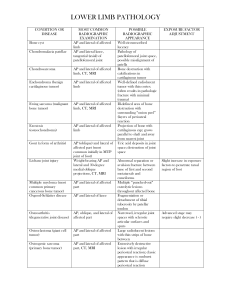
LOWER LIMB PATHOLOGY CONDITION OR DISEASE Bone cyst Chondromalacia patellae MOST COMMON RADIOGRAPHIC EXAMINATION AP and lateral of affected limb AP and lateral knee, tangential (axial) of patellofemoral joint Chondrosarcoma AP and lateral of affected limb, CT, MRI Enchondroma (benign cartilaginous tumor) AP and lateral of affected limb Ewing sarcoma (malignant bone tumor) AP and lateral of affected limb, CT, MRI Exostosis (osteochondroma) AP and lateral of affected limb Gout (a form of arthritis) AP (oblique) and lateral of affected part (most common initially in MTP joint of foot) Weight-bearing AP and lateral and 30-degree medial oblique projections, CT, MRI Lisfranc joint injury Multiple myeloma (most common primary cancerous bone tumor) Osgood-Schlatter disease AP and lateral of affected part Osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) AP, oblique, and lateral of affected part Osteoclastoma (giant cell tumor) AP and lateral of affected part Osteogenic sarcoma (primary bone tumor) AP and lateral of affected part, CT, MRI AP and lateral of knee POSSIBLE RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCE Well-circumscribed lucency Pathology of patellofemoral joint space, possible misalignment of patella Bone destruction with calcifications in cartilaginous tumor Well-defined radiolucent tumor with thin cortex (often results in pathologic fracture with minimal trauma) Ill-defined area of bone destruction with surrounding “onion peel” (layers of periosteal reaction Projection of bone with cartilaginous cap; grows parallel to shaft and away from nearest joint Uric acid deposits in joint space; destruction of joint space EXPOSURE FACTOR ADJUSTMENT Abnormal separation or avulsion fracture between base of first and second metatarsals and cuneiforms Multiple “punched-out” osteolytic lesions throughout affected bone Fragmentation or detachment of tibial tuberosity by patellar tendon Narrowed, irregular joint spaces with sclerotic articular surfaces and spurs Large radiolucent lesions with thin strips of bone between Extensively destructive lesion with irregular periosteal reaction; classic appearance is sunburst pattern that is diffuse periosteal reaction Slight increase in exposure factors to penetrate tarsal region of foot Advanced stage may require slight decrease ( - ) LOWER LIMB PATHOLOGY Osteoid osteoma (benign bone lesions) Osteomalacia (rickets) AP and lateral of affected part AP and lateral of affected limb Paget disease (osteitis deformans) AP and lateral of affected parts Reiter syndrome AP and lateral of affected part Small, round-to-oval density with lucent center Decreased bone density, bowing deformity in weight-bearing limbs Mixed areas of sclerotic and cortical thickening and lytic or radiolucent lesions; cotton wool appearance Asymmetric erosion of joint spaces; calcaneus erosion, usually bilateral Loss of bone matrix requires decrease ( - ) Extensive sclerotic areas may require increase ( + )