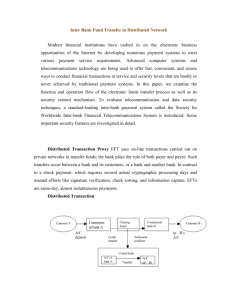
Acronyms 3DES (Triple Digital Encryption Standard) o Deprecated and considered insecure. Replaced by AES o Symmetric o Applies the DES cipher algorithm 3 times to each data block AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) o Often used to describe RADIUS, or some other form of networking protocol that provides Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting ABAC (Attribute-based Access Control) o Rights granted through policies that combine attributes together Active Directory o Database and identity service used to provide identity management ACL (Access Control List) o Set of rules that allow/permit or deny any traffic flow through routers o Looks at the packet to determine whether it should be allowed or denied o Works at layer 3 to provide security by filtering & controlling the flow of traffic from one router to another AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) o Industry-standard for data security o 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit (strongest) implementations AES256 (Advanced Encryption Standards 256bit) o This is the 256-bit implementation of AES o The 256 references the bit size of keys AH (Authentication Header) o Used to authenticate origins of packets of data transmitted o These headers don’t hide any data from attackers, but they do provide proof that the data packets are from a trusted source and that the data hasn’t been tampered with o Helps protect against replay attacks AI (Artificial Intelligence) o For the exam, be aware of what’s called data poisoning (or tainted training) & adversarial AI AIS (Automated Indicator Sharing) o DHS and CISA free program o Enables organizations to share and receive machine-readable cyber threat indicators (CTIs) and defensive measures (DMs) in real-time o Useful to monitor and defend networks against known threats ALE (Annualized Loss Expectancy) o i.e.: can expect x number of devices to fail per year AP (Access Point) o Networking hardware device that provides Wi-Fi access, typically then connected via wire to the router, or directly integrated in the router itself API (Application Programming Interface) o APIs are used to allow applications to talk to one another o For example: an application can query an API to retrieve data and then display that data or process it in some way APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) o Stealthy threat actor (usually nation-state or state-sponsored group) that gains unauthorized access to a system and remains undetected for a period of time ARO (Annualized Rate of Occurrence) o The calculated probability that a risk will occur in a given year ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) o Helps connect IP devices to MAC addresses ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomization) o Prevent exploitation of memory corruption vulnerabilities ASP (Active Server Page) o Microsoft server-side scripting language and engine to create dynamic web pages o Superseded by ASP.NET in 2002 ATT&CK Adversarial Tactics, Techniques, and Common Knowledge o Knowledge base framework of adversary tactics and techniques based on real-world observations o Helpful to build effective threat models and defenses against real threats AUP (Acceptable Use Policy) o Terms that users must accept in order to use a network, system, website, etc... AV (Antivirus) o Antivirus software o Typically uses signature-based detection o Not effective against zero-days or polymorphic malware BASH (Bourne Again Shell) o Powerful UNIX shell and command language o Used to issue commands that get executed, which can also be turned into shell scripts o Often used for automation BCP (Business Continuity Planning) o Plan used to create processes and systems of both prevention and recovery to deal with threats that a company faces o This plan outlines how a business can continue delivering products and services if crap hits the fan BIA (Business Impact Analysis) o Used to predict the consequences a business would face if there were to be a disruption BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) o "The postal service of the Internet" o BGP finds the best route for data to travel to reach its destination BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) o Firmware that performs hardware initialization when systems are booting up, and to provide runtime services for the OS and programs o First software to run when you power on a device BPA (Business Partnership Agreement) o Defines a contract between two or more parties as to how a business should run BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) o Frames that have spanning tree protocol information o Switches send BPDUs with a unique source MAC address to a multicast address with a destination MAC BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) o When employees use personal devices to connect to their organization’s networks and access work-related systems CA (Certificate Authority) o An organization that validates the identities of entities through cryptographic keys by issuing digital certificates o If you check the padlock on this website (next to the domain name), you'll see that it says "Connection is secure" and then you can click on "Certificate is valid" You'll then see info about how the certificate is "Issued to" and "Issued by" as well as the valid date range If you click on the "Certification Path" tab, you'll see that it says "DigiCert Baltimore Root" which is the issuer, aka the certificate authority CAC (Common Access Card) o Smart card for active-duty personnel CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart) o These are the “problems” you have to solve from time to time to make sure that you are not a robot o Typically used for forms (signup, login, purchase, search, etc...) to defend against bots CAR (Corrective Action Report) o Lists defects that need to be rectified CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker) o Acts as an intermediary between the cloud and on-prem o Monitors all activity o Enforces security policies CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) o CBC is a mode of operation for block ciphers o Block ciphers (for encryption) by themselves would only work for a single block of data…a mode of operation like CBC can be used to give instructions on how to apply encryption to multiple blocks of data o CBC helps prevent issues of identical blocks, even if you have identical inputs. It does that by using an operation called XOR (exclusive-OR) o o o o Each block gets XORed with the previous ciphertext before being encrypted (the first block uses an initialization vector, aka IV) CBC requires that blocks be processed in order, so you can’t parallelize encryption which means it runs slower than some of the other modes (i.e.: ECB) Think of CBC as building a chain from left to right CBC does have vulnerabilities, including POODLE and Goldendoodle CBT (Computer-based Training) o An online, self-paced, and interactive training system o Students can set their own goals and learn at their own pace CCMP (Counter-Mode/CBC-Mac Protocol) o Encryption protocol designed for Wireless LAN products CCTV (Closed-Circuit Television) o Camera monitoring system, especially one that transmits back to a centralized location with a limited number of monitors o Could be monitored by security personnel or simply set to record CERT (Computer Emergency Response Team) o Expert group that handles computer security incidents o Could also be called CSIRT CIRT (Computer Incident Response Team) o Same as above CFB (Cipher Feedback) o When a mode of operation uses the ciphertext from the previous block in the chain o i.e.: look up Cipher Feedback Mode (CFB) CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol) o Authenticates a user or network host to an authenticating entity o Provides protection against replay attacks o Requires that both the client and server know the plaintext of the secret, but it's never sent over the network CIO (Chief Information Officer) o Company executive responsible for implementing and managing IT o Mostly considered to be IT generalists o Useful way to think about it: CIO aims to improve processes within and for the company CTO (Chief Technology Officer) o CTO is different from CIO, and typically focuses on development, engineering, and research & development departments o Useful way to think about it: CTO uses technology to improve or create products and services for customers CSO (Chief Security Officer) o Executives that specialize in security o Much more focused of a responsibility than CIO CIS (Center for Internet Security) o Non-profit organization that helps put together, validate, and promote best practices to help people, businesses, and governments protect themselves against cyber threats CMS (Content Management System) o i.e.: WordPress COOP (Continuity of Operation Planning) o Effort for agencies to make sure they can continue operations during a wide range of emergencies o Requires planning for various types of events such as natural or human-caused disasters COPE (Corporate Owned Personal Enabled) o Organization provides its employees with mobile computing devices CP (Contingency Planning) o Used to restore systems and information in the event that systems become compromised CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) o Used to detect accidental changes in digital networks and storage devices CRL (Certificate Revocation List) o List of digital certificates that have been revoked by the issuing CA CSP (Cloud Service Provider) o i.e.: AWS, GCP, Azure CSR (Certificate Signing Request) o Contains information that the Certificate Authority (CA) will use to create your certificate o Contains the public key for which the certificate should be issued, and other identifying information CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) o Unauthorized actions are performed on behalf of a legitimate user CSU (Channel Service Unit) o Device used for digital links to transfer data CTM (Counter-Mode) o Converts a block cipher into a stream cipher o Combines an IV with a counter and uses the result to encrypt each plaintext block CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) o List of publicly disclosed computer security flaws o These security flaws get assigned a CVE ID number which people can use to reference them CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) o Public framework used to rate the severity of security vulnerabilities o i.e.: if you find a vulnerability as a bug bounty or in your own organization’s systems, and you report that vulnerability, assigning a CVSS number to it will help decision makers understand the severity and impact so that they can properly assign priority CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) o Employee can choose a company-assigned device from a limited number of options DAC (Discretionary Access Control) o Restrict access based on the identity of subjects and/or groups that they belong to DBA (Database Administrator) o Personal responsible for maintaining databases and the data that they contain DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) o An attacker that aims to take a service offline by flooding it with an overwhelming amount of requests from multiple different locations/devices… o …as opposed to DoS or Denial of Service attacks which are only sending requests from one location/device DEP (Data Execution Prevention) o Microsoft security feature o Monitor and protects pages or regions of memory o Prevents data regions from executing (potentially malicious) code DER (Distinguished Encoding Rules) DES (Digital Encryption Standard) DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) o Used to automatically assign IP addresses to devices on a network o DHCP doesn’t include security features by default, which means that attackers can leverage it to launch attacks o Two examples of DHCP attacks include: DHCP starvation which causes a Denial of Service DHCP spoofing which leads to on-path attacks o To prevent attacks, we can use : Authenticated DHCP - This approach replaces the normal DHCP messages with authenticated messages. From then on, clients and servers check the authentication information and reject any messages that come from invalid sources We can also use something called Port Security, which limits the number of MAC addresses that can be seen through a particular switch interface. If the switch sees a large number of new MAC addresses being sent through that interface, then it can automatically block connections to prevent an attack. DHE (Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral) o Way of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over public channels DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) o Email authentication technique - applies signatures by the mail server of the sender’s domain o Used to detect email spoofing (someone pretending to send email from an organization they don’t belong to). Can help protect against certain phishing attempts o Allows the receiver to make sure that an email was sent by the authorized owner of that domain via digital signatures o This is different from S/MIME because S/MIME signatures are used to verify the actual sender and not just the domain being used o DKIM does not offer encryption of the email o DKIM and S/MIME can be used together, but typically S/MIME is regarded as a better proof of sender, so if you had to use just one, it should be S/MIME DLL (Dynamic Link Library) o Library that contains code and data that can be used by programs to function in Windows o DLL injections can run malicious code within an application by exploiting DLLs DLP (Data Loss Prevention) o DLP is about detecting and preventing data breaches, exfiltration, or any other unwanted destruction of sensitive business data o DLP can include both tools and processes, since there is software specifically designed for DLP DMARC (Domain Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance) o Authenticates emails with SPF and DKIM o Used to prevent phishing and spoofing o Weak encryption algorithm DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) or Screened subnet o Designed to expose externally-facing services to the Internet without unnecessarily exposing resources in internal networks o You may have resources that have to be exposed to the Internet, but rather than open up the internal LAN, we can create a separate network specifically for those resources and then add firewalls in between the networks DNAT (Destination Network Address Transaction) DNS (Domain Name Service (Server)) o DNS is the phonebook of the Internet o Whenever you type in a domain name in your browser (i.e.: cybr.com) DNS gets used to figure out where to route your request DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) o Provides cryptographic authentication of data, authenticated denial of existence, and data integrity DoS (Denial of Service) o Denial of Service is any type of attack that aims to prevent normal operations o For example, if someone purposefully overwhelms a website to prevent real users from accessing it, that is a form of DoS DPO (Data Privacy Officer) o A DPO is a role/person responsible for protecting an organization’s data DRP (Disaster Recovery Plan) o A DRP is a formal document created by an organization to detail instructions how it should respond to unplanned incidents (natural disasters, cyber-attacks, power outages, terrorist attacks, etc) DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) o A public-key algorithm that’s used for generation and verification of digital signatures DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) o o DSL transmits data over telephone lines This was a common method of getting internet access before cable/fiber EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) o Authentication framework used in LANs ECB (Electronic Code Book) o Doesn't hide data patterns well, so it wouldn't work to encrypt images for example ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography) o Good for mobile devices because it can use smaller keys ECDHE (Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral) o Key exchange mechanism based on elliptic curves o Cloudflare uses this, for example ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) o Digital signature algorithm based on elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) o What's the difference between this and ECDHE? EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) o Technology that continuously monitors endpoints to mitigate cyber threats EFS (Encrypted File System) o EFS on Windows provides filesystem-level encryption o This helps protect data from attackers who have physical access to the drives EOL (End of Life) o Date set where manufacturer will no longer create the product EOS (End of Service) o Original manufacturer no longer offers updates, support, or service ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) o Software used by orgs to manage day-to-day business activities ESN (Electronic Serial Number) o Electronic serial numbers were created by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to uniquely identify mobile devices, from the days of AMPS in the United States starting in the early 1980s. ESP (Encapsulated Security Payload) o Member of IPsec set of protocols o Encrypts and authenticates packets of data between computers using VPNs FACL (File System Access Control List) FDE (Full Disk Encryption) FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) o Integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or designer after manufacturing FRR (False Rejection Rate) o Likelihood that a biometric security system will incorrectly reject an access attempt by an authorized user FTP (File Transfer Protocol) FTPS (Secured File Transfer Protocol) GCM (Galois Counter Mode) o High speeds with low cost and low latency o Provides authenticated encryption GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) GPG (Gnu Privacy Guard) GPO (Group Policy Object) o Contains two nodes: a user configuration and computer configuration o Collection of group policy setting GPS (Global Positioning System) GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) o Tunneling protocol HA (High Availability) HDD (Hard Disk Drive) HIDS (Host-Based Intrusion Detection System) o Detects and alerts upon detecting an intrusion in a host (such as computers) as well as network packets in network interfaces (similar to NIDS) o Can't take action on it, though HIPS (Host-Based Intrusion Prevention System) o Like HIDS, but can take action toward mitigating a detected threat HMAC (Hashed Message Authentication Code) o Combines a shared secret key with hashing o Can be used to verify data integrity and authenticity of a message HOTP (HMAC based One Time Password) o One-time password algorithm based on hash-based message authentication codes o Event-based OTP (One-Time Password) o Yubikey is an example of an OTP generator that uses HOTP o Not time based (has a longer window before expiration) HSM (Hardware Security Module) o Physical device that safeguards and manages digital keys (i.e.: private CA keys) o Performs encryption/decryption functions for digital signatures HTML (HyperText Markup Language) HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol over SSL/TLS) HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning) IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) o Used by network devices (such as routers) to send error messages or other operational information indicating success/failure when communicating with another IP address ICS (Industrial Control Systems) o General term to describe control systems associated with industrial processes IDEA (International Data Encryption Algorithm) o Symmetric-key block cipher IDF (Intermediate Distribution Frame) o Cable rack in a central office that cross connects and manages IT or telecom cabling between a main distribution frame (MDF) and remote workstation devices o Used for WAN and LAN environments, for example IdP (Identity Provider) o Service that stores and manages digital identities o Provides authentication services to apps within a federation or distributed network o User authentication as a service o i.e.: Google, Facebook, or Twitter login IDS (Intrusion Detection System) IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) IKE (Internet Key Exchange) o UDP port 500 o Protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite IM (Instant Messaging) IMAP4 (Internet Message Access Protocol v4) o API that enables email programs to access the mail server o i.e.: Outlook can be configured to retrieve email via IMAP4 (or POP3 as an alternative) IoC (Indicators of Compromise) o Forensic data found in systems via log entries or files that identify potentially malicious activity on a system or network IoT (Internet of Things) IP (Internet Protocol) IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) o In the Internet Layer of the TCP/IP Stack o Secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts the packets of data to provide encrypted communication o Used in VPNs o Can be used to protect data flows between two hosts (host-to-host), two networks (network-tonetwork) or between a security gateway and host (network-to-host) o Protects against replays IR (Incident Response) IRC (Internet Relay Chat) IRP (Incident Response Plan) o Preparation o Detection & Analysis o Containment, Eradication, and Recovery o Post-Incident Activity ISO (International Organization for Standardization) o Organization that develops and published International Standards ISP (Internet Service Provider) ISSO (Information Systems Security Officer) ITCP (IT Contingency Plan) o Plans, policies, procedures, and technical measures that enable the recovery of IT operations after unexpected incidents IV (Initialization Vector) o Used in cryptography is an input to a cryptographic primitive o Used to provide the initial state KDC (Key Distribution Center) o Used to reduce risks in exchanging keys o A user requests to use a service. The KDC will use cryptographic techniques to authenticate requesting users as themselves, and it will check whether a user has the right to access the service requested o If the user has the right, the KDC can issue a ticket permitting access KEK (Key Encryption Key) o A key that encrypts another key for transmission or storage L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) o Used to support VPNs or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs o Uses encryption only for its own control messages, not for content itself o Uses IPSec for data encryption over Layer 3 LAN (Local Area Network) LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) o o o Open and vendor-neutral application protocol for managing and interacting with directory servers Often used for authentication and storing information about users, groups, and applications Can be susceptible to LDAP Injections LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) o Wireless LAN authentication method o Dynamic WEP keys and mutual authentication (b/t a wireless client and a RADIUS server) MaaS (Monitoring as a Service) MAC (Mandatory Access Control) o Access control used to limit access to resources based on the sensitivity of the information that the resource contains and the authorization of the user o Uses labels which are made up of a security level and zero or more security categories o Security levels indicate a level or hierarchical classification of the information (ie: "confidential" or "restricted") o Security categories define the category or group to which the information belongs o If the user does not have the proper label for a piece of information, they cannot access it MAC (Media Access Control) MAC (Message Authentication Code) o Authenticates the source of a message and its integrity o Piece of information used to authenticate a message and make sure it came from the intended sender without any unintended modifications o o o MAM (Mobile Application Management) Used to control enterprise applications and app data on end users' devices Provides application-level control to IT admins Different from MDM because MDM aims to control the entire mobile device and requires a service agent to be running on the mobile device. MAM instead focuses purely on apps and their data o Functionality includes: Control the installation, updating, or removal of mobile apps via an enterprise app store Remotely wipe data from managed apps Monitor application usage Control user and group access Control user authentication MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) o Computer network larger than a single building MBR (Master Boot Record) o Special type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned storage o Holds information about how logical partitions are organized MD5 (Message Digest 5) o Hash function that can very easily be cracked MDF (Main Distribution Frame) MDM (Mobile Device Management) o Software that allows administration of devices as a whole o Different from MAM because MAM focuses on specific applications, while MDM focuses on controlling entire devices MFA (Multifactor Authentication) MFD (Multi-Function Device) o Device that incorporates the functionality of multiple other devices MFP (Multi-Function Printer) o Also includes fax, scanning, copy, etc... MITM (Man in the Middle) o Attacker interrupts a data transfer to eavesdrop o AKA on-path attacks ML (Machine Learning) MMS (Multimedia Message Service) o Used to send messages that include multimedia content MOA (Memorandum of Agreement) o Legally-binding agreement between two parties MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) o Non-legally binding agreement o Used to signal willingness between parties to move forward with a contract MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) o Routing technique to direct data from one note to the next based on the short path labels o MSA (Measurement Systems Analysis) Mathematical method of determining the amount of variation that exists within a measurement process MSCHAP (Microsoft Challenge Handshake) o Encrypted authentication used in a wide area network (WAN) o Authentication Protocol MSP (Managed Service Provider) MSSP (Managed Security Service Provider) MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) o Predicted time in between failures of a system MTTF (Mean Time to Failure) o Used to predict when a system will fail (and can't be repaired) MTTR (Mean Time to Recover) o Aka mean time to restore o Average time it takes to recover from a system failure MTTR (Mean Time to Repair) o Represents the average time it takes to repair a system o MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) Largest packet or frame size that can be sent in a packet or frame-based network such as the Internet NAC (Network Access Control) o Provides visibility, access control, and compliance o Can define and implement strict access management controls for networks o Centralized solution to end-point security o Uses IEEE 802.1X standard o Usually works with TACACS or RADIUS to verify authentication NAS (Network Attached Storage) NAT (Network Address Translation) NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement) NFC (Near Field Communication) o Mobile payment o Key cards o Smart cards NFV (Network Functions Virtualization) o Virtualizes entire classes of network node functions into building blocks NIC (Network Interface Card) NIDS (Network Based Intrusion Detection System) o Detects malicious traffic on a network NIPS (Network Based Intrusion Prevention System) o Detects and prevents malicious traffic on a network NIST (National Institute of Standards & Technology) NTFS (New Technology File System) Used by Windows NT to store, organize, and find files on an HD efficiently - NTLM (New Technology LAN Manager) Used to authenticate user identity and protect the integrity and confidentiality of their activity SSO tool Relies on a challenge-response protocol to confirm the user without requiring them to submit a password NTLM has known vulnerabilities and is typically only still used for legacy clients and server Replaced by Kerberos NTLM relies on a three-way handshake between the client and server to authenticate a user, while Kerberos uses a two-part process that leverages a ticket granting service or key distribution center (KDC) NTP (Network Time Protocol) o o Port 123 (UDP) Sync time OAuth (Open Authorization) o Token-based authentication o Lets an organizations share info across third-party services without exposing their users' usernames/passwords OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol) o Used by CAs to check the revocation status of an X.509 digital certificate OID (Object Identifier) o Standard for naming any object, concept, or thing OS (Operating System) OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) o Conceptual model OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) o Distributes routing information between routers OT (Operational Technology) o Hardware/software that detects or causes a change by directly monitoring and/or controlling industrial equipment, assets, processes, and events OTA (Over The Air) o Pushing updates for software, configuration settings, or even encryption keys, on remote devices OTG (On The Go) OVAL (Open Vulnerability Assessment Language) o Community standard to promote open and publicly available security content, and to standardize the transfer of this information OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) o o o P12 (PKCS #12) Archive file format for storing cryptography objects as a single file Used to bundle a private key with its X.509 certificate, or to bundle the members of a chain of trust Think of it as a container for X.509 public key certs, private keys, CRLs, and generic data P2P (Peer to Peer) PaaS (Platform as a Service) o o PAC (Proxy Auto Configuration) Used to define how web browsers and other user agents can automatically choose the appropriate proxy server for fetching URLs Contains a JavaScript function that returns a string with one or more access method specifications PAM (Privileged Access Management) o Safeguarding identities with special access or admin capabilities PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) o Used to separate the tasks of authentication from applications o Apps can call PAM libraries to check permissions PAP (Password Authentication Protocol) o Two-way handshake to provide the peer system with a simple method to establish its identity PAT (Port Address Translation) PBKDF2 (Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2) o Key derivation functions with a sliding computation cost, which is used to reduce vulnerabilities of brute-force attacks o Applies a pseudorandom function (like HMAC) to the input password along with a salt value, and repeats this process multiple times to produce a derived key o Derived key can then be used as a cryptographic key PBX (Private Branch Exchange) o Telephone system that switches calls between users on local line o Multiline telephone system PCAP (Packet Capture) o Collects and records packet data from a network which can then be analyzed o PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) Security standards to use when accepting, processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information PDU (Power Distribution Unit) o Provides multiple electric power outputs PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol) o Provides a method to transport securely authenticated data including legacy password-based protocols, via 802.11 Wi-Fi o Uses tunneling between PEAP clients and an auth server PED (Personal Electronic Device) o Devices like phones, laptops, pagers, radios, etc.. PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) o File format for storing and sending cryptographic keys, certificates, and other data o For example, when using SSH, you will often use a .pem file o Encodes the binary data using base64 o Starts with -----BEGIN a label and then ----PFS (Perfect Forward Secrecy) o Feature of specific key agreement protocols that give assurances that session keys will not be compromised, even if long-term secrets used in the session key exchange are compromised o i.e.: for HTTPS, the long-term secret is usually the private key of the server PFX (Personal Information Exchange) o o PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) Encryption program used to provide cryptographic privacy and authentication for data communication Useful for signing, encrypting, and decrypting texts, e-mails, files, directories, and whole disk partitions PHI (Personal Health Information) PII (Personally Identifiable Information) PIV (Personal Identity Verification) o MFA on a smartcard o Used for identity proofing PKCS (Public-Key Cryptography Standards) o Group of standards for public keys PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) o Roles, policies, hardware, software, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption o POP (Post Office Protocol) Most commonly used message request protocol for transferring messages from e-mail servers to e-mail clients POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service) PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) o Communication between two routers directly without any hosts or other networks in between o Data Link Layer PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) o Obsolete method of implementing virtual private networks o Port 1723 PSK (Pre-Shared Key) o Shared secrets sent using a secure channel before it needs to be used PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) o Camera that can be remotely controlled, including zoom and directional control QA (Quality Assurance) QoS (Quality of Service) o Performance of systems by the users of the network/systems PUP (Potentially Unwanted Program) RA (Recovery Agent) RA (Registration Authority) RACE (Research and Development in Advanced Communications Technologies in Europe) RAD (Rapid Application Development) o Agile software development approach o Focuses on ongoing software projects and user feedback and less on following a strict plan o Emphasizes rapid prototyping over costly planning RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in User Serve) o Provides centralized authentication to protect networks against unauthorized use o Could also be used for device administration, but its primary purpose is network authentication o Combines authentication and authorization o Encrypts only the password field, not the entire packet. o o o o o RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) Storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units Used to increase data redundancy, performance, or both Striping - spreads blocks of data across multiple disks. Great for increased performance but provides zero data redundancy or protection Mirroring - copies the same data across disks. Provides data redundancy and protection from failure, but requires more disks which increases cost Parity - calculated value that gets used to restore data from multiple drives if one of the drives were to fail. This prevents the need to mirror using separate drives since parity is spread among disks. RAID 0 - striping o Needs 2 drives minimum RAID 1 - mirroring o Needs 2 drives minimum RAID 4 - striping and parity o Needs 3 drives minimum RAID 5 - striping and parity o Needs 3 drives minimum RAID 6 - striping and parity o Needs 4 drives minimum RAM (Random Access Memory) RAS (Remote Access Server) RAT (Remote Access Trojan) o Malware that gives the attacker admin control over the target computer o Typically used to then take further action RBAC (Role-based access control) o Used to assign rights and permissions based on roles of users o Roles are usually assigned by groups RC4 (Rivest Cipher version 4) o Insecure o WEP RCS (Rich Communication Services) RFC (Request for Comments) RFID (Radio Frequency Identifier) o Uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects o Consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver, and a transmitter o Made up of tags and readers RIPEMD RACE Integrity Primitives o Family of hash functions Evaluation Message Digest o Helps guarantee a low number of collisions ROI (Return on Investment) RPO (Recovery Point Objective) o The maximum amount of data (measured by time) that can be lost after a recovery from a disaster or failure o Used to determine the frequency of backups o ie: if an RPO is 70 minutes, you require system backups every 70 minutes RSA (Rivest, Shamir, & Adleman) o Algorithm used to encrypt and decrypt messages (public-key cryptosystem) o Asymmetric...the public key can be known to everyone o Messages encrypted using the public key can only be decrypted with the private key o Slower than some RTBH (Remote Triggered Black Hole) o Can be used to drop traffic before it enters a protected network o A common use is to mitigate DDoS RTO (Recovery Time Objective) o Max amount of time it can take to recover after a failure or disaster before the business is significantly impacted RTOS (Real-Time Operating System) o Event-driven and preemptive o Switches between tasks based on their priorities (event-driven) or on a regular clocked interrupts and on events (time-sharing) RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) o Used to transfer audio/video over IP networks o Streaming media, for example S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) o Provides a way to integrate public-key encryption and digital signatures into most modern email clients. o This would encrypt all email information from client to client, regardless of the communication used between email servers SaaS (Software as a Service) SAE (Simultaneous Authentication of Equals) o Secure password-based authentication and password-authenticated key agreement method SAML (Security Assertions Markup Language) o XML-based markup language for security assertions o Allows an IdP to authenticate users and then pass an auth token to another application (service provider) SAN (Storage Area Network) o Dedicated, independent high-speed network that interconnects and delivers shared pools of storage devices to multiple servers SAN (Subject Alternative Name) o Extension to X.509 that allows various values to be associated with a security certificate SCADA (System Control and Data Acquisition) o Control system for high-level supervision of machines and processes SCAP (Security Content Automation Protocol) SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) o Makes the request and issuing of digital certificates as simple as possible SDK (Software Development Kit) o Collection of software development tools you can install in one package SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle) SDLM (Software Development Life-cycle Methodology) SDN (Software Defined Networking) o Makes networking a bit more like cloud computing than traditional network management by defining network technology via software SDV (Software Defined Visibility) o Framework that allows customers, security and network equipment vendors, as well as MSPs, to control and program Gigamon's Visibility Fabric via REST-based APIs SED (Self-Encrypting Drives) o Data gets encrypted as it gets added to disk (HDD and SSD) SEH (Structured Exception Handler) o A way of handling both software and hardware exceptions/failures gracefully SFTP (Secured File Transfer Protocol) SHA (Secure Hashing Algorithm) o One-way functions SHTTP (Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol) o Obsolete alternative to HTTPS SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) o SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) Used to initiate, maintain, and terminate real-time sessions that include voice, video, and messaging apps SLA (Service Level Agreement) SLE (Single Loss Expectancy) o Monetary value of an asset o % of loss for each realized threat S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Exchanger) o Widely accepted protocol for sending digitally signed and encrypted messages SMS (Short Message Service) SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) o Protocol for electronic mail SMTPS (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure) SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) o Networking protocols used for the management and monitoring of network-connected devices in IP networks SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) o Lightweight XML-based protocol that's used for exchanging information in decentralized, distributed application environments o Versus REST, which mostly uses JSON SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, Response) o Technologies that enable orgs to collect inputs monitored by the security operations team o i.e.: alerts from the SIEM and other security tech where incident analysis and triage can be performed by leveraging a combination of human and machine power SoC (System on Chip) o Raspberry Pi is an example of SoC o Multiple components running on a single chip SOC (Security Operations Center) SPF (Sender Policy Framework) o Email-authentication technique which is used to prevent spammers from sending messages on behalf of your domain SPIM (Spam over Internet Messaging) SQL (Structured Query Language) o SQL is used to communicate with SQL databases in order to create, read, update, or delete data SQLi (SQL Injection) o SQL injections are a type of web-based attack that target SQL databases to either extract data, insert data, modify database settings, or — in extreme cases — take control of the host server SRTP (Secure Real-Time Protocol) o Provides encryption, message authentication and integrity, and replay attack protection to the RTP data SSD (Solid State Drive) o Physical storage device comparable to hard drives but that uses different technology SSH (Secure Shell) SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) SSO (Single Sign-On) STIX (Structured Threat Information eXchange) o XML structured language for sharing threat intelligence o Like TAXII, STIX is a community-driven project STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) SWG (Secure Web Gateway) o Protects users from web-based threads and applies and enforces corporate acceptable use policies o Instead of connecting directly to a website, the user accesses the SWG, which then connects the user to the desired website o This helps with URL filtering, web visibility, malicious content inspection, web access controls, and more TACACS+ o Authentication protocol used for remote communication with any server in a UNIX network or terminals o Uses allow/deny mechanisms with auth keys that correspond to usernames and passwords o Primarily used for device administration, but can technically be used for some network management o Encrypts the entire packet o Separates authentication and authorization o Port 49 TAXII (Trusted Automated eXchange of Indicator Information) o Aims to enable robust, secure, and high-volume exchanges of cyber threat information TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket) o Files created by the key distribution center (KDC) portion of the Kerberos authentication protocol o Used to grant users access to network resources o Once the user has the TGT, they use it to obtain a service ticket from the Ticket Granting Service (TGS), at which point the user is granted access TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) o Security protocol used in IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard TLS (Transport Layer Security) o Successor of deprecated SSL o Provides secure communications TOTP (Time-based One Time Password) o String of dynamic digits of code who change values based on time o Used for MFA TPM (Trusted Platform Module) o Dedicated microcontroller/chip designed to secure hardware with integrated crypto keys TSIG (Transaction Signature) o Computer-networking protocol, primarily enables DNS to authenticate updates to a DNS database TTP (Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures) o Behaviors, methods, tools, and strategies that cyber threat actors and hackers use to plan and execute cyber attacks on business networks UAT (User Acceptance Testing) o Last phase of the software testing process o Actual software users test the software to make sure it can handle necessary, real-world tasks and scenarios, according to specifications o Aka User Acceptability Testing or End-User testing UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) UDP (User Datagram Protocol) UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) o Specification that defines a software interface between an OS and platform firmware o Replaces the legacy BIOS firmware interface, but provides legacy BIOS services o UEFI can support remote diagnostics and repair of computers, even if no OS is installed UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) o Allows you to manage, secure, and deploy resources and apps on any device from a single console o Goes beyond just MDM since it can also control PCs, or IoT devices, for example UPS (Uninterruptable Power Supply) o Provides an emergency power to a load in the event of power failure URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) o Identifier for a specific resource URL (Universal Resource Locator) o All URLs are URIs, but not all URIs are URLs o If the protocol (http, https, ftp, etc) is present or implied, then it's a URL USB (Universal Serial Bus) USB OTG (USB On The Go) o Allows USB devices to act as a host, allowing other USB devices to attack to them o o Those devices can then switch back and forth between the roles of host and device For example, a phone may read from the removal media as the host, but then act as a mass storage device UTM (Unified Threat Management) o When a single hardware or software provides multiple security functions o This is in contrast of having individual solutions for each security function UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) VBA (Visual Basic) o Event-driven programming language from Microsoft VDE (Virtual Desktop Environment) VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) o When the desktop and application software is separated from the hardware VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) o A partitioned and isolated part of a LAN created with logic (not physical separation) VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) o A design where subnets can have varying sizes VM (Virtual Machine) VoIP (Voice over IP) o Voice communications over Internet Protocol networks VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) o On-demand pool of shared resources in a public cloud environment o Provides isolation between organization and resources o Lets you essentially carve out a piece of the public cloud to host your private resources VPN (Virtual Private Network) o Encrypted connection over the Internet from a device to a network o Helps ensure that you can communicate with remote systems securely and prevents eavesdropping on the traffic VTC (Video Teleconferencing) WAF (Web Application Firewall) o A WAF, or Web Application Firewall, is often placed in front of web apps and APIs to help defend against common attacks (like DDoS, XSS, SQL injections, etc) o This is not a silver bullet and can oftentimes be bypassed by skilled attacks o It can also only really defend web apps and APIs, not things like internal networks WAP (Wireless Access Point) o Allows other Wi-Fi devices to connect to a wired network WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) o Security protocol that used to be used until it was found that it was inadequate WIDS (Wireless Intrusion Detection System) o Can detect the presence of unauthorized access points and create alerts o They can also identify network break-in attempts WIPS (Wireless Intrusion Prevention System) o Can detect the presence of unauthorized access points and automatically take action such as quarantining devices or kicking them off networks WORM (Write Once Read Many) o Data storage device where information, once written, can't be modified o Great to ensure the data doesn't get tampered with WPA (WiFi Protected Access) o Designed to be more secure than WEP o WPA vs WPA2 WPA uses TKIP, while WPA2 can use TKIP or AES (which is usually preferred) WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) o Flawed security mechanism used for routers - can be brute forced WTLS (Wireless TLS) o Security level for WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) apps XaaS (Anything as a Service) o Term used to describe anything that can be used or sold as a service. For example, you can have Database as a Service (DaaS), Authentication as a Service (AaaS), etc… XML (Extensible Markup Language) o XML is markup language, kind of like HTML (take a look at some examples on Google) o XML has vulnerabilities that can be exploited, such as with XXE XOR (Exclusive Or) o Logical operator that returns true (represented by a 1) if its arguments are different (ie: one argument is 0 and the other is 1) o If the arguments are the same, then XOR returns a 0 XSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) o Same as CSRF XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) o XSS, or Cross-Site Scripting is a type of web-based attack X.509 o Standard defining the format of public-key certificates 802.1X o Network authentication protocol o Defines the standards for using EAP to authenticate clients through authenticators (router/switch/network device), using an authentication server (such as RADIUS) o Devices/users connecting need to provide credentials and prove their identity to get access to the network o Usually authenticated by AD, RADIUS