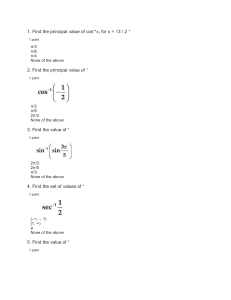
Course Outline: Business Statistics Course code: QM502 Credit:3 , Core Course Area: Operations and Quantitative Method Program: PGDM Term II Academic Year 2022-23 _______________________________________________________________________ Prof. Shraddha Mishra (Sec A & B) 003 (MDP Bldg.) Prof. Arvind Seth (Sec E) Room no. Prof. Deepak Chawla (Sec C & D) 203 Email dchawla@imi.edu Shraddha.mishra@imi.edu arvindseth99@gmail.com Phone (Extn no.) 7838744410 9717261384 9205453637 Meeting Hours Friday (2:30-4:30 pm) Monday (2:00-4.00 pm) Instructor(s) Name ______________________________________________________________________ 1. COURSE DESCRIPTION The course aims to enhance an understanding of quantitative information by building analytical skills. The students will learn how to develop models, carry out data analysis, interpretation and make objective decisions related to problems faced in business. The students will use EXCEL & SPSS software for analyzing statistical data. The course also aims to prepare the students to use various quantitative tools which can be applied for decision making. 2. COURSE OUTCOMES (COs) After going through the course, the students would be able to: COs >> COs and POs >> COs, POs and CECs >> Course Outcome 1 (CO1): Formulate the decision problem by identifying various alternatives. Course Outcome 2 (CO2): Identify the data analysis needs. Course Outcome 3 (CO3): Analyze the data using appropriate technique to reach valid conclusions. Course Outcome 4 (CO4): Apply the knowledge to interpret the findings and communicate the same to management through written and oral presentation. COs >> COs and POs >> COs, POs and CECs >> 3. MAPPING OF THE PROGRAM OUTCOMES (POs) AND COURSE OUTCOME (COs) Course Outcomes (COs) Program Outcomes (POs) CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 PO1: Student should be able to write well organized and grammatically correct business reports and letters. 2 PO2: Student should be able to make effective oral presentations. 2 PO3: Student should be able to demonstrate critical thinking skills by understanding the issues, evaluating alternatives on the basis of multiple perspectives and presenting a solution including conclusions and implications. PO4: Student should be to demonstrate problem solving skills by understanding and defining the problem, analyzing it and solving it by applying appropriate theories, tools and techniques from various functional areas of management. 2 3 3 3 3 3 PO5: Student should be able to illustrate the role of responsible leadership in management. PO6: Student should be able to identify social concerns and ethical issues in management. 1 PO7: Student should be able to identify challenges faced by the organization at the global level. PO8: Student should be able to take decisions in the global business environment. 4. PEDAGOGY The course will be based on Class room lectures, Exercises based on class-discussions, cases, and groupproject. Students would have to work individually as well as in groups. Students are expected to read the relevant chapters from the book and any other reading material provided before they come to the class. 5. COURSE EVALUATION COMPONENTS (CECs) CEC1: Quizzes (2 out of 3) CEC2: Mid-term Examination CEC3: End-term Examination CEC4 : Group Project/Case Presentation/Assignment Total 20% 30% 40% 10% 100% 6. MAPPING BETWEEN COs, POs and CECs Course Evaluation Components (CECs) COs POs CO1 CO2 CO3 CO4 PO4 PO3, PO4 PO3, PO4, PO6 PO1, PO2, PO3 CEC1: Quiz CEC2: Midterm Examination CEC3: Endterm Examination √ √ √ √ √ CEC4: Group Project/Case Presentation/Assignment √ √ √ 7. RESOURCES 7.1 Textbook 1. R I Levin, and David S Rubin (2017), “Statistics for management”, (Pearson Education India. Eight edition). 7.2 Reference Books 1. Aczel Amir D and Sounderpandian J Complete Business Statistics, Tata McGraw Hill (7th edition, 2012). 2. David R Anderson, Dennis J Sweney and Thomas A Williams (2007), “Statistics for Business and Economics”, Thompson South Western (Ninth edition). 3. Gerald Keller, “Statistics for Management”, 4th Indian edition (Thomson South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning Inc., 2009), 718 pp. 4. Naval Bajpai, “Business Statistics”, (Pearson Education South Asia, 2013 edition), 794 pp. 5. Ken Black, “Business Statistics”, (Wiley India 5th edition), pp 839 6. D. Chawla & N. Sodhi “Research Methodology, Concepts and Cases” 7.3 Online References (if any) Click or tap here to enter text. 8. SESSION PLAN Session No. Topic DECISION THEORY 1-2 Decision Environment Expected profit under uncertainty assigning probability values Expected values of perfect information Decision tree analysis SAMPLING AND SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONS (NON-PROBABILITY & PROBABILITY SAMPLING) 3-5 Various sampling concepts Random and Nonrandom Sampling Sampling vs. census Sampling error Non-sampling error Probability and non-probability sampling methods Sampling distribution of mean, Central Limit Theorem Sampling distribution of proportion Sampling from a Finite Population ESTIMATION 6-7 Point estimation Interval estimation Confidence interval for mean using Z distribution Confidence interval for mean using t distribution Confidence interval for proportion using Z distribution Determination of sample size while estimating mean and proportion Reading & Cases Read: Pages 897 - 907, 925-934 Attempt: SC 17.1, 17.7, 17.8, 17.6, 17.8 Read: Pages 268 to 308 from Text Attempt: Exercises 6.6, 6.8, 6.12, 6.17, SC 62. SC 6-3, 6.24, 6.25, 6.26, 6.28, 6.34, 6.35, 6.36, 6.37, 6.40, 6.41, 6.44, SC 6-8 from text Read: Pages 316 - 362 from Text Attempt: Exercises SC 7-1, 7.12, 7.15, 7.17, SC7-6, 7.25, 7.28, 7.34, 7.38, SC 710, 7.40, 7.42, 7.44, 7.45, 7.49 and 7.51 from text Case : Presidential Polling TESTING OF HYPOTHESES 8-9 Various concepts One tailed test and two tailed test Type 1 error and type II error Level of significance Power of test Testing hypotheses concerning population mean Large sample test Sampling sample test TESTING OF HYPOTHESES CONCERNING DIFFERENCES OF POPULATION 10-11 The case of population standard deviation being known The case of population standard deviation being unknown The case of paired sample TESTING OF HYPOTHESES CONCERNING PROPORTION AND DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PROPORTIONS 12 Test of proportion (single population) Test of proportion (two population) Read: Pages 371 - 390 and 397 – 403 from Text Attempt: Exercises SC 8-3, 8.19, 8.20, SC 85, 8.28, 8.33, 8.45 and 8.48 from Text Cases Cut Craft Cutlery Perception of people about ban on plastic bags in Delhi Read : Pages 411 - 441 from Text Attempt: Exercises 9.2, 9.3, 9.8, SC 9-6 and 9.13 from Text Cases Compensation for Faculty Member Tiresome Tires II Comparative perception of Mess Food vis a via Dhabas – A case of IIFT Read: Pages 405 - 411 and 455 – 463 from Text Attempt: Exercises 8.39, SC 8-10, 8.43, 9.18 and 9.20 from Text Cases: Airline Satisfaction Survey Ice cream markets in India Tata tea 13-15 NON-PARAMETRIC STATISTICS Test for equality of more than two population proportion Relationship between variables – contingency table Test of population standard deviation Confidence internal for standard deviation Goodness of fit of distribution Read : Pages 732-736, 758-761 Attempt : 14.25, 14.27, 14.29, SC 11.1, SC 11.8, 11.38, 11.40, 11.42, 11.44, 11.45 Cases: Quality Associates, Inc. Indian Bicycle Industry Data Facts Research TEST FOR EQUALITY OF TWO VARIANCE 16 Read : Pages 576-580 Attempt: 11.46, 11.50, 11.51 17 18-20 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ONE WAY CLASSIFICATION) INCLUDING POST-HOC ANALYSIS Read: Pages 542-547, SC 11.5, 1.25, 1.26 CORRELATION AND REGRESSION ANALYSIS Read: Pages 596 – 649 from Text Attempt: Exercises 12.16, 12.31 and 12.37 Concept, Correlation coefficient from Text Rank order correlation coefficient, Limitation of correlation theory Simple linear regression model estimation Cases Exercise on Demand Function Test of significance of regression Estimation coefficient 2 2 Mountain States Potato Co. r , significant of r Multiple regression, test of significance R2, Use of regression in point & interval forecast (exact & approximate interval) 9. ACADEMIC INTEGRITY & CLASS RULES a) Plagiarism is the use of or presentation of ideas, works that are not one’s own and which are not common knowledge, without granting credit to the originator. Plagiarism is unacceptable in IMI and will invite penalty. Type and extent of penalty will be at the discretion of the concerned faculty. b) Cheating means using written, verbal or electronic sources of aid during an examination/ quiz/ assignment or providing such assistance to other students (except in cases where it is expressly permitted by the faculty). It also includes providing false data or references/list of sources which either do not exist or have not been used, having another individual write your paper or assignment or purchasing a paper for one’s own submission. Cheating is strictly prohibited at IMI and will invite penalty as per policies of the Institute.