before starting benzonatate or any new medication, inform your healthcare provider about your complete medical history, including any medications you are currently taking. This will help your doctor identify potential drug interactions and make appropriate adjustments to your treatment plan. 2. Avoid Self-Medication: Benzonatate is a prescription medication, and its use should be supervised by a qualified healthcare professional. Avoid self-medication and always follow your doctor's instructions regarding the dosage and duration of treatment. 3. Follow Dosage Recommendations: Stick to the prescribed dosage and schedule provided by your healthcare provider. Taking higher doses or using the medication more frequently than recommended can increase the risk of adverse effects and drug interactions. 4. Be Cautious with Over-the-Counter Medications: Even over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and vitamins can potentially interact with benzonatate. Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are taking, including those purchased without a prescription. 5. Report Adverse Effects: If you experience any unusual or bothersome side effects while taking benzonatate, such as difficulty breathing, rash, swelling, or confusion, seek immediate medical attention and inform your healthcare provider. Conclusion: Benzonatate is an effective medication for relieving coughs associated with various respiratory conditions. However, to ensure its safe and effective use, it is essential to be aware of potential drug interactions. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting benzonatate or any new medication, and inform them about your complete medical history and current medications to prevent any adverse interactions. Following these precautions will help you make the most of your benzonatate treatment and promote your overall well-being.