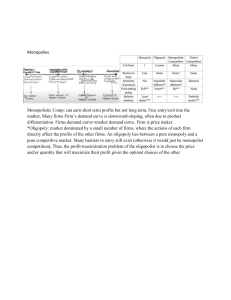
ECONOMICS (2281): key concepts Chapter#1: Nature of economic problem: Economic problem Scarcity of resources Difference between free goods and economic goods Chapter#2: Factors of Production: All four FOPS Difference between capital and consumer goods Mobility of the FOPS Quantity and quality of FOPS Chapter#3: Opportunity Cost Definition of opportunity cost Influence on consumers, workers, producers and government Chapter#4: Production Possibility curves Production points Shape of PPC curve Movement along the PPC curve Shift in PPC curve Consequences of a shift in PPC Chapter#5: Macro-economics and Micro-economics Definition of both macro and micro economics Connection between micro and macro economics Aims of economic agents in both macro and micro level Chapter#6: Role of Markets in Allocating Resources The involvement of what, how and who to produce in decisions Planned economy, mixed economy and market economy Role of price mechanism Chapter#7: Demand definition relationship with price types of demand determinants of change in demand shape of demand curve plotting graphs of both sift in demand curve and movement in demand curve Chapter#8: Supply definition relationship with price types of supply determinants of change in supply shape of supply curve plotting graphs of both sift in supply curve and movement in supply curve Chapter#9: Price determination difference between equilibrium and disequilibrium understanding excess supply and excess demand Chapter#10: Price changes Effect of changes in demand on price Effect of changes in supply on price Chapter#11: Price Elasticity of Demand Definition and formula of calculating PED Degrees of PED, differences in shape of PED Determinants of PED Effect of changes in PED Chapter#12: Price Elasticity of Supply Definition and formula of calculating PES Degrees of PES, differences in shape of PES Determinants of PES Effect of changes in PES Chapter 13: Market Economic System Features of market economic system Importance of competition and incentives Types of sectors Merits and demerits of Market Economic System 3 types of efficiency and their features Chapter#14: Market Failure Nature of market failure Types of costs and benefits Reasons of market failure Merit and demerit goods Public goods and private goods Chapter#15: Mixed Economic System Features of a mixed economy Maximum and minimum price Steps govt takes to overcome market failure Difference between privatization and nationalization Merits of government intervention in economy Chpter#16: Money and Banking Forms of money Functions of money Characteristics of money Commercial banks (definition, role, importance, aims) Central banks (definition, role, importance, aims) Chapter#17: Households Reason and influence of spending Reason and influence of savings Relationship between income and consumption Reason and influence of borrowing Chapter#18: Workers Definition of all types of wages Wage factors Nonwage factors National minimum wage Reasons for changes in occupation Reasons for variation in earnings Chapter#19: Trade Unions Definition of trade union Role of trade unions in an economy Factors influencing the strengths of trade unions Merits and de merits of trade union membership for (workers, producers, govt) Chapter#20: Firms Classifying firms in terms of sectors, ownerships, size Small firms merits and de merits Describing the cause of the growth of firms Advantages and disadvantages of different types of mergers Types of Internal and external economies of scale Chapter#21: Firms and Production Influence of demand on FOPS Reasons for having capital/labor intensive production Difference between productivity and production Chapter#22: Firms, costs, revenue and objectives Define and calculate 6 types of costs Interpret and draw all diagrams of costs Total and average revenue difference Sales affecting revenue List and describe objectives of the firms Chapter#23: Market Structure Behavior and performance of competitive markets Characteristics of monopoly market Rise and continuity of the monopoly markets Behavior and performance of monopoly markets Chapter#24: The Role of Government Influence on local economy Influence on national economy International role of government Chapter#25: Macro-economic Aims of Government The macro-economic aims Reasons for choosing these aims Government’s criteria for each aim conflicts that each aim brings Chapter#26: Fiscal Policy reasons for government spending reasons for levying taxes types pf taxes principles of taxation impact of taxation on consumer, producers, workers, government and economy tools of fiscal policy types of fiscal policy and their influence on aggregate demand and macroeconomic aims Chapter#27: Monetary Policy define money supply define and explain monetary policy analyse measures of monetary policy effects of monetary policy aggregate demand and macro-economic aims Chapter#28: Supply-side Policy definition of supply-side policy supply-side policy measures and their effect on macro-economic aims Chapter#29: Economic Growth definition causes and consequences of recession causes and consequences of economic growth effectiveness of both fiscal, monetary and supply side policies to promote economic growth Chapter#30: Employment and Unemployment difference between employment, unemployment and full employment causes of changes in the pattern of employment measuring unemployment causes and types of unemployment consequences of unemployment effectiveness of policies to reduce unemployment Chapter#31: Inflation and deflation definition of inflation and deflation measuring inflation and deflation causes and consequences of inflation effectiveness of policies to control inflation causes and consequences of deflation effectiveness of policies to control deflation policy conflicts Chapter#32: Living Standards indicators of living standards advantages and disadvantages of each indicator measuring income and wealth inequality reasons for differences of living standards and income distribution in and between countries chapter#33: Poverty difference between absolute and relative poverty causes of poverty and how to measure it policies to reduce poverty and re distribute income Chapter#34: Population factors affecting the growth of population reasons for different rates of growth of population in different countries changes in the size and structure of population Chapter#35: Differences in economic development between countries nature of economic development causes of differences in economic development between countries impacts of differences in economic development between countries Chapter#36: International Specialization basis of specialization at national level advantages and disadvantages of specialization at national level difference between international and internal trade Chapter#37: Free Trade and protection globalization role of MNCs benefits of free trade Methods of protections Reasons and consequence of protection Chapter#38: Foreign Exchange Rates Definition Fixed exchange rate and merits and demerits of it Floating/flexible exchange rate and merits and demerits of it Reasons for demand and supply of currency in foreign exchange market Causes and consequences of changes in exchange rate International competitiveness Chapter#39: Current Account of Balance of Payment Structure of current account Causes of current account surplus and current account deficit Consequence of current account surplus and current account deficit Policies of achieving balance of payment stability