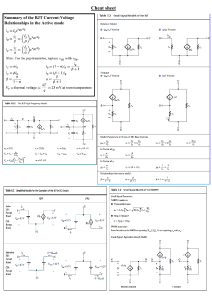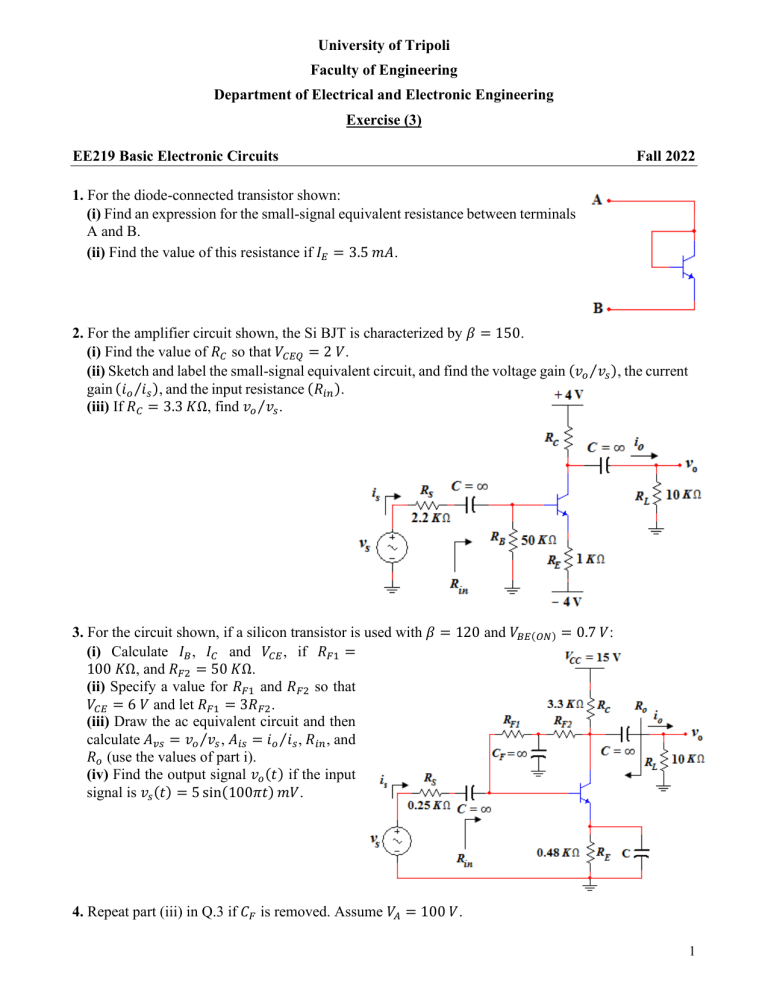
University of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Exercise (3) EE219 Basic Electronic Circuits Fall 2022 1. For the diode-connected transistor shown: (i) Find an expression for the small-signal equivalent resistance between terminals A and B. (ii) Find the value of this resistance if 𝐼𝐸 = 3.5 𝑚𝐴. 2. For the amplifier circuit shown, the Si BJT is characterized by 𝛽 = 150. (i) Find the value of 𝑅𝐶 so that 𝑉𝐶𝐸𝑄 = 2 𝑉. (ii) Sketch and label the small-signal equivalent circuit, and find the voltage gain (𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 ), the current gain (𝑖𝑜 ⁄𝑖𝑠 ), and the input resistance (𝑅𝑖𝑛 ). (iii) If 𝑅𝐶 = 3.3 𝐾Ω, find 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 . 3. For the circuit shown, if a silicon transistor is used with 𝛽 = 120 and 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7 𝑉: (i) Calculate 𝐼𝐵 , 𝐼𝐶 and 𝑉𝐶𝐸 , if 𝑅𝐹1 = 100 𝐾Ω, and 𝑅𝐹2 = 50 𝐾Ω. (ii) Specify a value for 𝑅𝐹1 and 𝑅𝐹2 so that 𝑉𝐶𝐸 = 6 𝑉 and let 𝑅𝐹1 = 3𝑅𝐹2 . (iii) Draw the ac equivalent circuit and then calculate 𝐴𝑣𝑠 = 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 , 𝐴𝑖𝑠 = 𝑖𝑜 ⁄𝑖𝑠 , 𝑅𝑖𝑛 , and 𝑅𝑜 (use the values of part i). (iv) Find the output signal 𝑣𝑜 (𝑡) if the input signal is 𝑣𝑠 (𝑡) = 5 sin(100𝜋𝑡) 𝑚𝑉. 4. Repeat part (iii) in Q.3 if 𝐶𝐹 is removed. Assume 𝑉𝐴 = 100 𝑉. 1 5. Consider the amplifier circuit shown below where the BJT is characterized by 𝛽 = 175, 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7 𝑉, and assume that 𝑉𝐴 = 100 𝑉. (i) Find the DC operating point. (ii) Draw the small-signal equivalent circuit. (iii) Find 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 , 𝑅𝑖𝑛 and 𝑅𝑜 if the switch (SW) is connected to position 1. (iv) Find 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 , 𝑅𝑖𝑛 and 𝑅𝑜 if the switch (SW) is connected to position 2. (v) From parts (iii) and (iv), what are the advantages and disadvantages of connecting the switch (SW) to position 1 compared to connecting it to position 2 ? 6. Consider the following amplifier circuit where the BJT is characterized by 𝛽 = 150, 𝑉𝐴 = ∞, and 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7 𝑉, and Zener diode is modelled by 𝑉𝑍 = 4.7 𝑉, 𝐼𝑍𝐾 = 0.5 𝑚𝐴 and 𝑟𝑍 ≅ 0. (i) What do you think the main reason of using Zener diode? (ii) What would happen if the resistor 𝑅1 is removed? (iii) What are the purposes of 𝐶1 and 𝐶𝐵 ? (iv) Find the operating point. (v) Determine 𝑅𝑖𝑛 , 𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑡 , 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 , and 𝑖𝑜 ⁄𝑖𝑠 . (vi) What is the main disadvantage (weakness) of this voltage amplifier design? 7. Consider the following amplifier circuit, where the BJT is characterized by 𝛽 = 100, 𝑉𝐴 = ∞ and 𝑉𝐵𝐸 (𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒) = 0.7 𝑉. (i) Determine the DC currents, 𝐼𝐶 , 𝐼𝐸 and 𝐼𝐵 , and the collector-to-emitter voltage 𝑉𝐶𝐸 . (ii) Draw and label the small-signal equivalent circuit for this amplifier and determine the voltage gain (𝐴𝑣 = 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 ), the current gain (𝐴𝑖 = 𝑖𝑜 ⁄𝑖𝑠 ), the input resistance 𝑅𝑖𝑛 and the output resistance 𝑅𝑜𝑢𝑡 . 2 8. Consider the following amplifier circuit where the BJT is characterized by 𝛽 = 100, 𝑉𝐴 = 50 𝑉, and 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7 𝑉. (i) Find the Q-point. (ii) Calculate 𝑣𝑜1 ⁄𝑣𝑠 and 𝑅𝑜1 . (iii) Calculate 𝑣𝑜2 ⁄𝑣𝑠 and 𝑅𝑜2 . (iv) Compare and comment on your results of parts (ii) and (iii). 9. For the circuit shown, assume 𝛽 = 100, 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7 𝑉 and 𝑉𝐴 = 100 𝑉. (i) Find the value of 𝑅1 and 𝑅2 to get the maximum undistorted output voltage. Assume that 10(𝑅1 //𝑅2 ) = (1 + 𝛽)𝑅𝐸 . (ii) Draw the DC and ac load lines. (iii) Calculate 𝑣𝑜 ⁄𝑣𝑠 , 𝑅𝑖𝑛 and 𝑅𝑜 . 10. (i) For the circuit shown, derive an expression for the input resistance and the voltage gain as a function of the h-parameters and the resistors. (ii) Determine the input resistance and the voltage gain if ℎ𝑖𝑒 = 2 𝐾Ω, ℎ𝑓𝑒 = 200, ℎ𝑜𝑒 = 25 µ𝐴⁄𝑉, ℎ𝑟𝑒 = 2.5 × 10−4 , and 𝑅𝐶 = 𝑅𝐸 = 𝑅𝑆 = 1 𝐾Ω. Assume that 𝑽𝑻 = 𝟐𝟔 𝒎𝑽. Good luck... 3