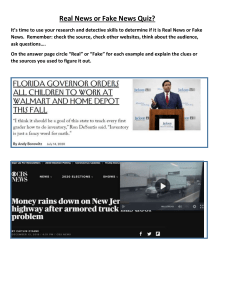
MEDIA AND INFORMATION SOURCES Indigenous Sources ➢ A material is indigenous when it exists naturally in particular region or environment. When we refer to someone as indigenous, it connotes that the person belongs to an ethnic tribe who has preserved and still practice the culture and tradition of their ancestors Indigenous Knowledge ➢ understanding, skills, practices and beliefs confined to a particular culture or society intended to preserve, communicate and contextualize. Indigenous Communication Practices: INDIGENOUS MEDIA AND INFORMATION Indigenous Media ➢ forms of media expression conceptualized, produced, and circulated by indigenous peoples worldwide as vehicles for communication, including cultural preservation, cultural and artistic expression, political self-determination, and cultural sovereignty. It also refers to diverse audiovisual production activities involving indigenous people. Characteristics of Indigenous Media - The oral tradition of communication - Stores information in memories - Information exchange is face-to-face - Information is contained within the border of the community - Knowledge is unique to a given culture and society - Relayed through people media and community media - Varies from one place to another - Popular media cannot reach rural areas. - Indigenous media are credible. - Channels for change, education & development - Ignoring indigenous media can result in development & education programs that are irrelevant & ineffective. FORMS OF INDIGENOUS MEDIA - Folk of traditional media - Gatherings and social organizations - Direct observation - Records – may be written, carved or oral - Oral instruction Oral tradition - is a form of narration wherein the elders recount their culture, beliefs, history and tradition to their children and grandchildren through legends, folktales, epics, mythologies, and folk songs. Legend – it is a fiction which tells about origin of something. Example: Legend about Piña. Folktale – similar to legend, a folktale is a narration about the characteristics of the time and place in which the story is told. Epic – an epic tells a heroic adventure of main character that sometimes possesses extraordinary powers. PRIMARY SOURCES - Relics or artifacts such as pottery, ornaments, accessories, and other objects found on historical burial sites are considered primary sources of information as these are concrete evidence of things used by people in the past. - Records of events or evidence as they are first described or happened without any interpretation or commentary - Display original thinking, report on discoveries, or share fresh information - Raw materials under study SECONDARY SOURCES - secondary sources give second-hand accounts about a particular event, person, or information. It provides another angle and analysis from the perspective of another person. Some history books are regarded as secondary sources of information. - If you need to do an extensive research, it would be best to go to the library so you can choose form wide range of books, magazines, and other reference materials. INFORMATION LITERACY Information - Data that has been collected, processed, and interpreted in order to be presented in a useable form. A broad term that can cover processed data, knowledge derived from study, experience, instruction, signals or symbols. In the media world, information is often used to describe knowledge of specific events or situations that has been gathered or received by communication, intelligence, or news reports. Why do you need Information? - to be updated with the news - for learning/education purposes - for communication - to acquire knowledge needed for decisionmaking ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS OF SOME MEDIA FORMS Where do you search for information? - internet - television - library - radio - newspaper How do you acquire and store nformation? - write - print - photocopy - photograph - download - cloud storage - record - external memory drives - memory cards How will you determine the quality and accuracy of the information that you have? - it should come from a reputable source - don’t reply on a single source only How do you use the information that you have - share - apply - announce - post - archive - reminder - answer a query - clarify confusion How will you communicate information? - announcement - text - post to social media - face to face session - note - chat - email - save file Stages/ Elements of Information Literacy Information Literacy - A set of individual competencies needed to identify, evaluate and use information in the most ethical, efficient and effective way across all domains, occupations and professions. - Refers to the ability to recognize when information is needed and to locate, evaluate, effectively use and communicate information in its various formats. 5 Components of information Literacy by Seminole State Library FAKE NEWS - According to the website of the Merriam– Webster Dictionary, ‘fake’ was little used as an adjective prior to the late 18th century, and before that point, the most common collocation in use was ‘false news’ - An authoritative paper by economists Allcott and Gentzkow defines ‘fake news’ as “news articles that are intentionally and verifiably false, and could mislead readers” - The lawyers Klein and Wueller leave out the impact of the information on the reader and employ the following working definition: “the online publication of intentionally or knowingly false statements of fact” - Overall, as an extensive study by Tandoc et al. found, academic articles between 2003 and 2017 used the term ‘fake news’ to refer to a range of different phenomena including news satire, news parody, fabrication, manipulation, advertising and propaganda. - Within the legislative domain, the concept of fake news is even more ambiguous, as evidenced by the recent debates around the efforts to introduce national ‘anti-fake news’ laws. - In France, the law against the “manipulation of information” attempts to define fake news as “any allegation of a fact that is inaccurate or misleading”, which is likely to “distort the fairness of the election” , if propagation on the internet was made "deliberately” and “in an artificial or automatized and massive way”. - In Italy, the bill proposed but not adopted in 2017 defined fake news as “false, exaggerated, or biased” news reports online - As pointed out by Martens et al., there is no consensus on the definition of ‘fake news’ .32 The definitions discussed tend to be constructed, to a varying degree, around four dimensions: (i) type of information; (ii) falsity of information; (iii) intention of the author; and (iv) consequences of dissemination of information, including personal (perception of the receiver) and societal effects (disruption of democratic processes). TYPES OF FAKE NEWS MISINFORMATION - When false information is shared, but no harm is meant. DISINFORMATION - When false information is knowingly shared to cause harm. MAL-INFORMATION - When genuine information is shared to cause harm. FAKE NEWS PURVEYOR HYPERPARTISAN WEBSITES, FACEBOOK PAGES, AND SOCIAL MEDIA ACCOUNTS - may share a combination of fake news and partisan content (misleading stories, partisan memes and videos, et cetera) that is not considered fake news, but could still contain misleading or out-of- context information designed to confirm a particular ideological view. MISLEADING INFORMATION - Misleading or outof-context information does not on its own constitute fake news. This kind of information is not wholly fabricated, and it can exist within a news report that is based on actual events that occurred. CLICKBAIT - Clickbait pieces are articles that feature headlines designed to get people to click on them, often by presenting a misleading or warped sense of what the post is about. SATIRE - Satire is writing or art designed to make social commentary based on mockery and imitation of real-life events or actors. Some fake news sites may claim to be satirists but do not openly advertise themselves as satire, therefore suggesting an intent to deceive. PROPAGANDA - Propaganda is misleading or highly biased information that is specifically designed to confirm or promote a particular ideological viewpoint. CONSPIRACY THEORY - A conspiracy theory is an explanation or interpretation of events that is based on questionable or nonexistent evidence of a supposed secret plan by a group – often governments and mainstream media outlets -- to obscure events. MISTAKES IN REPORTING - A legitimate news outlet that makes an error in reporting is not creating fake news. Journalists may sometimes lack necessary facts, be misled by a source, or choose poor wording to convey news stories. MEDIA AND INFORMATION LANGUAGES (genre, codes, and conventions) What is genre? What are codes and conventions? TYPES OF CODES Techincal – ways in which equipment is used to tell the story (cam techniques, graming, depth of fields, lighting and etc.) Camera Techniques Symbolic Codes – show what is beneath the surface of what we see (objects, setting, body language, clothing, color, etc.) Written Codes – use of language style, and textual layout (headlines, captions, speech bubbles, language style, etc.) Formative Assessment: Poster Analysis - color: comedy=yellow Convention Conventions of an action movie: guns, explosions, bombs, cars, fighting, chasing, etc WHAT IS PLAGIARISM? Plagiarism - an act or instance of using or closely imitating the language and thoughts of another author without authorization; the representation of that author's work as one's own, as by not crediting the original author. What are the consequences of plagiarism in writing? - Plagiarism can have serious consequences. Depending on the nature of the plagiarism and the university or instructor’s policy, here are some possible consequences: - Academic probation - Failure of the assignment - Failure of the course - Suspension - Dismissal from the program or the institution - Additionally, you can seriously damage your academic and/or professional reputation. - Plagiarism isn’t limited to academic writing. It’s also possible to plagiarize creative writing and online content.