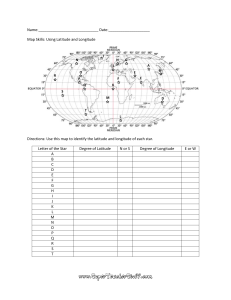
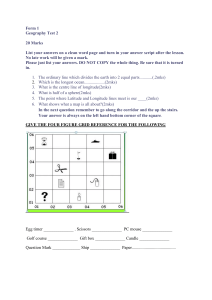
Longitude and latitude are the two primary coordinates used to determine locations on the Earth's surface. Longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian, which runs through Greenwich, England. It is measured in degrees, with 360 degrees representing a full circle around the Earth. Latitude, on the other hand, measures the distance north or south of the Equator. It is also measured in degrees, with 90 degrees representing the North and South Poles. These coordinates are essential for navigation and mapping purposes. They allow us to pinpoint any location on Earth with precision. Longitude helps us determine time zones and calculate the time difference between different regions. It also plays a crucial role in determining the direction of travel, as it helps us understand the angular relationship between two points. Latitude, on the other hand, helps us understand the climate and weather patterns of a particular region. It is used to divide the Earth into different climate zones, such as the tropics, temperate zones, and polar regions. Latitude also affects the length of daylight hours, with regions closer to the poles experiencing longer days in summer and shorter days in winter. Both longitude and latitude are represented as a series of numbers, with degrees, minutes, and seconds. For example, the coordinates of New York City are approximately 40.7128 degrees North latitude and 74.0060 degrees West longitude. These coordinates allow us to precisely locate any place on Earth's surface. In conclusion, longitude and latitude are essential tools for navigation, mapping, and understanding the Earth's physical characteristics. They provide a universal language for identifying locations and help us navigate the world with accuracy. Whether you're a sailor, a pilot, or simply looking for directions, understanding longitude and latitude is crucial for finding your way around the globe.