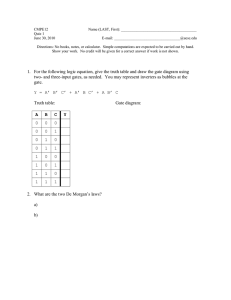
Bagmati Boarding Secondary School Project work on Word Processor Operating System Boolean algebra HTML Mailing Submitted By: Name: Bibesh basnet Class: 11 ‘b’ Roll No.: 9 Registration Number: Internal Examiner Mr. Raja Ram Thapa (Computer Instructor) External Examiner Contents OPERATING SYSTEM ...................................................................................................................................................3 INTRODUCTION AND ROLE OF OPERATING SYSTEM: ............................................................................................3 FUNCTIONS OF THE OPERTING SYSTEM:................................................................................................................4 Word Processor ..........................................................................................................................................................5 Introduction on word processor ............................................................................................................................5 Features of word processor....................................................................................................................................6 MAIL MERGE ...............................................................................................................................................................7 ID CARD DESIGN .........................................................................................................................................................9 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA ................................................................................................................................................. 10 LOGIC GATE ......................................................................................................................................................... 10 AND Gate ............................................................................................................................................................. 11 OR Gate................................................................................................................................................................ 12 NOT Gate ............................................................................................................................................................. 13 NAND GATE ......................................................................................................................................................... 14 NOR Gate ............................................................................................................................................................. 15 Exclusive-OR (X-OR) Gate .................................................................................................................................... 16 Computer Architecture............................................................................................................................................ 17 OPERATING SYSTEM INTRODUCTION AND ROLE OF OPERATING SYSTEM: O perating system (O.S) is an integrated set of the program that controls the resources (the CPU, memory, I/O devices etc.) of the operating system. It provides an interface to its user which is more convenient to use the bare machine. The two primary objectives of an operating system are; 1) Making a computer system convenient to use. 2) Managing the resources of the computer system. An operating system is the collection of the program that controls the overall operation of the computer system. Operating system controls and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various application programs for the various users. So it acts as an interface between the user and the computer hardware. An operating system manage and coordinates the function performed by the computer hardware, including the CPU, input/output devices, secondary storage devices and communication and network equivalent. Operating system is the most important program that runs on a computer. Every general purpose computer must have an operating system to run other programs. It performs basic task, such as recognizing inputs from keyboard, sending outputs to displays units, keeping tracks of files and the direction on the disks and controlling peripheral devices such as disk driver and printer. FUNCTIONS OF THE OPERTING SYSTEM: 1) I/O MANAGEMENT: Input/output (IO) is the essential for the operation of the computer. It allows the computer to interact with the peripheral devices such as keyboard, mouse, terminals (like modem, TV, cards and NIC cards), disk or tapes (CD, DVD and floppy disk) printer etc. 2) Command interpreter: The command interpreter reads the commands that a user types in at a terminal, interpret them and translate them into a detailed set of the instruction that the computer hardware can understand. It varies widely from one OS to another. Every OS must provide command interpret for its operation. 3) Data management: Data management allows organizing their data into logical grouping called files. Earlier, only few OS provided data management, containing limited flexibility and usefulness at the present, most of the OS provides this features. 4) Memory management: Memory is a large array of the words or bytes each with its own address. When the user request CPU for the read/write operation, OS determine the amount of the memory required for the program instruction and data. Then, OS allocates required memory to load the program and data into RAM. When program terminates, its memory space is free and the same memory area can be allocated to other program. 5) Process management: The process management allocates a process to execute a chosen process. It finds the status of the processor and processes (traffic controller), chooses job (job schedules), chooses process in the job (process scheduler), allocates the processor to the process (dispatcher), and frees the processor when the process I executed. 6) Device management: The device management allocates a device to process. It finds the status of the, channel and controls unit, finds answer to the question like which process, which device- how much and allocates device to the process (IO scheduling), initiates the IO operating and finally frees the devices when the process is completed. 7) File management: The file management keeps track of all the information on files. It opens and closes files. It finds and records the following for all files: location, size, usages (attributes) status etc. it also finds as to which process wants which files, check through the protection routine, open the file if allowed and allocated it to the process. Finally, it closes the file when the process is executed. Processor management is at a low level, very near to the machine and file management is at higher level, very near to the user. 8) Time sharing: Time sharing management, a function of O.S, involve the CPU to allocate the time to a number of the user on the same computer, property generally found in the network operating system. Word Processor Introduction on word processor W ord processor is application software that helps in the creation of a document. It facilitates the creation of documents through computerized text editing, formatting, storing and printing. It allows the user to type text, make corrections without retyping the entire matter and has the feature to make the text look attractive. It can enhance documents in many ways such as: user can add image and animation, link different documents together, use of speller and thesaurus. Features of word processor The following are the common features of word processor software: Fast operation: Typing in a word processor becomes very fast as there is no mechanical carriage movement associated. Editing text features: Any type of operations, likewise insert, delete, modify the documents, and undo/redo, find/replace can be performed very easily. These insertion, deletion or correction can be performed at any time in place of the text. These alternations can be made after typing the entire document. Similarly, move or copy a section or block of the text or object from any location of the same document to another location in the entire document or other document to another location in the entire material of the document too. Formatting features: The electronic typed text can be appear on insert in any form or style like bold, italic, underline, different fonts, font size, its color and paragraph[h formatting can be made. Permanent storage: by the help of word p[processor, files and documents can be saved as long as preferred and saved files and documents can be retrieved whenever desired. Graphics: it provides facilities to insert text, objects (picture graph etc) anywhere in the document whenever necessary. OLE (object linking and embedding): modern word processors provide facilities to link or embed objects in a document. OLE is a program-integration technology that can use to share information between programs through objects. Objects are saved entities of different types of charts and thesaurus (synonyms and antonyms words). Mail merge: it is an option used to merge a list of information such as names, addresses, e-mail, phone numbers (data source) with the main document. The main document contains original text (merge fields) with data area at appropriate places to produce a number of original texts (merge fields) with data area appropriate places to produce a number of copies of merged document while defined the merging task. The main document is created using the mail merge helper dialogue box. Searching: it facilitates to search for any word or text and replace or delete with other necessary ones in the entire material of the document very easy. MAIL MERGE Bagmati High school Name: Grade: Rollno: Valid Date: Photo Name Bibesh Amish Bagmati High school Name: Grade: Rollno: Valid Date: Bibesh XI 1 12/10/2020 Photo Grade XI XI Rollno Validity 1 10/12/2020 2 10/12/2020 BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name:Amish Grade:XI Rollno:1 Parents name:aa Contact number:1122 BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name:Asim Grade:Xi Rollno:3 Parents name:cc Contact number:1124 BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name: Grade: Rollno: Parents name: Contact number: BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name: Grade: Rollno: Parents name: Contact number: BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name:Bbes Grade:XI Rollno:2 Parents name:bb Contact number:1123 BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name: Grade: Rollno: Parents name: Contact number: BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name: Grade: Rollno: Parents name: Contact number: BAGMATI HIGH SCHOOL Name: Grade: Rollno: Parents name: Contact number: ID CARD DESIGN BAGMATI BOARDING S. SCHOOL Bibesh Basnet Basundhara, KTM Science (Physical Group) ID No. : 2725076/59 Grade : XI(B) Contact : 9841696803 Blood Group: B+ DOB : 2059/10/13 Parent’s Name : Babu Ram Basnet P H O T Principal O Validity : 2077-03-31 Sukedhara-4,Kathmandu/+977014374881/www.bmcollege.edu.np BOOLEAN ALGEBRA LOGIC GATE A logic gate is an electric circuit that operates on one or more input signals to produce an output signal. The logic gate is used for binary operation and is the basic component of digital computer. It is embodied into Integrated Circuit (IC). Each gate has its specific function and graphical symbol. The function of gate is expressed by means of an algebraic expression. In a digital computer, there are three basic gates, which are: 1. AND gate 2. OR gate 3. NOT gate Apart from the basic gates, there are other gates derived from basic gates, which are: 4. 5. 6. 7. NAND gate NOR gate Exclusive OR (XOR) gate Exclusive NOR (XNOR) gate AND Gate AND gate is an electric circuit, which produces high (1) output when all the inputs are high. Otherwise, the output will be low (0). The output is equal to the product of the logic inputs. It can have two or more inputs and produces a single output. The graphical symbol, algebraic expression and truth table of AND gate is shown below. Graphical symbol A X = A.B B Algebraic expressions X = A.B Where ‘.’ stands for AND operation, A and B are inputs and X is output. Truth table: Inputs Output Inputs Output A B X = A.B A B X = A.B 0 0 0 False False False 0 1 0 False True False 1 0 0 True False False 1 1 1 True True True OR OR Gate OR gate is an electronic circuit, which produces high (1) output when one of the input is high (1). If all inputs are low (0), then the output will also be low (0). The output is equal to the sum of the logic inputs. It has two or more inputs and produces a single output. Graphical symbol A X=A+B B Algebraic expression: X=A+B Where ‘+’ stands for OR operation, A and B are inputs and X is output. Truth table: Inputs Inputs Output Output A B X = A.B False False False False True True A B X = A+B 0 0 0 0 1 1 True False True 1 0 1 True True True 1 1 1 OR NOT Gate NOT gate is an electronic circuit whose output is the complement of the input. It is also called inverter. If we provide high input (1) to this gate, it will produce low output (0) & vice-versa. It has only one input and an output. Graphical symbol: A X=A’ Algebraic expression: X = A’ = A Where, A is input and X is output Truth table: Inputs Output A X = A’ 1 0 0 1 Inputs OR Output A X = A’ False True True False NAND GATE The NAND gate is the combination of AND and NOT gate. This electronic gate produces low (0) output, when all inputs are high (1), otherwise the output will be high (1). It is the complement of AND gate. It has two or more inputs and produces a single output. Graphical symbol: A X = (A.B)’ B Algebraic expression: X = (A.B)’ Where, A and B are inputs and X is output. Truth table: Inputs A 0 0 1 1 Output B 0 1 0 1 A.B 0 0 0 1 X = (A.B)’ 1 1 1 0 NOR Gate NOR gate is the combination of OR gate and NOT gate. This electronic gate produces high (1) output when all inputs are low (0) otherwise, output will be low (0). It is the combination of OR gate. It has two or more inputs and produces a single output. Graphical symbol: A X = (A + B)’ B Algebraic expression: X = (A + B)’ Where, A and B are inputs an X is output. Truth Table: Inputs A 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 Output A+B X = (A + B)’ 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 Exclusive-OR (X-OR) Gate The XOR gate produces low output (0 when both the inputs are same otherwise, the output will be high (1). It can also have two or more inputs which produces single output. Graphical symbol: A X = A’.B + A.B’ B Algebraic expression: X = A’.B + A.B’ Where, A and B are inputs and X is output. Truth table: Inputs A 0 0 1 1 B 0 1 0 1 A’ 1 1 0 0 B’ 1 0 1 0 A’.B 0 1 0 0 A.B’ 0 0 1 0 Output X = A’.B A.B’ 0 1 1 0 Computer Architecture The processor Control Unit Interprets stored instruction in sequence. Issue commands to all elements of the computer. ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT perform arithmetic and logic operation Input Data Instruction Output Information The result of processing Main Memory(Primary Memory) Holds data, instruction and results of processing Data/instruction Command/signal flow Auxiliary storage(secondary memory) To supplement main memory.