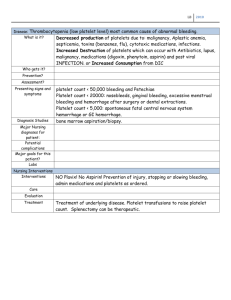
Name: ______________________________________________ Date: __________________ Group: __________________ Score: _________________ I. Multiple Choice HEMATOLOGY 2 1. The anticoagulant of choice for most routine coagulation studies is: A. Sodium oxalate B. Sodium citrate C. Heparin D. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) 2. Which ratio of anticoagulant-to-blood is correct for coagulation procedures? A. 1:4 B. 1:5 C. 1:9 D. 1:10 3. What reagents are used in the PT test? A. Thromboplastin and sodium chloride B. Thromboplastin and potassium chloride C. Thromboplastin and calcium D. Actin and calcium chloride 4. Which test would be abnormal in a patient with factor X deficiency? A. PT only B. APTT only C. PT and APTT D. Thrombin time 5. Which clotting factor is not measured by PT and APTT tests? A. Factor VIII B. Factor IX C. Factor V D. Factor XIII 6. Which of the following clotting factors are measured by the APTT test? A. II, VII, IX, X B. VII, X, V, II, I C. XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, V, II, I D. XII, VII, X, V, II, I 7. Which coagulation test(s) would be abnormal in a vitamin K–deficient patient? A. PT only B. PT and APTT C. Fibrinogen level D. Thrombin time 8. A protein that plays a role in both coagulation and platelet aggregation is: A. Factor I B. Factor VIII C. Factor IX D. Factor XI 9. A standard 4.5-mL blue-top tube filled with 3.0 mL of blood was submitted to the laboratory for PT and APTT tests. The sample is from a patient undergoing surgery the following morning for a tonsillectomy. Which of the following is the necessary course of action by the technologist? A. Run both tests in duplicate and report the average result B. Reject the sample and request a new sample C. Report the PT result D. Report the APTT result 10. Thrombocytopenia may be associated with: A. Postsplenectomy B. Hypersplenism C. Acute blood loss D. Increased proliferation of pluripotential stem cells 11. Aspirin prevents platelet aggregation by inhibiting the action of which enzyme? A. Phospholipase B. Cyclo-oxygenase C. Thromboxane A2 synthetase D. Prostacyclin synthetase 12. Normal platelet adhesion depends upon: A. Fibrinogen B. Glycoprotein Ib C. Glycoprotein IIb, IIIa complex D. Calcium Hemostasis 13. Which of the following test results is normal in a patient with classic von Willebrand’s disease? A. Bleeding time B. Activated partial thromboplastin time C. Platelet count D. Factor VIII:C and von Willebrand’s factor (VWF) levels 14. When performing platelet aggregation studies, which set of platelet aggregation results would most likely be associated with Bernard–Soulier syndrome? A. Normal platelet aggregation to collagen, ADP, and ristocetin B. Normal platelet aggregation to collagen, ADP, and epinephrine; decreased aggregation to ristocetin C. Normal platelet aggregation to epinephrine and ristocetin; decreased aggregation to collagen and ADP D. Normal platelet aggregation to epinephrine, ristocetin, and collagen; decreased aggregation to ADP 15. Which set of platelet responses would be most likely associated with Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia? A. Normal platelet aggregation to ADP and ristocetin; decreased aggregation to collagen B. Normal platelet aggregation to collagen; decreased aggregation to ADP and ristocetin C. Normal platelet aggregation to ristocetin; decreased aggregation to collagen, ADP, and epinephrine D. Normal platelet aggregation to ADP; decreased aggregation to collagen and ristocetin 16. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia is a disorder of: A. Platelets B. Clotting proteins C. Fibrinolysis D. Connective tissue 17. Which defect characterizes Gray’s syndrome? A. Platelet adhesion defect B. Dense granule defect C. Alpha granule defect D. Coagulation defect 18. Which factor deficiency is associated with a prolonged PT and APTT? A. X B. VIII C. IX D. XI 19. A prolonged APTT is corrected with factor VIII– deficient plasma but not with factor IX–deficient plasma. Which factor is deficient? A. V B. VIII C. IX D. X 20. The following results were obtained on a patient: normal platelet count and function, normal PT, and prolonged APTT. Which of the following disorders is most consistent with these results? A. Hemophilia A B. Bernard–Soulier syndrome C. von Willebrand’s disease D. Glanzmann’s thrombasthenin 21. The most suitable product for treatment of factor VIII deficiency is: A. Fresh frozen plasma B. Factor VIII concentrate C. Prothrombin complex concentrate D. Factor V Leiden 22. Which of the following is associated with an abnormal platelet aggregation test? A. Factor VIII deficiency B. Factor VIII inhibitor C. Lupus anticoagulant D. Afibrinogenemia 23. Which results are associated with hemophilia A? A. Prolonged APTT, normal PT B. Prolonged PT and APTT C. Prolonged PT, normal APTT D. Normal PT and APTT 24. Which of the following is associated with multiple factor deficiencies? A. An inherited disorder of coagulation B. Severe liver disease C. Dysfibrinogenemia D. Lupus anticoagulant Hemostasis 25. Fletcher factor (prekallikrein) deficiency may be associated with: A. Bleeding B. Thrombosis C. Thrombocytopenia D. Thrombocytosis 26. A prolonged APTT and PT are corrected when mixed with normal plasma. Which factor is most likely deficient? A. VIII B. V C. XI D. IX 27. What test is used to monitor heparin therapy? A. INR B. APTT C. TT D. PT 28. What test is commonly used to monitor warfarin therapy? A. INR B. APTT C. TT D. Ecarin time 29. Which of the following tests is most likely to be abnormal in patients taking aspirin? A. Platelet morphology B. Platelet count C. Bleeding time D. Prothrombin time 30. 262. In the platelet count procedure using phase microscopy, A. Platelets appear dark against a light background. B. The entire ruled counting surface of the hemacytometer is used. C. Ammonium oxalate will lyse the WBCs. D. Platelets should be counted immediately after plating the hemacytometer 31. To evaluate normal platelet numbers in an appropriate area of a blood smear, approximately how many platelets should be observed per oil immersion field? A. 1-4 B. 4-10 C. 8-20 D. 20-50 32. 1/3 of platelets are in: A. Circulation B. Liver C. Spleen 33. Von Willebrand's Factor are produced in A. Glial Cells B. Endothelial cells C. Mesothelial cells 34. Which is not a content of Alpha Granules? A. vWF B. ADP C. PDGF D. PF4 35. Shape of platelets A. Spherical B. Helical C. Discoid D. Leukoid BLOOD BANKING 1. What is the maximum volume of blood that can be collected from a 110-lb donor, including samples for processing? a. 450 mL b. 500 mL c. 525 mL d. 550 mL 2. How often can a blood donor donate whole blood? a. Every 24 hours b. Once a month c. Every 8 weeks d. Twice a year 3. When RBCs are stored, there is a “shift to the left.” This means: a. Hemoglobin-oxygen affinity increases, owing to an increase in 2,3-DPG. b. Hemoglobin-oxygen affinity increases, owing to a decrease in 2,3-DPG. c. Hemoglobin-oxygen affinity decreases, owing to a decrease in 2,3-DPG. d. Hemoglobin-oxygen affinity decreases, owing to an increase in 2,3-DPG. 4. Which of the following anticoagulant preservatives provides a storage time of 35 days at 1°C to 6°C for units of whole blood and prepared RBCs if an additive solution is not added? a. ACD-A b. CP2D c. CPD d. CPDA-1 5. What are the current storage time and storage temperature for platelet concentrates and apheresis platelet components? a. 5 days at 1°C to 6°C b. 5 days at 24°C to 27°C c. 5 days at 20°C to 24°C d. 7 days at 22°C to 24°C 6. Which of the following is approved for bacterial detection specific to extending the expiration of apheresed platelets to 7 days? a. BacT/ALERT b. eBDS c. Gram stain d. Pan Genera Detection (PGD) test 7. Which of the following immunoglobulins is produced in the primary immune response? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM 8. Which of the following immunoglobulins is produced in the secondary immune response? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM 9. Which complement pathway is activated by the formation of antigen-antibody complexes? a. Classical b. Alternative c. Lectin d. Retro 10. Which of the following is known as the “recognition unit” in the classical complement pathway? a. C1q b. C3a c. C4 d. C5 11. Which of the following is known as the “membrane attack complex” in the classical complement pathway? a. C1 b. C3 c. C4, C2, C3 d. C5b, C6, C7, C8, C9 12. Which of the following immunoglobulin classes is capable of crossing the placenta and causing hemolytic disease of the newborn? a. IgA b. IgE c. IgG d. IgM 13. Which of the following is not involved in the acquired (adaptive) immune response? a. Phagocytosis b. Production of antibody or complement c. Induction of immunologic memory d. Accelerated immune response upon subsequent exposure to antigen 14. Which cells are involved in the production of antibodies? a. Dendritic cells b. T lymphocytes c. B lymphocytes d. Macrophages 15. The role of the macrophage during an antibody response is to: a. Make antibody. b. Lyse virus-infected target cells. c. Activate cytotoxic T cells. d. Process antigen and present it 16. Which of the following terms refers to the net negative charge surrounding red blood cells? a. Dielectric constant b. Van der Waals forces c. Hydrogen bonding d. Zeta potential 17. Polyspecific AHG reagent contains: a. Anti-IgG and anti-IgA. b. Anti-IgG and anti-IgM. c. Anti-IgG and anti-C3d. d. Anti-IgA and Anti-C3d. 18. Monoclonal anti-C3d is: a. Derived from one clone of plasma cells. b. Derived from multiple clones of plasma cells. c. Derived from immunization of rabbits. d. Reactive with C3b and C3d. 19. After the addition of IgG-coated RBCs (check cells) to a negative AHG reaction during an antibody screen, a negative result is observed. Which of the following is a correct interpretation based on these findings? a. The antibody screen is negative. b. The antibody screen cannot be interpreted. c. The saline washings were adequate. d. AHG reagent was added. 20. RBCs must be washed in saline at least three times before the addition of AHG reagent to: a. Wash away any hemolyzed cells. b. Remove traces of free serum globulins. c. Neutralize any excess AHG reagent. d. Increase the antibody binding to antigen. 21. What do Coombs’ check cells consist of? a. Type A-positive cells coated with anti-IgG b. Type A-negative cells coated with anti-IgG c. Type O-positive cells coated with anti-D d. Type B-negative cells coated with anti-D 22. Which of the following would be cause for deferral for a male donor? a. Temperature of 99.2°F b. Hematocrit of 37% c. Spent 2 weeks in the United Kingdom in 1998 d. Weighs 80 kg e. Received a blood transfusion 2 years ago 23. Immunization for rubella would result in a temporary deferral for: a. 4 weeks. b. 8 weeks. c. 6 months. d. 1 year 24. Which of the following tests is not required as part of the donor-processing procedure for allogeneic donation? a. ABO b. Rh c. STS d. Anti-CMV 25. What is the causative agent of Chagas disease? a. Trypanosoma cruzi b. Yersinia pestis c. Treponema pallidum d. Plasmodium falciparum 26. Which of the following lists the correct shelf life for the component? a. Deglycerolized RBCs—24 hours b. RBCs (CPD)—35 days c. Platelet concentrate—10 days d. FFP—5 years e. RBCs (CPDA-1)—21 days 27. Each unit of cryoprecipitate prepared from whole blood should contain a minimum of how many units of AHF activity? a. 40 IU b. 80 IU c. 120 IU d. 160 IU e. 180 IU 28. Platelet concentrates prepared by apheresis should contain how many platelets? a. 5.5 × 10^10 b.6×10^10 c. 3 × 10^11 d. 5.5 × 10^11 e. 6 × 10^11 29. Once thawed, FFP must be transfused within__________ hours unless relabeled as thawed plasma: a. 4 b.6 c. 8 d. 12 e. 24 30. A single unit of FFP or PF24 should contain ____ mL of plasma. a. 100–150 b. 200–400 c. 150–250 d. 50–150 II. Critical Thinking 1. I never met my father. I am blood type o. My mother s blood type B. What are the possible blood types of my estranged father? 2. Prepare an 8ml 4.5% A Red Cell Suspension. Indicate the quantity of PRBCs and NSS to be used. 3. I prepared 2 tubes and placed 2 drops of the patient’s plasma on each tube. I then added 2 drops pf A cells on tube 1 and 2 drops of B cells o tube 2. What is the blood type of the patient?