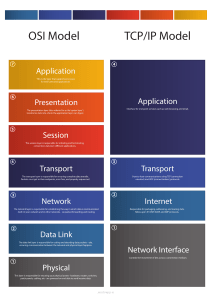
Computer Networks Code: PCC-CS602 Contact: 3L Theory: 3 hrs. / Week Credit Points: 3 Objective: 1. To develop an understanding of modern network architectures from a design and performance perspective. 2. To introduce the student to the major concepts involved in wide-area networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs) and Wireless LANs (WLANs). 3. To provide an opportunity to do network programming. 4. To provide a WLAN measurement ideas. Pre-Requisite: 1. Basic mathematics principal 2. Basic understanding of computer fundamentals Unit Content 1. Introduction: History and development of computer networks, networks topologies. Layering and protocols. Physical Layer: Different types of transmission media, errors in transmission: attenuation, noise. Repeaters. Encoding (NRZ, NRZI, Manchester, 4B/5B, etc.), LAN: Design, specifications of popular technologies, switching. Design of LAN of a campus or a building, FDM & TDM Data Link Layer: Error detection (Parity, CRC) & correction (Hamming distance), Sliding Window, Stop and Wait protocols. Go back – N ARQ, Selective Repeat ARQ Medium Access Control Sub Layer: MAC Layer: Aloha, CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA protocols. Examples: Ethernet, including Gigabit Ethernet and WiFi (802.11), Token Ring, Bluetooth and WiMax Network Layer: Internet Protocol, IPv6, ARP, DHCP, ICMP, Routing algorithms: Distance vector, Link state, Metrics, Interdomain routing. Subnetting, Classless addressing, Network Address Translation (NAT). Transport Layer: UDP, TCP Connection establishment and termination, sliding window revisited, flow and congestion control, timers, retransmission, TCP extensions, etc. Application Layer: Examples: DNS, SMTP, IMAP, HTTP etc.; Basics of Firewalls and Cryptography. Design issues in protocols at different layers. Network Programming: Socket Programming. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Hrs. / Unit 5 7 8 5 5 5 5 Text book and Reference books: 1. Introduction to Algorithms" by Cormen, Leiserson, Rivest, Stein. 2. "The Design and Analysis of Computer Algorithms" by Aho, Hopcroft, Ullman. 3. "Algorithm Design" by Kleinberg and Tardos. 4. Design & Analysis of Algorithms, Gajendra Sharma, Khanna Publishing House, New Delhi Course Outcomes: On completion of the course students will be able to PCC- CS602.1 Understand data communication system, components and the purpose of layered architecture. PCC- CS602.2 Relate the functionalities of each layer of OSI and TCP/IP reference model including their associated protocols. PCC- CS602.3 Apply the thoughts toward building the networks, secure devices in virtue of analyzing data. PCC- CS602.4 Analyse the growing demand of skilled people in the field of network and system administration. PCC- CS602.5 Evaluate today’s market of digital economy which is very much dependent on computer network skill to provide services in the field of finance, education, transportation, manufacturing, healthcare, retail and so on. PCC- CS602.6 Create the requirements of enterprises or global corporations to be placed there. Suggested Books: Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Name of Books / Authors Tanenbaum, A.S, “Computer Networks”, 4th Ed., PearsonEducation. Forouzan, B.A., “Data Communication and Networking”, 4th Ed.,Tata McGraw-Hill. Stallings W., “Data and Computer Communication”, 8th Ed., Prentice-Hall. Kurose, J.F. and Ross, K.W., "Computer Networking: A Top-DownApproach Featuring the Internet", 3rd Ed., Addison Wesley. Comer, D.E. and Droms, R.E., “Computer Networks and Internets”,4th Ed., Prentice-Hall. Modified Syllabus of the Course: Sl. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Contents Introduction: history and development of computer networks, networks topologies. Layering and protocols. Physical Layer: Different types of transmission media, errors in transmission: attenuation, noise. Repeaters. Encoding (NRZ, NRZI, Manchester, 4B/5B, etc.). Data Link Layer: Error detection (Parity, CRC), Sliding Window, Stop and Wait protocols. LAN: Design, specifications of popular technologies, switching. Design of LAN of a campus or a building Medium Access Control Sub Layer: MAC Layer: Aloha, CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA protocols. Examples: Ethernet, including Gigabit Ethernet and WiFi (802.11), Token Ring, Bluetooth and WiMax Network Layer: Internet Protocol, IPv6, ARP, DHCP, ICMP, Routing algorithms: Distance vector, Link state, Metrics, Inter-domain routing. Subnetting, Classless addressing, Network Address Translation (NAT). Transport Layer: UDP, TCP. Connection establishment and termination, sliding window revisited, flow and congestion control, timers, retransmission, TCP extensions, etc. Session, Presentation, and Application Layers. Examples: DNS, SMTP, IMAP, HTTP, etc. Design issues in protocols at different layers. Network Programming: Socket Programming Total Contact Hours 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 40 Computer Networks Lab Code: PCC-CS692 Contacts: 4P Practical: 4 hrs. / Week Credit Points: 2 Laboratory Experiments: 1. NIC Installation & Configuration (Windows/Linux) 2. Understanding IP address, subnet etc. Familiarization with Networking cables (CAT5, UTP) Connectors (RJ45, T-connector) Hubs, Switches 3. DHCP configuration Message queue TCP/UDP Socket Programming Simple, TCP based, UDP based Multicast & Broadcast Sockets 4. Implementation of Data Link Layer Flow Control Mechanism (Stop & Wait, Sliding Window) Data Link Layer Error Detection Mechanism (Cyclic Redundancy Check) 5. Server Setup/Configuration FTP, Telnet, NFS, DNS, Firewall; Any experiment specially designed by the college. (Detailed instructions for Laboratory Manual to be followed for further guidance) Course Outcomes: On completion of the course students will be able to PCC- CS692.1 Define the hardware, related to computer network. PCC- CS692.2 Understand the performance of network protocols such as message queue, stop-and-wait, CRC etc. PCC- CS692.3 Apply UNIX socket programs efficiently, based on the knowledge of client server paradigm. PCC- CS692.4 Analyse the network traffic in terms of congestion control mechanism. PCC- CS692.5 Evaluate the datagram forwarding and routing mechanisms compatible with UNIX platform. PCC- CS692.6 Create networks in small scale by configuring devices with the help of knowledge in network addressing.