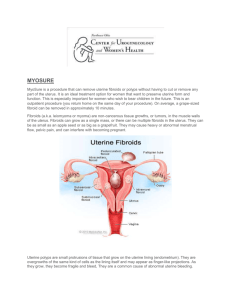
FIBROID Fibroids, also known as uterine fibroids or leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. They are made up of muscle and fibrous tissue and can range in size from small, undetectable nodules to large, bulky masses that can distort the shape of the uterus. 1 2 They consist of smooth muscle cells and connective tissue. A person may have one or multiple fibroids. They can also shrink or grow over time. Uterine fibroids are almost always noncancerous Uterine sarcomas are a rare form of cancer called leiomyosarcoma 3 3 Fibroid is more common from age 30 till menopause (MedicalNewsToday, 2020) Boafor, (2016), three to five fibroid surgeries daily at Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital. Fibroid cases are on the increase, and every three women above 30 years has the condition as well as those in their 20s (Boafor, 2016) presentation title 4 TYPES OF FIBROID • Fibroids are classified depending on their location in the uterus. • The four main types of fibroid. • Subserosal fibroids which are the most common type. They grow on the outside of the uterus. presentation title 5 TYPES OF FIBROID cont.’s • Intramural fibroids which grow inside the muscular wall of the uterus. • Submucosal fibroids which grow into the open space inside the uterus. 6 7 SYMPTOMS OF FIBROID Excessive menstrual bleeding Prolonged menstrual cycles Pelvic pain and pressure Frequent urination and incontinence Constipation Backache Leg pain 8 CAUSES OF FIBROID Estrogen, progesterone, growth hormones Genetic factor Stress and unbalanced micronutrients (such as iron and vitamin D) 9 DIAGNOSIS Ultrasound scans Plate 3. Ultrasound image by Fibroid treatment collaborative, 2021 10 DIAGNOSIS cont.’s Pelvic examination Plate 4. Pelvic examination image by Fibroid treatment collaborative, 2021 11 DIAGNOSIS cont.’s Hysteroscopy: a long flexible or rigid tube called a hysteroscope is used. It is inserted into the vagina and through the cervix to reach the uterus. A fiber optic light source and a tiny camera in the tube allow the doctor to view the cavity. The uterus is filled with saline or carbon dioxide to inflate the cavity and provide better viewing. 12 HYSTEROSCOPY Plate 5. Hysteroscopy image by NHS, 2021 13 DIAGNOSIS cont.’s Laparoscopy: They will insert a small, lighted tube into a small incision in the abdomen to examine the outside of the uterus and its surrounding structures. 14 TREATMENT Most fibroids do not cause symptoms and do not require treatment. In fact, they often shrink or disappear after menopause A doctor may recommend different treatments depending on the symptoms, the severity of the symptoms, and the location of the fibroids 15 MIDICATION • GnRH agonists • GnRH agonist causes the body to produce less estrogen and progesterone. This shrinks fibroids. • GnRH agonists stop the menstrual cycle without affecting fertility after the end of treatment. 16 MIDICATION CONT.’S Hormonal birth control Oral contraceptives help regulate the ovulation cycle, and they may help reduce the amount of pain or bleeding during periods 17 MIDICATION CONT.’S SURGERY Severe fibroids may not respond to more conservative treatment options. In these cases, surgery may be the best treatment option. The doctor may consider the following procedures 18 MIDICATION CONT.’S Hysterectomy Myomectomy Endometrial ablation Uterine fibroid embolization lifestyle 19 Thank you