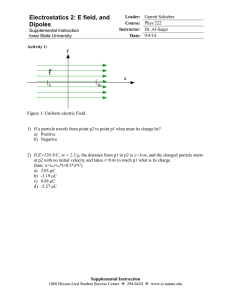
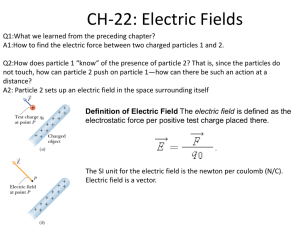
MNS Department Semester: Summer, 2023; Course No: PHY 112 Course Title: Principles of Physics II Time: 30 min Date: 9 July, 2023 Consider it for all problems: q1= Sum of the first 3 digits of your ID q2= Sum of the last 3 digits of your ID Q= q1 + q2 + q3 q3= Sum of the first and last digits of your ID d1= 1st digit of your ID d2= 2nd digit of your ID m = sum of your middle two digits. 1. The electric field in an xy plane produced by a single particle is (12 i^ +3 ^j) N /C at the ^ point (q 1 , q 2) and 50 i N /C at the point (d 1 , q 3) m .The particle is positively charged. What are the x and y coordinates of the source particle of the electric field? 2. A particle with charge q 1 nC is located at the origin. Two particles, with charges of q 2 nC and −q3 nC are placed at the points with coordinates (0, 4.00 cm) and (0,−4. oocm) . a) Determine the electric potential energy of the configuration of the three fixed charges. b) A fourth particle with mass m kg and charge 10 nC, is released from the rest at the point (3cm, 0). Find its speed after it has moved freely to a very large distance away. 3. The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom having the same amount of charges but opposite type, are separated by a distance of approximately d 1∗10−11 m . Find the magnitudes of the electric force and the gravitational force between the two particles. 4. An electron enters the region of a uniform electric field. Initial value of the velocity is 6 v i =3∗10 m/ s and E=Q N /C . The horizontal length of the plates is ι=4 cm . a) Find the acceleration of the electron while it is in the electric field. 5. A electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude Q∗105 N /C that is directed parallel to the plane of the figure. The charges are ±e C ; both lie in the plane and are separated by the 1.25 nm. Find (a) the net force exerted by the field on the dipole; (b) the magnitude and the direction of the electric dipole moment; (c)the magnitude and the direction of the electric dipole moment; (c) the magnitude and the direction of the torque; (d) the potential energy of the system in the position shown.