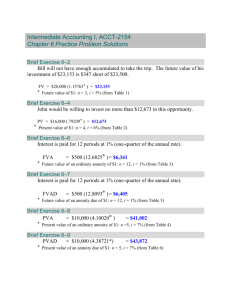
Bangladesh University of Professionals Term Paper on Annuity in Our Daily Life. Course Code and Tittle BUS 7102 (Mathamatices for Dicision) Submitted To Dr. Md. Showkat Ali Professor Faculty of Business Studies Bangladesh University of Professionals Submitted By Tanveer Ahmed Siddquee Student Id - 23230332008 Master of Business Administration (Professionals) Batch - 32 and Section - A. Letter of Transmittal February 28, 2023 AD Dr. Md. Showkat Ali Professor Department of Business Administration in Management Studies Faculty of Business Studies Bangladesh University of Professionals Subject : Term Paper on BUS 7102 (Mathamatices for Dicision) Annuity in our daily life. Dear Sir, It is a great pleasure to me to submit my term paper on “Annuity in our daily life”. I would like to recall with gratitude the generous support and encouragement I received from you. As an instructor and advisor, you have provided valuable insights and academic knowledge to improve the quality of my work. With your guidance, completing this term paper was possible. This Term Paper has been prepared based on collected data, through the interviewing process, text book and internet. All the annuity related question and problem has been formulated based on the requirement of this term paper. All the information has been organized to get the desired result. I will be pleased to answer any query you think is necessary, as of now and when needed. I want to draw attention, particularly to the matter that there is always a space for clarification of any relevant topic. I look forward to your kind and impartial appraisal of this term paper. Therefore, I hope this term paper will be up to your expectations, and it will be my pleasure to answer any clarifications and suggestions regarding this term paper. Sincerely yours, Sd/Tanveer Ahmed Siddquee Student Id - 23230332008 Batch - 32, Section - A Master of Business Administration (Professionals) Bangladesh University of Professionals. Annuity in our daily life | 2 Acknowledgement First and foremost, we want to express my gratitude to Almighty Allah for providing us the courage to successfully complete group term paper. Additionally, we want to thank our supervisor Dr. Md. Showkat Ali, Professor, Department of Business Administration in Management Studies, Faculty of Business Studies, Bangladesh University of Professionals (BUP), whose comments and direction on the report or term paper helped me write it correctly and finish it without any issues. We received cordial and sincere assistance from many concerns when preparing this term paper. In addition, we want to thank everyone in our family and circle of friends for always being there for us when we needed them. They made it feasible for us to do our term paper, without which it would not have been achievable. Annuity in our daily life | 3 Abstract Organizations have been compelled to improve their cost, quality, speed, and flexibility as a result of competitive advantages in today's global market. The success of a corporation depends on these four competitive elements. Service firms are not unique in this regard. This paper aim is to examine the idea of competitive priorities of safety regulations, health and environmental hazards which is very much essential for any organization management. To gain a deeper understanding of competitive priorities and why they are necessary to achieve employees and employers’ satisfaction. We have gathered 100 responses from office employees and executives at Robotech, RAK ceramics Limited, Bijoy TV Limited, Advance IT, Solution Art and Bangladesh Development Bank Limited (BDBL) in Bangladesh. In this research, we have found that safety plays a vital role in employee satisfaction and a positive relation between competitive priorities and employee satisfaction. This study will aid in future research on competitive priorities on safety regulations and minimizing hazards. Annuity in our daily life | 4 Table of content Executive Summary Letter of Transmittal Acknowledgement Abstract Table of Contents 02 03 04 05-06 Part One (Term Paper) Chapter - 01 Introduction 1.01 Introduction 1.02 How do annuities work? 1.03 Finding the right type of annuity 1.04 Select the right type of annuity 08 08 Chapter - 02 Objective of the Survey 2.01 Background of the Report 2.02 Origin of the Report 2.03 Statement of the Problem 2.04 Importance of the Study 2.05 Objective of the Report 2.06 Scopes of the Study 09-10 09 09 09 10 10 10 Chapter - 03 Literature Review 3.01 Literature Review 11-13 11 Chapter - 04 Methodology and Source of Data Collection 4.01 Methodology and Source of Data Collection 4.02 Data Collection 4.03 Sources of Data 4.04 Data Reliability 4.05 Limitations of the Study 14-16 Chapter - 05 Data Analysis 5.01 Data Analysis 5.02 Companies We Have Surveyed 5.03 Data Collection 5.04 Evaluation 17- 24 17 17 19 20 Chapter - 06 Findings Summary 6.01 Findings Summary 25-27 25 Chapter - 07 Survey Experiences Survey Experiences 28 28 Annuity in our daily life | 5 Chapter - 08 Recommendation Recommendation 29-31 29 Chapter - 09 Conclusion 32 Chapter - 10 References 33 Part Two (Appendix) APPENDIX Appendix - A Survey Form 35-36 Appendix - B Original Survey Sheet 37-38 Appendix - C Digital Survey Sheet 39-42 Annuity in our daily life | 6 PART - I (Term Paper) Annuity in our daily life | 7 Chapter - 01 Introduction 1.01 Introduction Annuities are powerful financial instruments designed to provide guaranteed income for life. Whether you’re planning for retirement, seeking long-term financial security or aiming to diversify your investment portfolio, annuities offer a customizable solution tailored to you. Discover how annuities can help secure your financial future. In investment, an annuity is a series of payments made at equal intervals. Examples of annuities are regular deposits to a savings account, monthly home mortgage payments, monthly insurance payments and pension payments. 1.02 How do annuities work? At their most basic, annuities work by converting a premium into a stream of payments. The amount and duration of the payments depend on various factors, including the type of annuity, the premium amount, the annuitant’s age and the chosen payout option. Annuities can be optimized for income or long-term growth, but they are not short-term investment strategies. Most annuities supply income through a process of accumulation and annuitization. The exception is immediate annuities that begin paying out as soon as within a month of purchase with no accumulation phase necessary. 1.03 Finding the right type of annuity Annuities can be classified by the frequency of payment dates. There are three main types of annuities: fixed annuities, fixed index annuities and variable annuities. Annuities can also be classified as immediate or deferred, indicating when you will begin receiving annuity payments. Your personal goals and objectives will help determine the best type of annuity for you. 1.04 Select the right type of annuity There are pros and cons to each type of annuity. You should consider how the features of different types of annuities work best for your current financial situation and how each can help you reach your long-term financial goals. Annuity in our daily life | 8 Figure 01.01 : Risk scale of annuity type You should also compare several different annuity options, ask yourself how each meets your needs and talk to a financial professional about how each annuity you’re considering will help you achieve your goals. 1.05 Uses of annuity Having a fixed and stable income is important to lead a financially independent life. An annuity is one of the few ways in which you can enjoy a fixed income at a pre-decided time. Whether trying to make a retirement plan or looking for a source of income, buying an annuity can be a great option. (a) Tax-deferred growth You will not pay income taxes on the earnings from your annuity investments till you begin making withdrawals or getting periodic payments. Note that withdrawals before age 59½ may be subject to an additional 10% tax. (b) Unlimited contributions There is no limit to the amount of after-tax money you can place into an annuity, despite your income level or sources of income. (c) Choice of investment options - Fixed annuities extends a stated rate of return for a specified period. Variable annuities include various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and money market instruments that vary with market conditions. (d) No necessary withdrawals If your annuity is not part of an IRA or a retirement plan, you are not expected to begin taking minimum distributions after age 72. Annuity in our daily life | 9 (e) Death benefit. Payout methods include insurance features that confirm payment to your designated beneficiaries if you die before your withdrawals begin. In most cases, this payment does not need to pass through probate. The annuity has many advantages but one of the biggest advantages is that it provides a regular income source throughout life, even after retirement. There are different annuity plans available for you to choose from. This allows you to choose the annuity plan that best suits your requirement at the time. Annuity plans are quite flexible and allow you to customize your plans according to your needs. You can choose a single life plan or a joint life plan for you and your partner. According to the Income Tax Act you get certain tax benefits by purchasing an annuity plan. So to conclude, an annuity investment is one of the best ways of having a fixed source of income throughout your lifetime. It is also a great way of planning your post-retirement life and keeping a steady income even after retirement. . Annuity in our daily life | 10 Chapter - 02 Fundamentals of Annuities 2.01 Annuity Meaning Many people have had the experience of making a series of fixed payments over a course of time - such as rent, premium or vehicle payments - or obtaining a series of payments for a course of time, such as the certificate of deposit (CD) or interest from a bond or lending money. These ongoing or recurring payments are technically called "Annuities”. 2.02 Types of Annuity Annuity may be classified in to 02 (Two) categories (a) Annuity certain (also known as a guaranteed or fixed annuity) Annuity certain (also known as a guaranteed or fixed annuity) This annuity pays you a set amount over a pre-determined period of time. For example, you can buy an annuity that will pay you $500 a month for 20 years. The annuity certain may be further classified into 02 (Two) categories (i) Annuity Due An annuity due is an annuity whose payment is due immediately at the beginning of each period. A common example of an annuity due payment is rent, as landlords often require payment upon the start of a new month as opposed to collecting it after the renter has enjoyed the benefits of the apartment for an entire month (ii) Annuity ordinary (immediate annuity) An ordinary annuity is a series of equal payments made at the end of consecutive periods over a fixed length of time. While the payments in an ordinary annuity can be made as frequently as every week, in practice they are generally made monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually. A common example of ordinary annuities are interest payments from bonds, which are generally made semiannually, and quarterly dividends from a stock that has maintained stable payout levels for years. Annuity in our daily life | 11 The present value of an ordinary annuity is largely dependent on the prevailing interest rate. (b) Contingent annuity Contingent annuity is an annuity that is subject to conditions or terms that must be met before the beneficiary will receive payments. The most common use of contingent annuities is for life insurance and pensions which are contingent on someone either being alive or deceased. Fixed-period annuities, also known as term deferred annuities, are a type of annuity that is paid out over a certain period of time. For example, it might pay out over the course of 10 or 20 years. If you unexpectedly pass away during the payment term, you can have payments continue to a beneficiary. 2.03 Present value and future value of annuity Present value and future value are terms that are frequently used in annuity contracts. The present value of an annuity is the sum that must be invested now to guarantee a desired payment in the future, while its future value is the total that will be achieved over time. (a) Present value of annuity The present value of an annuity refers to how much money would be needed today to fund a series of future annuity payments. Because of the time value of money, a sum of money received today is worth more than the same sum at a future date. Present value takes into account any interest rate an investment might earn. For example, if an investor receives $1,000 today and can earn a rate of return of 5% per year, the $1,000 today is certainly worth more than receiving $1,000 five years from now. (a) Future value of annuity The future value of an annuity is the value of a group of recurring payments at a certain date in the future, assuming a particular rate of return, or discount rate. Annuity in our daily life | 12 An example of future value of annuity would be if someone invested $1,000 today and received an annual payment of $100 for the next 10 years. The future value of this annuity would be $2,614.87 at the end of 10 years. 2.04 Importance of annuity Annuities allow the contract owner to choose, within contract limits, when and how to receive annuity income payments. Annuity options are available that can guarantee income for life, for a specific period of time, or both. Annuity in our daily life | 13 Chapter - 03 Mathematical Formulas of Annuities 3.01 information required for annuity formula The present value and future value of an annuity is affected by the interest rate, the length of time until the payments are received, and the amount of each payment. To calculate the present value of an annuity, you will need to know the interest rate, the length of time until the payments are received, and the amount of each payment. (a) Payment amount Amount of money you envision getting paid by period (monthly, quarterly or annually). (b) Interest rate The interest rate per period. (c) Number of time periods (d) Type of annuity The information is needed to calculate present value of an annuity. 3.02 Mathematical Symbol that used in formula To describe the mathematical we use the following symbol. Lets a n i P or PV F or FV 3.03 annual payment (instalment per period) number of year (Number of period) interest rate (interest rate per period) Present Value Future Value Present value of annuity calculation The present value of annuity is the current value of the total amount of annuity at the end of the given period. In others word, Present value of a given sum if money Annuity in our daily life | 14 due at the end of a certain period of time is the sum of principal amount plus interest accumulated at the given rate for the same period. 3.04 (a) Present value of ordinary annuity (or Immediate annuity) (b) Present value of annuity Due Future value of annuity calculation The future value of an annuity is the sum of all payments made and interest earned on them at the end of the term of annuities. (a) Future value of ordinary annuity (or Immediate annuity) (b) Future value of annuity Due Perpetual annuity is an annuity whose payment continues forever. As such the amount of perpetuity is undefined as the amount increases without any limit as time passeson. We know that the present value of P of immediate annuity is given by Annuity in our daily life | 15 Now as per the definition of perpetual annuity as We know that Since 1+i>1, Hence Annuity in our daily life | 16 Chapter - 04 Annuity function in Microsoft Excel 4.01 Annuity Functions in Excel Microsoft Excel provides various functions to perform constant annuity calculations. These functions can be used for both loans and investments. Constant annuities are streams of equal cash flows occurring at equal intervals. All annuities are governed by a set of variables. Excel provides functions for all these variables. These variables are: Rate The interest rate per period Nper Total number of periods in the annuity PMT The payment per period PV The present value of cash flows. The total amount that a series of future cash flows is worth now. FV The future value of cash flows based on periodic, equal cash flows. Type Select Annuity Type (Type is whether the annuity is a regular or an annuity due. Use 0 for regular annuities, and 1 for annuity due.) (By default type is 0.) An additional input is the “Type”, which is 0 for a regular annuity or annuity in arrears where the first payment occurs one period from now and 1 for an annuity due or annuity in advance where the first payment occurs now. Any variable given in squared brackets is optional. There are five key functions to calculate different aspects of an annuity: (a) PV( rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type]) This function calculates the present value of an annuity, once we have the periodic payments. (b) FV( rate, nper, pmt, [pv], [type]) This function calculates the present value of an annuity, once we have the periodic payments. Annuity in our daily life | 17 (c) PMT( rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type]) This function calculates the periodic payments in an annuity. (d) NPER( rate, pmt, pv, [fv], [type]) This function calculates the number of payments in an annuity. (e) RATE( nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type],[guess]) This function calculates the interest rate earned in the annuity. Guess is your guess for what the rate will. By default its value is 0.10. Figure 4.01: Annuity calculation in Microsoft Excel. We can easily calculate all types annuity using by using Microsoft Excel formulas or function and find the desire value. Annuity in our daily life | 18 Chapter - 05 Annuity calculation in Microsoft Excel 5.01 Annuity calculation in Microsoft Excel Now we solve some problem tha already calculate by paper and pencil from our Reference Books “Business Mathematics” by Dr. Md. Rafiqul Islam and Dr. M. Osman Gani. 5.02 Books Example Somes book example are shown below. Annuity in our daily life | 19 Books Example (Retained Out Profit) Annuity in our daily life | 20 Annuity in our daily life | 21 Chapter - 06 Findings Summary 6.01 Findings Summary Annuity in our daily life | 22 Chapter - 07 Survey Experiences 7.01 Survey Experiences Annuity in our daily life | 23 Chapter - 08 Recommendation Annuity in our daily life | 24 Chapter - 09 Conclusion 9.01 Conclusion Annuity in our daily life | 25 Chapter - 10 Reference 10.01 Reference (1) Reijula, K., & Sundman-Digert, E. (2004). Causes of indoor air complaints in office workplaces: A study based on 11,000 employees. Indoor and Built Environment, 13(5), 391-397. (2) Danna, K., & Griffin, R. W. (1999). Health and well-being in the workplace: A review and synthesis of the literature. Journal of management, 25(3), 357-384. (3) Conti, G., Federici, G., & Stenius, U. (2008). Health and safety practices in the nanomaterials workplace: Results from an international survey. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 10(3), 483-495. (4) Adamopoulos, C., & Syrou, V. (2022). Occupational health and safety hazards in the public health sector in Greece: A systematic review. Safety Science, 139, 106369. (5) Chu, C., & Dwyer, S. (2002). Employer role in integrative workplace health management: A new model in progress. Disease Management and Health Outcomes, 10, 175-186. (6) Klein, L. W., Miller, D. L., Balter, S., Laskey, W., Haines, D., Norbash, A., ... & Goldstein, J. A. (2009). Occupational health hazards in the interventional laboratory: time for a safer environment. Radiology, 250(2), 538-544. (7) Bhandari, P. (2023, January 16). What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/likert-scale/ Annuity in our daily life | 26 PART - II (Apendex) Annuity in our daily life | 27 Appendix - A Appendix - B Annuity in our daily life | 28