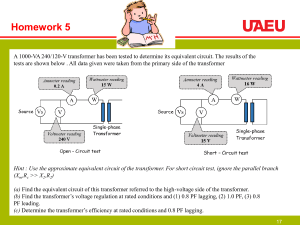
Internship Report SUBMITTED TO: RESIDENT ENGINEER AMJAD HUSSAIN SUBMITED BY MUHAMMAD YASIR KHALIL REGISTRATION # 15PWELE4807 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (POWER) STUDENT OF UET PESHAWAR INTERNSHIP AT PESHAWAR UNIVERSITY GRID STATION, DANISH ABAD PESHAWAR | CONTENTS 1) Introduction a) Power system b) Grid station c) Single line diagram 2) Switch Yard 3) Tower 4) Green Tree 5) Lightning arrester 6) Wave Trap 7) Line Isolator along with Earth Switch 8) Circuit Breaker a) Quenching Media b) Operating Media 9) Current Transformer: 10) Potential Transform: 11) Grounding: 12) Bus bar 13) Transformer Bay 14) Power transformer a) Core b) Winding c) Main Tank d) Conservator Tank e) Breather f) Buchholz’s Relay g) Cooling System h) Tape Changer i) Oil Drain Valve j) Oil Filter Valve 15) Relays 16) Capacitor Bank 17) Battery 1) Introduction: University Grid 132kV is located at Danish Abad Peshawar. It is powered by the following Four Transmission lines : PUN-1: Peshawar Cantt Grid JMR-2: Jamrud Grid Peshawar PIN-3: Small industrial Kohat Road Grid PUN-4: Sheikh Muhammad Grid a) Power system: The electrical system in which different systems are connected to transfer the power from the source to consumer. It is divided into Generation Transmission Distribution The electrical power is achieved by using different source of energy. Hydro Energy is the cheapest source of energy, so the turbine produces 11.5 kV or 6.6 kV at generation station. This voltage is step up to 500 kV to reduce the power losses. 500 kV is used as primary transmission then it step down to 220 kV which is known as secondary transmission then again step down to 132 kV which is known as primary distribution, 66 kV is also included in primary distribution but gradually it is obsoleting. This voltage is again step down to 11kV which is known as secondary distribution. b) Grid Station: Grid station is a place where many circuits are interconnect for the purpose of controlling and voltage regulations. c) Single Line Key Diagram: The grid system is consisting of 3 phase 3 wire system. We draw the circuit diagram of grid station for the purpose of studying the power flow and fault detection. If we draw the circuit diagram for many incoming and outgoing circuit so it will be very complicated for us to analyze. To remove complexity, we draw the circuit diagram as a single line diagram in which 3 phase 3 wire system is represented as a single line. We use symbols for different components, which is international accepted. The single line key diagram of University Grid station is given below. 2) Switch Yard: The region in which different components are physically connected for the sake of protection, controlling and distribution of Electrical power. The components which are used in switch yard is listed below. 3) Tower: Tower is a long stand like a Minar which carry the transmission line from one station to another. Towers are usually at free spaces like fields and not in towns to avoid hazards from magnetic field of high voltage transmission. Towers are triangular in shape having Shielding wire at top and transmission lines at its arms. Shield wire protect the tower from thunders and acts as a neutral wire. Towers have Insulation Discs which is at the end of one transmission line and beginning of adjacent transmission line. Discs provide insulation to tower as a result being a conductor, tower do not conduct high voltage to the ground. Each disc represents 11kv. Counting number of discs connected to a line will show the voltage across the respective transmission line. Transmission lines have vibrations due to high voltage across it or due to wind, to avoid such vibrations Damper weight / Balancing weight are use which result in regulation of vibrations. 4) Lightning / Surge Arrester: It provide voltage regulation to the system and keep constant voltage by removing the excess voltages which may occur due to thunder lightening. 5) Line Isolator along with Earth Switch: Line isolator along with earth switch helps in protection of the grid system. It isolates the grid electrical machinery from the input supply of 132kV during fault or tripping condition. Isolator work on no load. On full load it should not operate because high arc will produce which is dangers for human body ! 6) Circuit Breaker: Circuit breaker provide isolation to the grid station in case of tripping. The breaker operates on DC and DC is provided by DC System . It can operate in faulty condition means abnormal current or at full load or at no load because it has quenching media. At full load it produces arcs and this quenching media helps to absorb the arc. In 11kv circuit breakers we mostly use vacuum tube in which there is no flam produce in vacuum because of absences of oxygen. There is different type of circuit breakers like: Vacuum circuit breaker Air blast circuit breaker Oil filed circuit breaker Vacuum Cricuit Breaker SF6 circuit breaker. Due to high voltage there is a spark inside the circuit breaker. To absorb or eliminate the spark we use different quenching media such as SF6(Sulfur Hexa Flouride) Gas in modern circuit breakers while oil in old age breakers. 7) Current Transformer: Current transformer is used to step down the current. At University Grid station the CT ratio is 400/5 that means it convert 400 A to 5 A. Protection is very important for any high rated device. CT step down the current to 5A which is then use by different Relays as they operate on 5A only. CT helps in protection of the system through Relays. Through CT we measure the input and output current and we can detect the fault if incase occur through its readings or directly from Auxiliary panel of respected CT in control room. CT lies on each line. Use of current transformer is due to following reasons: a) Protection b) Measurement c) Metering 8) Potential Transformer: Potential Transformer converts 132 kV to 110 V which is then suitable for Bus Bar and other power cables to work on. Secondly for single common Bus Bar there will be only one PT while there could be many CTs depending upon circuits connected to bus bars. Use of potential transformer is due to following reasons: a) Protection b) Measurement c) Metering 9) Grounding: Earth is a protection element. Grounding provides a very low resistive path to the flow of high current in an abnormal condition. Each equipment is grounded in University grid station for safety and protection purpose and there is an earth mesh under the yard and the bodies of all devices are grounded on different points in the yard. And also each pole is grounded in the yard. The yard has floor made from crushed stone and sand. The following are the reason why we use ground like that : a) b) c) d) 10) In a Rainy day we can easily walk in the yard It has property of rigidity It is highly insulated material It has less chances of formation of standing water in rainy weather. Bus Bar: Bus Bar is a set of conductors in the grid station which energizes the transformers. Here in Uni Grid station the bus bar energizes four transformers but one of them is damaged and will repair by the company soon. The voltage on the bus bar is constant, here we have 132kV bus bar at the yard. Bus bar is perpendicular to the line bay. Bus Bar may be of 132Kv or 11Kv. 11) Transformer: Transformer comprises of following units. a) b) c) d) CT 132 kV circuit Breaker Lightening Arrester Power transformer We are familiar with the work of CT as it can step down the current from 400A to 5A so that the Relay woks with their rated current. Likewise, Circuit Breakers provide protection and act as a switch to disconnect the grid system when needed. Now sometime thunderstorm take place which are hazardous to whole system, to avoid the effects of Surge Voltages and Thunder voltage we use Lightening Arrester. Lightening Arrestor act as protection element for the Power transformer. 12) Power transformer: Power transformers at Uni Grid Station has an apparent power of 40 MVA, 31.5/40 MVA. At normal condition it can give us power approximately about 31.5MVA and if we turn ON the fans it can give us upto 40MVA. Power transformer works on the principle of Mutual Induction. There are various important parts of power transformer: a) Core: Core of transformer is made up of Ferromagnetic Material which has the property to get quickly magnetize and help in Quick Mutual Induction phenomena. b) Winding: There are two main important windings in Transformer, Primary and Secondary but sometime Tertiary winding is also present in auto transformer . c) Main Tank: Main tank contain core with windings and is filled of special type of Oil (Difloro Dichloro ethyl benzene) which act as a cooling reagent. The oil has latent heat of vaporization higher than any other liquids though less than water. We cannot use water as a cooling reagent because it has the ability to corrode the Core which made up of Pure Iron. d) Conservator Tank: This tank also contains Oil of similar nature and is at the top of Power Transformer. This tank provides additional oil to the Main tank when it is needed. Conservator tank is not fully filled, it has 30% free space in upper portion, which is filled with air by Breather when the oil from conservator tank moves to main tank. The above is the cross section of conservator tank. e) Breather: Breather is a tube which contain oil and Silica gel(SiO2). Silica gel is hygroscope agent which helpe in absorbing the moisture in air. Breather breathe the air when conservator tank provide oil to the main tank. This is due to low pressure at the top of conservator tank and air moves from outside to inside of Power Transformer. f) Buchholz’s Relay: Buchholz’s Relay is installed between main tank and conservator tank. It detect interior fault of the transformer. It operates when a bubble is formed inside the oils then it tries to evaporate and then the Buchholz relay perform its function and the bubble is captured by relay and if the size of the bubble is small then alarm operates and P&I team visits the grid and if the bubble is large then it trip the transformer and also alert the staff by alarm. g) Cooling System: There are two types of nature of Power transformer for cooling purpose. i. ii. Oil Nature Air Nature Oil is use as a cooling reagent whereas air is also use as cooling reagent. Oil is pass through pipes horizontally which is Cooling Fan known as radiators. Tubes are exposed to high power fans that create strong cool blow towards the pipes and cool the oil inside it. Cooling fans are on either side of the transformer in order to confirm the Radiator cooling nature of power transformer. h) Tape Changer: Tap Changer is a device which is used to change the turn ratio. usually we install the tap changer at primary side of the step down transformer (11kV) because primary side contain high voltage (132kV) but low current and 11kV at the secondary side of the power transformer. And it is controlled remotely from the control room .If it is doesn’t operate from the Control Room then we operate it from the tap changer panel at the transformer side if it fails then we operate manually by using a specific tool which is inside the tap changer panel. i) Oil Drain Valve(DN-80): It is also called bottom valve. It is used to extract water vapours from the main tank by connecting a dehydration plant and the oil of the main tank passes through the dehydration plant and it filters the oil by extracting the water vapours this phenomena is just like dialysis and it happens for 3 days. j) Oil Filter Valve(DN-40): It is used for testing purposes. When P&I team visits the grid stations they want to test the Quality of the Oil and Quantity of vapours in it. Using DN-40 they collect a sample of the transformer oil. Then they analyze the sample and perform the required operation. Relays: a) Buchholz’ Relay: Buchholz relay are of two types; Main Tank Buchholz Relay: Buchholz’s Relay is installed between main tank and conservator tank. It detect interior fault of the transformer. It operates when a bubble is formed inside the oils then it tries to evaporate and then the Buchholz relay perform its function and the bubble is captured by relay and if the size of the bubble is small then alarm operates and P&I team visits the grid and if the bubble is large then it trip the transformer and also alert the staff by alarm. Tap Changer Buchholz Relay: It detects the fault inside the housing (shell like) of the tap changer winding of the transformer. b) Impedence /Distance Relay: The relay whose working depends on the distance between the impedence of the faulty section and the position on which relay installed is known as the impedence relay or distance relay. It divides the distance in zones ie Zone 1: it operate on 85% area. It works in 20msec Zone 2: it operate on 130% area. It works in 0.75msec Zone 3: it operate on 150% area. It works in 0.35msec d) Differential Relay: It is installed between 132kV and 11Kv current transformer. When it detect the difference in current between 11kV and 132kV CT it operates. d)Over Current Relay: An overcurrent relay is a type of protective relay which operates when the load current exceeds a pickup value. It is of two types: Instantaneous over current (IOC) relay Definite time overcurrent (DTOC) relay e) Earth Fault relay: Earth Fault Relay (EFR) It is a safety device used in electrical installations with high earth impedance. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment. The result is to interrupt the circuit if a dangerous voltage is detected. Capacitor Bank: Capacitor Bank is for improving power Factor. Improving Power factor means reducing losses and reduce reactive power. It also decreases the load and provide Relief. Each Transformer has its capacitor Bank. Number of cells in capacitor bank depends upon the Power Rating of Transformer 13) Battery: 200KVAR Small Size cell Batteries are used to operate the DC system of the grid station because all the relay, panels and circuit breaker works on DC. If the DC fails then we have to shut down the grid station because we will not be in such a state to operate the grid station. then we will not tackle the fault as a result it may damage the grid station in faulty condition because the relays sense faults and 400KVAR then the circuit breaker operates and circuit breaker and Capacitor cell relays need DC supply. These batteries are rechargeable. They are charged by Battery charger which take three phase AC and Rectify it to 110 V DC. Batteries are connected in series to provide 110 V DC. The electrolyte use in these batteries is combination of Distillated water and sulphuric acid in ratio of 1 and 4 respectively. We have to check the specific Gravity every morning with Hydrometer. 1 cell produce 2 – 2.5 volts 110 volts we use 55 cells connected in series. Overall battery capacity is 150AH which means if we have 10A load we can supply power to it for 15 hours, non-stop or 150Amps for an hour continuously.