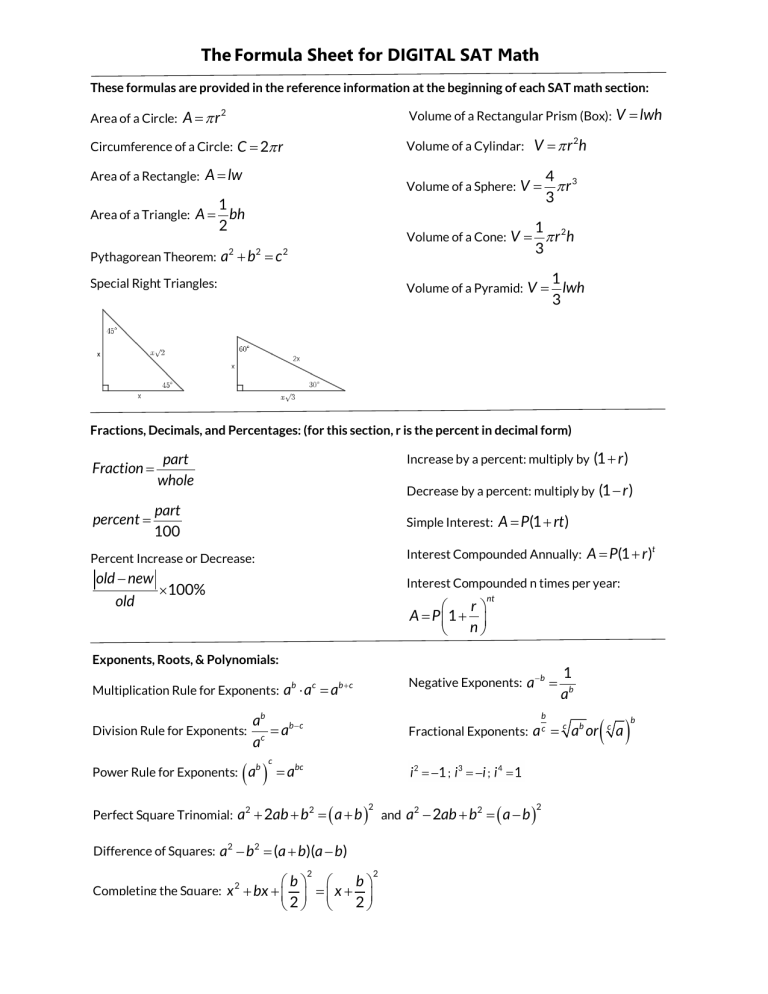
The Formula Sheet for DIGITAL SAT Math These formulas are provided in the reference information at the beginning of each SAT math section: Area of a Circle: A = π r2 Volume of a Rectangular Prism (Box): Circumference of a Circle: C = 2π r Area of a Rectangle: Area of a Triangle: A = Pythagorean Theorem: V = π r 2h Volume of a Cylindar: A = lw Volume of a Sphere: V = 1 bh 2 Volume of a Cone: V = a2 + b 2 = c2 Special Right Triangles: V = lwh 4 3 πr 3 1 2 πr h 3 Volume of a Pyramid: V = 1 lwh 3 Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages: (for this section, r is the percent in decimal form) Fraction = percent = part whole Increase by a percent: multiply by Decrease by a percent: multiply by part 100 Simple Interest: = A old (1 − r ) P(1 + rt ) Interest Compounded Annually: = A P(1 + r ) t Percent Increase or Decrease: old − new (1 + r ) Interest Compounded n times per year: ×100% r = A P 1 + n nt Exponents, Roots, & Polynomials: Multiplication Rule for Exponents: Division Rule for Exponents: Power Rule for Exponents: Negative Exponents: a ab ⋅ a c = ab + c ab = ab − c ac (a ) b c b = abc 2 ( ) 2 Difference of Squares: a − b = (a + b)(a − b) 2 2 2 b b Completing the Square: x + bx + = x + 2 2 2 = 1 ab Fractional Exponents: a c = a or Perfect Square Trinomial: a + 2ab + b = a + b 2 −b 2 ( and a − 2ab + b = a − b 2 2 ) 2 c b ( a) c b Systems of Linear Equations One solution: The lines intersect at one point. No solutions: The lines intersect If the slopes of two lines are different. If the slopes of two lines are the same (they are parallel) but the y-intercept is different. Infinite Solutions: The lines intersect at infinite points (they are overlapping lines). nowhere. If the slopes and y-intercepts are the same for both lines. Parabolas: Standard Form: f ( x ) = ax + bx + c ; 2 b b ,f − ; 2a 2a vertex= − 2 Factored Form: f ( x ) =a( x − m)( x − n) ; x-intercepts are m and n; y-intercept = c; −b ± b2 − 4ac x-intercepts = 2a Sum of solutions = Discriminant = b − 4 ac ; Pos=2 real roots Zero= 1 real root; Neg=2 imaginary roots −b a x-coordinate of vertex = m+n 2 Vertex Form: f ( x ) = a( x − h) + k ; 2 vertex = (h, k ) ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC Systems of Linear Inequalities y ≤ 3x + 1 y ≤ 3x + 1 and y > -x + 2 graphed together. The solution is the overlapping region. y > -x + 2 Data and Probability: average = sum _ of _items number _ of _items median = middle _number Strong positive association Weaker positive association = range maximum −minimum probability = No association desired _outcomes possible _outcomes Weaker negative association Strong negative association Data Set A has a larger standard deviation than Data Set B since the values are spread farther from the mean in general for Data Set A than for Data Set B. Sample Size: For SAT, a sample size of 30 is considered large enough to make accurate calculations for any size population. Still, the larger the sample, the more accurate the statistics are that can be calculated from it. Graphing Lines: Slope Formula: m = y 2 − y1 x2 − x1 Standard Form: Ax + By = C Slope-Intercept Form:= y Slope of horizontal line = 0 mx + b Point-Slope Form: y − y1 = m( x − x1 ) Slope of vertical line = undefined Distance Formula: d= ( x2 − x1 )2 + (y 2 − y1 )2 x1 + x2 y1 + y 2 , 2 2 Midpoint Formula: M = Parallel lines: equal slopes ⊥ Lines: slopes are opposite reciprocals Similar Triangles Angles: Vertical ∠’ s are ≅ ∠’s that form a linear pair are supplementary (add up to 180°) Triangles: The three ∠’ s of a ∆ add up to 180° ∠’ s that form a circle add up to 360° When ∥ lines are cut by a transversal, all acute ∠’ s are ≅ and all obtuse ∠’ s are ≅ Pythagorean Triples: 3-4-5 and 5-12-13 An exterior ∠ is equal to the sum of the two remote interior ∠’ s Circles: A central ∠ is double the inscribed ∠ A radius and tangent make a right ∠ x arc = 360 circumference and x sec tor = 360 area _ of _ circle where x = central angle Formula for a Circle: ( x − h) + (y − k ) = r , where (h,k) is the center and r is the radius 2 2 2 ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC Polygons: (for this section, n is the number of sides) Area of a trapezoid: 1 (b1 + b2 )h 2 Properties of Parallelogram 1. Opp sides are ∥ and ≅ 2. Opp ∠’ s are ≅ Sum of the interior angles: 180(n − 2) 3. Consec ∠’s are supplementary Sum of the exterior angles: 360° 4. Each diagonal forms a pair of ≅∆’s 5. Diagonals bisect each other If they are ≅ it is a rectangle If they are ⊥ it is a rhombus 6. Area = base × height Trigonometry: sin = opp hyp cos = adj hyp tan = opp adj 360°=2π radians = sin( x ) cos(90 − x ) The sine of an ∠ is equal to the cosine of its complement. Parent Graphs & Transformations: y=x Transformation f (x) + k f (x) − k f ( x + h) f ( x − h) −f ( x ) cf ( x ) 1 f (x) c y= x y = x2 y = x3 y = ax y= x Visual effect Shift up by k units Shift down by k units Shift left by h units Shift right by h units Reflect over the x axis (flip upside down) Stretch vertically by a factor of c (becomes skinnier) Shrink vertically by a factor of c (becomes fatter) ©2020, Test Prep for Success LLC