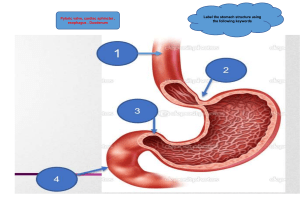
Stomach is the largest and most distensible organ of G.I.T Lies in : Left hypogasterium + Epigasterium + Umbilical regions of Abdomen Stomach appear as J-Shaped “Vertically” and Steer horn “Horizontally” SURFACES OF STOMACH : 1- Anerior-Superior surface covered completely by peritoneum (Greater sac) 2- Posterior-Inferior surface covered by peritoneum (Lesser sac) except small bare area, This small bare area located close to Cardiac orifice and covered by Left crus.of Diaphrgam. Before discussed of Stomach parts, we must know 2 lines 1- The Horizontal line from Cardiac Notch to Greater curvature 2- The Imaginary line from Angular notch to Bulge of Greater curvature “Bulge is small convex point at Lower most part of Greater curvature” PARTS OF STOMACH : 1- Fundus It’s Dome-shaped area lies Above “The Horizontal line” Between Cardiac Orifice and Greater curvature “ connects them together” 2- Body It’s largest part of stomach, Area that extends from “The Horizontal line” To “The Imaginary line” 3- Pyloric Lies distal (Next to) Imaginary line, Divided into 3 segments - Proximally The Dilated segment : Pyloric Antrum - Distally The Narrow segment : Pyloric Canal - 3RD segment : Pyloric sphincter ENDS OF STOMACH : 1- Cardiac end - Take 1 inch LEFT to Median plane - At level behind 7th Left Costal cartilage - Lies 4 inch DEEP to Anterior Abdominal wall - At junction with Lower end of Esophagus Anteriorly It’s related to : 1- Anterior gastric N. 2- Left lobe of Liver Posteriorly It’s related to : 1- Posterior gastric N. 2- Diaphragm Has No Anatomical sphincter, So It’s sphincter are Physiologically depends on: A- Acute angle that created at junction between Cardiac end and Esophagus B- Contraction of Circular muscle fiber of “Esophagus” witch close the end preventing, Reguregation of gastric contents that’s High Acidic C- At lower end of Esophagus the Mucosa become Thicker witch give Mucosal-Valve, Close and open the end D- Encircle of Lower end of Esophagus by Right Crus.of Diaphragm 2- Pyloric End - Take 1 inch to RIGHT from Median plane - At level of Transpyloric plane –L1 Anteriorly : Quadrate lobe “Middle Part” Posteriorly : Neck of Panceras Has True Anatomical sphincter BORDERS OF STOMACH : 1- Lesser curvature Right + Concave “inside” At lower most part there’s Angular notch “Help us to Draw Imaginary line” Gives 1 ligament attachment called Lesser Omentum The Lesser Omentum Fold (2-Layers) of peritoneum Connects LIVER to LESSER CURVATURE STOMACH and 1st inch of DUEDENUM 1- Gastric border = Rise from Lesser curvature + 1st inch of Duedneum 2- Hepatic border = Continution of Gastric border, But divides into Long and Short extensions - Long extension gives attach to Porta Hepatis - Short extension gives attach to Ligamentum Venosium 3- Right free border = Continution of Long extension of Hepatic border And return back to 1st inch of Duedneum *Form ANTERIOR boundary of Epiploic F. 4- Upper / Diaphragmatic border = Rise from Lesser curvature to Under surface of Diaphragm Then Enclose Abdominal part of Esophagus Contents of Lesser omentum : (8) Gastric Border - Left + Right Gastric Vessels - Left Gastric L.Ns Hepatic Border - Portal V - Hepatic A - Common Bile Duct - Ex.peritonial fatty tissue - Hepatic Plexus of A.Ns 2- Greater Curvature Left + Convex “Outside” - At Beginning or Upper most part or also site of junction between Esophagus and Cardiac orifice.. We find Cardiac notch Help us to Draw the Horizontal line - Gives 3 ligaments attachment *Gastro-Phrenic Fundus to Diaphragm *Gastro-Splenic Left 1/3 or Upper part of Greater curvature to Hilum of Spleen Contents: 1- Short gastric Vessles 2- Left Gastrepiploic Vessels 3- Splenic-panceratic L.Ns 4- Ex.peritonial fatty tissue 5- A.Ns *Greater Omentum From Right 2/3 to Intestine Content : 1- Right and Left gastrepiploic Vessels 2- Gastrepiploic L.Ns 3- Ex.peritonial fatty tissue 4- A.Ns Relations of Stomach : 1- Fundus 2- Anteriorly 3- Posteriorly 4- Cardiac 5- Pyloric Ant.gastric N + Left lobe of liver (Anteriorly) Post.gstric N + Diaphragm (Posteriorly) Quadrate lobe (Anteriorly) Neck of panceras (Posteriorly) 6- Peritonieal A- Anterio-superior surface = Peritoneum (Greater sac) B- Postero-inferior surface = Peritoneum (Lesser sac) Except small bare area that’s close to Cardiac Orifice