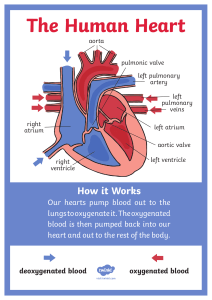
CHAPTER 9 TRANSPORT IN ANIMALS Y9 BIOLOGY LEARNING OBJECTIVES DOUBLE CIRCULATION OF MAMMALS ADVANTAGES OF DOUBLE CIRCULATION • More efficient • High blood pressure for sufficient blood supply. • Allow different pressure in each loop. • Prevent mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. • Allows animals to have high metabolic rate. LEARNING OBJECTIVES HEA RT PATHWAY OF BLOOD THROUGH THE HEART • Deoxygenated blood coming from the body flows into the right atrium via the vena cava • Once the right atrium has filled with blood the heart gives a little beat and the blood is pushed through the tricuspid (atrioventricular) valve into the right ventricle • The walls of the ventricle contract and the blood is pushed into the pulmonary artery through the semilunar valve which prevents blood flowing backwards into the heart • The blood travels to the lungs and moves through the capillaries past the alveoli where gas exchange takes place (this is why there has to be low pressure on this side of the heart – blood is going directly to capillaries which would burst under higher pressure) PATHWAY OF BLOOD THROUGH THE HEART • Oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary vein • It passes through the bicuspid (atrioventricular) valve into the left ventricle • The thicker muscle walls of the ventricle contract strongly to push the blood forcefully into the aorta and all the way around the body • The semilunar valve in the aorta prevents the blood flowing back down into the heart CONTROL OF BLOOD FLOW THROUGH THE HEART METHODS FOR MEASURING HEART ACTIVITY ➢ Pulse Rate ➢ Heart sounds ➢ Electrocardiograms (ECGs) PULSE RATE PULSE RATE MEASUREMENT MANUAL METHOD PULSE RATE MEASUREMENT ELECTRONIC METHOD HEART SOUNDS HEARD BY USING STETHOSCOPE ELECTROCARDIOGRAMS (ECGS) EFFECT OF PHYSICAL ACTIVITY ON HEART RATE • A heartbeat is a contraction. Each contraction squeezes blood to the lungs and body. • The pulse is a pressure wave passing through the arteries as a result of the heartbeat. • At rest, the heart beats about 70 times a minute, but this varies according to a person’s age, sex and fitness. It is higher if you are younger and/or female, and lower if you are fit. • An increase in physical activity increases the pulse rate, which can rise to 200 beats per minute. WHY PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AFFECTS THE HEART RATE • This is because during exercise the muscles need more energy, so the heart has to deliver more oxygen and glucose for respiration. • After exercise has stopped, the pulse rate gradually drops to its resting state. • If the individual is fit, this happens quickly, but an unfit person’s pulse rate will take longer to return to normal. CORONARY HEART DISEASE CORONARY ARTERY ANGINA POSSIBLE CAUSES OF CORONARY HEART DISEASES ➢Diet ➢Stress ➢Smoking ➢Genetic predisposition ➢Age & Gender ➢Lack of exercise LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OBJECTIVES COMPOSITION OF BLOOD • Blood transports materials through out the body inside blood vessels. • PLASMA Straw colored, nonliving part of blood. • 90% Water • Helps to regulate body temperature • Contains Electrolytes • Plasma transports blood cells, products of digestion and hormones throughout the body. ✓ Tiny, disc like, biconcave cells RED CELLS ✓ Do not have nuclei ✓ Spongy cytoplasm enclosed in an elastic cell membrane ✓ Cytoplasm contains a red pigment Haemoglobin. ✓ One RBC live for about 4 months ✓ 200 000 million red cell (1 % of the total) wear out and replaced each day ✓ Red cells are made by the red bone marrow of certain bones HAEMOGLOBIN & OXYHAEMOGLOBIN WHITE BLOOD CELLS • White blood cells are involved with phagocytosis and antibody production. • The two most numerous types of white blood cells are phagocytes and lymphocytes. • The phagocytes can move about by a flowing action of their cytoplasm and can escape from the blood capillaries into the tissues by squeezing between the cells of the capillary walls. • They collect at the site of an infection, engulfing and digesting harmful bacteria and cell debris – a process called phagocytosis . In this way they prevent the spread of infection through the body. One of the functions of lymphocytes is to produce antibodies. PLATELETS • Pieces of blood cells • No nucleus • Live 2-4 days • Involved in clotting of blood • Produced in red bone marrow