Key Design Considerations: Learning Outcomes & Training Transfer
advertisement

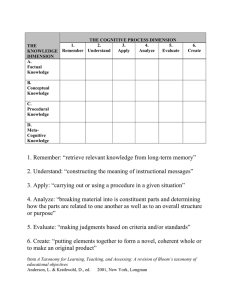
Key Design Considerations Topics covered: • The learning outcomes: Benefits of learning outcomes • Hierarchy of learning outcomes • Behavioural and non-behavioural learning outcomes • Program and session learning outcomes • • Transfer of training/learning Learner characteristics • Training design • Work environment characteristics • Learning Outcomes • After studying this topic you should understand: • how to write learning outcomes for an entire training program and for the individual sessions within the training program; • the key factors that facilitate transfer of learning from the training environment to the work environment. Benefits of Learning Outcomes (LO) • Guides trainer in developing instruction. • Helps motivate trainees and focuses their learning. • Used to evaluate effectiveness of training. • Informs potential trainees and their direct managers about capabilities a trainee will develop. Needs analysis and LOs Needs analysis Closed or open skills? Behavioral or non-behavioural LOs? Closed skills Open skills LOs tied to learning specific skills that are to be applied identically in the workplace as in the learning context. LOs tied to learning principles and concepts that are to be applied flexibly in the workplace. Often involves relatively simpler motor skills and trainee is often given opportunity to apply learned skills immediately on the job. More difficult to train, require higher-level cognitive components and are subject to more rapid decay. (See Blume et al., 2010) (See Krathwohl, 2002). Components of Behavioural Learning Outcomes (BLOs) (1/2) Has three components: • • • • what someone should be able to do (do what) conditions under which ‘doing’ will occur (with what) criteria by which performance will be judged (how well) (See Noe, 2017) Components of BLOs (2/2) • Performance component: Specifies what the person will be able to do as a result of training. It must therefore contain an action orientated verb, e.g.: Make, Operate, Construct, Complete. • Condition component: Describes the conditions under which the person will be able to carry out the performance component. For instance, factors such as: Using certain equipment, Using certain materials, Given certain information, Within a certain environment. • Standards component: Specifies the level of performance, how well the person is expected to perform. It focuses on factors such as: Speed, Amount, Accuracy, Time. Sample BLO – Basic Selling Skills • Given a model 678 vacuum cleaner, be able to follow the steps for closing a sale. • Criteria: Customer needs accurately identified; all product features and benefits correctly described; each objection effectively dealt with; no errors in product demonstration. Sample BLOs – Effective Presentation Skills • Given a speech topic, be able to organise your speech in a logical manner. • Criteria: Speech uses a basic three-part format: • Opening • Body • Conclusion • Given technical material, be able to convey technical information to a general audience. • Criteria • Material is tailored to the needs, interests and knowledge levels of the audience • Use of technical jargon is minimised • Material is presented clearly and logically Non-behavioural LOs • Tend to be more flexible and open-ended. • Allow for broader notions of learning to be used, not just behaviour change. • Are used when intended learning is: • more complex or less specific • developmental • difficult to view in terms of behaviour • Still need to be expressed clearly and simply. Sample Non-Behavioural LOs • At the completion of the training course, trainee managers should be able to: • Resolve interpersonal conflict among parties • At the completion of the training session, trainee managers should be able to: Identify sources of interpersonal conflict in organisations • Describe the conflict handling styles • Recognise their own preferred conflict handling style • Program and Session LOs • LOs must be written for the entire training program. For example: At the completion of the training program, trainees should be able to: • Recognise how perceptual problems can affect performance appraisals. • LOs must also be written for each session within a training program. For example: At the completion of this session, trainees should be able to: • Identify attribution errors in conducting performance appraisals. • Distinguish between primacy and recency effects. Summary Learning outcomes arise from needs investigation. Learning outcomes have several benefits, but they can be difficult to write. Learning outcomes can be tied to ‘closed’ or ‘open’ skills. Learning outcomes can be ‘behavioural’ or ‘non-behavioural’. Behavioural learning outcomes have three components: do what, with what, how well. ‘Non-behavioural’ learning outcomes are more open-ended and allow for broader notions of learning. Learning Activity • Write 5-8 learning outcomes for a two-day training program that will be attended by 10 line managers. The title of the training program is “Conducting effective performance appraisals”. • The learning outcomes must include knowledge outcomes and behavioural skill outcomes. • The proper format is: After completing the training program, trainees will be able to: Describe.., Demonstrate…, Justify…, Develop…Apply… and so forth. Each learning outcome must start with an action verb. Key references • Anderson, L.W. (Ed.), Krathwohl, D.R. (Ed.), Airasian, P.W., Cruikshank, K.A., Mayer, R.E., Pintrich, P.R., Raths, J., & Wittrock, M.C. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (Complete edition). New York: Longman. • Bloom, B.S. (Ed.), Engelhart, M.D., Furst, E.J., Hill, W.H., & Krathwohl, D.R. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook 1: Cognitive domain. New York: David McKay. • Delahaye, B. & Choy, S. (2018). Human resource development: Learning for innovation and productivity (5th edition.) Prahran, Victoria, Australia: Mirabel Publishing. • Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of Bloom's taxonomy: An overview. Theory into practice, 41(4), 212-218. • Noe, R. A. (2017). Employee training and development (7th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.