Trouble shooting flow chart
Feb 2016
Contents
› Accessibility (blocked call troubleshooting)
– signaling connection setup
– RRC (Radio Resource Control) Connection setup
›
›
›
›
›
mp load
admission control
licensed capacity
node blocking
transport network blocking
– RAB (radio access bearer) establishment
›
›
›
›
node blocking
transport blocking
utran
congestion
-
dl power
code
ase
hardware resources
connection limit
› hardware fault
› retainability (dropped call troubleshooting)
– Retainability counters
Accessibility (blocked call troubleshooting)
Blocked Call Troubleshooting
CS/PS
Accessibility
RRC
RAB
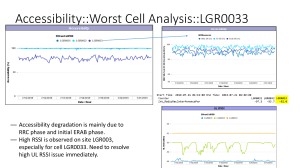
Blocked calls and problems in Accessibility are occurring either due to problems in RRC (Radio
Resource Control) Connection or due to problems with establishment of RAB (Radio Access
Bearer). Accessibility problems also may occur due to Signaling Connection Setup which is
performed before RRC and RAB procedures and due to failures after Admission (after RRC
Connection and RAB Establishment procedures).
3 (40)
Accessibility >
Signaling Connection setup
› Signaling Connection Setup is a procedure of successful or
unsuccessful attempt to set up an Iu connection. Iu connection is the
interface between the RNC and Circuit-Switched (CS) or PacketSwitched (PS) Core Network.
› Main counters for this procedure are:
pmNoIuSigEstablishAttemptCs: Number of Iu signaling connection setup attempts towards the CS
domain. This counter is incremented by one on reception of an RRC Initial Direct Transfer for the CS CN
from a UE, when no signaling connection to the CS CN exists.
pmNoIuSigEstablishAttemptPs: Number of Iu signaling connection setup attempts towards the PS
domain. This counter is incremented by one on reception of an RRC Initial Direct Transfer for the PS CN
from a UE, when no signaling connection to the PS CN exists.
pmNoIuSigEstablishSuccessCs: Number of successful Iu signaling connection setups towards the CS
domain. This counter is incremented by one on reception of an SCCP Connection Confirm from the CS CN,
indicating successful establishment of an Iu signaling connection towards the CS CN.
pmNoIuSigEstablishSuccessPs: Number of successful Iu signaling connection setups towards the PS
domain. This counter is incremented by one on reception of an SCCP Connection Confirm from the PS CN,
indicating successful establishment of an Iu signaling connection towards the PS CN.
4 (40)
Accessibility >
RRC (Radio Resource Control)
Connection setup
5 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
RRC connection setup - ps
› RRC Connection Setup procedure describes successful or unsuccessful attempt to
setup an RRC connection for an originating or terminating packet-switched call
› Main counters relevant for this procedure are:
pmTotNoRrcReq
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSucc
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqPsSucc
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqSucc
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqPsSucc
pmTotNoUtranRejRrcConnReq
pmNoReqDeniedAdm
pmNoRrcPsReqDeniedAdm
pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnPs
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlChnlCode
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmUlHw
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockNodePs
pmTotNoRrcConnectUeCapability
6 (40)
pmTotNoRrcConnectReq
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqPs
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReq
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqPs
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSubTr
pmNoRejRrcConnMpLoadC
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdm
pmNoLoadSharingRrcConn
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlPwr
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlHw
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockTnPs
pmTotNoRrcConnectSetup
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
RRC CONNECTION SETUP - cs
› This procedure describes successful or unsuccessful attempt to set up an RRC
connection for an originating or terminating circuit-switched call.
› Main counters relevant for this procedure are:
pmTotNoRrcReq
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSuccess
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqCsSucc
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqSucc
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqCsSucc
pmTotNoUtranRejRrcConnReq
pmNoReqDeniedAdm
pmNoRrcCsReqDeniedAdm
pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnCs
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlChnlCode
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmUlHw
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockNodeCs
pmTotNoRrcConnectUeCapability
7 (40)
pmTotNoRrcConnectReq
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqCs
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReq
pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqCs
pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSubTr
pmNoRejRrcConnMpLoadC
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdm
pmNoLoadSharingRrcConn
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlPwr
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlHw
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockTnCs
pmTotNoRrcConnectSetup
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
RRC connection setup – total counters
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReq: Total number of RRC Connection Requests. This counter is incremented by one when a
RRC Connection Request message is received by RNC from UE for ANY Establishment Cause. Note: The counter is
always incremented in the SRNC for the UE and incremented once per connection. Subsequent retransmissions are not
counted.
› pmTotNoRrcReq: Total number of RRC Requests received during the ROP, including repetitions.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReq: Number of mobile terminating RRC connection attempts.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqPs: Number of mobile terminating Interactive & Background RRC connection attempts.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqCs: Number of mobile terminating conversational RRC connection attempts.
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSubTr: Number of RRC Connection Requests with Establishment Cause 'originating
subscribed traffic call'.
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqPs: Total number of Interactive and Background (Originating & Terminating) RRC Connection
attempts
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqCs: Total number of Conversational Call (Originating & Terminating) and Emergency Call
RRC Connection attempts
› pmTotNoRrcConnectSetup: Total number of RRC Connection Setup messages sent to UEs, not including repetitions.
› pmTotNoUtranRejRrcConnReq: Total number of UTRAN rejected RRC Connection Requests. This counter is
incremented by one when an RRC Connection Request is received and a connection setup to the RBS fails due to the
following reasons:
- no internal UE identity is available in the RNC
- MP load control function
- Admission Control function does not grant permission to proceed
- any internal parameter retrieving or calculations fail
- a downlink channelization code fails to be allocated
Note: The counter is not incremented if there is inter-frequency load sharing.
8 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
RRC connection setup – total counters
› pmTotNoRrcConnectUeCapability: Number of times that a UE with certain capabilities has successfully setup an RRC
connection.
The individual counter elements are stepped based on the following UE capabilities:
[0] : A-GPS positioning support
[1] : HS-DSCH support, all UE categories
[2] : HS-DSCH 10 and 15 codes support, UE category 7-10 and 13-18
[3] : HS-DSCH 64 QAM support, UE category 13-14
[4] : HS-DSCH MIMO support, UE category 15-16
[5] : HS-DSCH MIMO and 64 QAM support (not simultaneously), UE category 17-18
[6] : HS-DSCH MIMO and 64 QAM support (simultaneously), UE category 19-20
[7] : E-DCH support, all UE categories
[8] : E-DCH support 2ms TTI, UE category 2, 4, 6 and 7
[9] : E-DCH 16 QAM support, UE category 7
Condition:
An individual counter element is incremented by one when an RRC Connection Setup Complete message has been
received with cause Conversational (originating or terminating), Emergency, Subscribed, Interactive (originating or
terminating), or Background (originating or terminating), if the UE capabilities received in the message are the same as
those for that counter element.
9 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
RRC connection setup – total counters
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqSuccess: Total number of successful RRC Connection Requests. This counter is
incremented by one after both the NBAP Radio Link Restore Indication message and the RRC Connection Setup
Complete message have been received by the RNC, indicating that the RRC connection is considered to be successfully
established.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqSucc: Number of successful mobile terminating RRC connections.
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqPsSucc: Total number of successful Interactive and Background (Originating & Terminating)
RRC Connection attempts.
› pmTotNoRrcConnectReqCsSucc: Total number of successful Conversational Call (Originating & Terminating) and
Emergency Call RRC Connection attempts.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqPsSucc: Number of successful mobile terminating Interactive & Background RRC
connections.
› pmTotNoTermRrcConnectReqCsSucc: Number of successful mobile terminating conversational RRC connections.
10 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
CS/PS Accessibility
(RRC)
MP Load
Check MP load for Main
Racks / Extension Sub
Racks – High??
Check for Core Network
(Call servers / SGSN )
outages .
Re-module Sites
Re-home Sites
Admission Control
Check Parameter
settings for:
a)Feeder length/TMA
b)OCNS
c) Adm Control
d) Check available
resources (Downlink Tx
power, Channelization
codes).
License
a) Verify /correct
individual licensed
capacity levels for
the node.
b) Check Channel
elements usage
trends
UTRAN
› Check for RRC
rejections due to
High MP Load,
Admission control,
failures due to DL
channelization
codes.
Node Blocking
› Check for node
configuration error,
node limitations or
transport network
layer service
unavailability.
Transport Blocking
› a) Check for
congestion on
user plane
(AAL2)/ control
plane (UniSaal
/SCTP) for IuB
resources.
› b) Expand TN
bandwidth
› Check IuCs/IuPs
11 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > mp load
accessibility problems due to mp load
› If the Load Control is not successful, pmNoRejRrcConnMpLoadC,
pmTotNoUtranRejRrcConnReq are increased
pmNoRejRrcConnMpLoadC represents Total amount of rejected calls due to MP Load Control. This counter is
incremented by one when sending a RRC message RRC Connection Reject with rejection cause congestion, when
the congestion cause has been indicated by internal load control.
pmTotNoUtranRejRrcConnReq represents Total number of UTRAN rejected RRC Connection Requests. This
counter is incremented by one when an RRC Connection Request is received and a connection setup to the RBS
fails due to the following reasons:
- no internal UE identity is available in the RNC
- MP load control function
- Admission Control function does not grant permission to proceed
- any internal parameter retrieving or calculations fail
- a downlink channelization code fails to be allocated
This counter is not incremented if there is inter-frequency load sharing.
› In case of unsuccessful Load Control event:
– Main Processor load for Main Racks and Extension Subracks should be examined for high or
irregular load
– Core Network (Call Server and SGSN) errors should be examined
12 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
admission control
› Admission Control is one of the most important Functions in the Capacity
Management of WCDMA networks, which aims to control the load in the
WCDMA radio access network.
› Admission Control blocks new incoming calls as well as handover attempts
when the load in the system is high (by taking the input from set of monitors
either located in the RBS or in the SRNC), by using measurements of UL
interference, DL power as well as the actual number of users.
13 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
admission control
› When a new resource request is made, Admission control will check the amount of
the resources needed by the requester and the system load based on the below
main monitors which are updated during the addition, deletion and modification of
existing radio connections in the cell:
-
DL TX Cell power (total non HS power used in the cell)
Air Interface Speech Equivalent in UL and DL
DL and UL spreading factor (SF) usage
DL Channelization Codes usage
RBS Hardware utilization in the UL and DL (Channel Elements)
Number of users in compressed mode
Number of HS users in the cell
UL Received total Wide Band Power (RTWP)
14 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup >
Admission control blocking
› Admission blockings can be triggered during 2 stages, either at the RRC
establishment or during the RAB establishment phase.
› To differentiate at which stage the blocking is triggered, we have to check
the following set of counters.
15 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > ADMission control
accessibility problems due to admission control
› If Admission Control prevent RRC connection to be established, counters
pmNoRrcPsReqDeniedAdm (for PS), pmNoRrcCsReqDeniedAdm (for CS),
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdm and pmNoReqDeniedAdm are increased.
› pmNoReqDeniedAdm represents Number of both RAB establishment and RRC requests rejected by admission control.
This counter is increased by one when admission to this cell is denied to a UE. The reason for denial can be power,
code utilization limits, ASE limit, or compressed mode limit reached. If the UE is in macro diversity, the counter is
incremented for the first cell to which admission control denies access. The remaining cells will not be checked by
admission control after admission to the first cell is denied. This counter is not incremented at a reject of a repeated RRC
connection request.
› pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdm represents Number of RRC requests denied by admission control. The counter is trigged
when an RRC connection request with any cause value is denied by Admission Control.
› pmNoRrcPsReqDeniedAdm represents Number of PS calls denied by admission control and is Incremented by one
after denied admission after an RRC CONNECTION REQUEST with any of the cause values 'Originating Interactive
Call', 'Terminating Interactive Call', 'Originating Background Call', 'Originating Subscribed Traffic Call' or 'Terminating
Background Call' has been received.
› pmNoRrcCsReqDeniedAdm represents Number of CS calls denied by admission control. This counter is incremented
by one when RRC connection request with cause 'Originating Conversational Call' or 'Terminating Conversational Call'
or 'emergency call' is denied by Admission Control.
16 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > ADMission control
accessibility problems due to admission control
› If Admission Control rejected RRC connection due to problem with load sharing,
counters pmNoLoadSharingRrcConn, pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnPs (for PS)
and pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnCs (for CS) are increased.
› pmNoLoadSharingRrcConn represents Number of Load Sharing diversions when establishing an RRC connection.
This counter is incremented by one when a RRC message RRC CONNECTION REJECT is sent to a UE because
another cell (frequency) is selected by Load Sharing.
› pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnPs represents Number of Packet (originating & terminating) Load Sharing RRC
Connection attempts. This counter is incremented by one when a RRC CONNECTION REJECT message is sent to a
UE using the PS service, because another cell (frequency) has been selected by Load Sharing.
› pmNoLoadSharingRrcConnCs represents Number of Conversational (emergency, originating & terminating) Load
Sharing RRC Connection attempts. This counter is incremented by one when a RRC CONNECTION REJECT message
is sent to a UE using the CS service, because another cell (frequency) has been selected by Load Sharing.
17 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > ADMission control
accessibility problems due to admission control
› Counters that are increased in cases of Accessibility problems within
Admission Control procedure due to other reasons are:
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlPwr: Number of RRC Connection Requests denied by admission control due to lack of DL
Power. This counter is incremented by one at reception of an RRC Connection Request denied by Admission Control
due to lack of DL Power.
or
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlChnlCode: Number of RRC Connection Requests denied by admission control due to
lack of DL Channelisation Codes. This counter is incremented at reception of an RRC Connection Request denied by
Admission Control due to lack of DL Channelisation Codes.
or
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmDlHw: Number of RRC Connection Requests denied by admission control due to lack of DL
hardware resources. This counter is incremented at reception of an RRC Connection Request denied by Admission
Control due to lack of DL hardware resources.
or
pmNoRrcReqDeniedAdmUlHw: Number of RRC Connection Requests denied by admission control due to lack of UL
hardware resources. This counter is incremented at reception of an RRC Connection Request denied by Admission
Control due to lack of UL hardware resources.
18 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > license
accessibility problems due to licensed capacity
› The capacity licensing can be a reason for limiting the traffic processing.
There are a number of counters that should be monitored to ensure that the
licenses are sufficient:
19 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > license
accessibility problems due to licensed capacity
› If Accessibility problems occur due to Licenced Capacity, these counters
are also considered:
pmNoFailedRrcConnectReqHw: Number of RRC requests denied by admission control due to insufficient licensed
capacity in the RBS. This counter is incremented by one when an RRC connection request with any cause value is
denied by Admission Control due to insufficient licensed capacity in the RBS.
pmNoFailedRrcConnectReqCsHw: Number of CS calls denied by admission control due to insufficient licensed
capacity in the RBS. This counter is incremented by one when an RRC connection request with cause 'Originating
Conversational Call', 'Terminating Conversational Call' or 'emergency call' is denied by admission control due to
insufficient licensed capacity in the RBS.
pmNoFailedRrcConnectReqPsHw: Number of PS calls denied by admission control due to insufficient licensed
capacity in the RBS. This counter is incremented by one when an RRC connection request with cause 'Originating
Interactive Call', 'Terminating Interactive Call', 'Originating Background Call', 'Originating Subscribed Traffic Call' or
'Terminating Background Call' is denied by admission control due to insufficient licensed capacity in the RBS.
20 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > node blocking
Accessibility problems due to node congestion
› If Accessibility problems occur due to Node Congestion, these
counters are considered:
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockNodePs: Number of RRC Connection Setup attempts for
Packet Switched calls that fail due to node blocking. This counter is incremented by one
at the establishment of an RRC Connection Request with Establishment Cause =
Originating/Terminating Interactive or Background or Originating Subscribed Traffic
Call, fails due to node blocking (node configuration error), node limitation or transport
network layer service unavailability.
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockNodeCs: Number of RRC Connection Setup attempts for
Circuit Switched calls that fail due to node blocking. This counter is incremented by one
if the establishment of an RRC Connection Request with Establishment Cause =
Originating/Terminating Conversational or Emergency, fails due to node blocking (node
configuration error), node limitation or transport network layer service unavailability.
21 (40)
Accessibility > rrc connection setup > transport blocking
Accessibility problems due to transport network
congestion
› If Accessibility problems occur due to Transport Network Congestion, these
counters are considered:
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockTnPs: Number of RRC Connection Setup attempts for Packet
Switched calls that fail due to Transport Network blocking. This counter is incremented
by one at the establishment of an RRC Connection Request with Establishment Cause
= Originating/Terminating Interactive or Background or Originating Subscribed Traffic
Call, fails due to congestion on the user plane (AAL2) or control plane (UniSaal or
SCTP) of the transport network as a result of user dimensioned transport network
resource shortages.
pmNoRrcConnReqBlockTnCs: Number of RRC Connection Setup attempts for Circuit
Switched calls that fail due to Transport Network blocking. This counter is incremented
by one if the establishment of an RRC Connection Request with Establishment Cause =
Originating/Terminating Conversational or Emergency, fails due to congestion on the
user plane (AAL2) or control plane (UniSaal or SCTP) of the transport network as a
result of user dimensioned transport network resource shortages.
22 (40)
Accessibility >
RAB (radio access bearer)
establishment
23 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment >
RAB establishment
› RAB Establishment procedure describes successful or unsuccessful attempts to set
up a Radio Access Bearer for a requested service.
› Main counters for this procedure are:
pmNoNormalNasSignReleaseCs, pmNoNormalNasSignReleasePs, pmNoSuccRbReconfPsIntDch, pmNoSuccRbReconfOrigPsIntDch,
pmNoSuccRbReconfPsIntHs, pmNoSuccRbReconfOrigPsIntHs, pmNoSuccRbReconfPsIntEul, pmNoSuccRbReconfOrigPsIntEul,
pmNoRabEstablishAttempts, pmNoRabEstablishSuccess, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptSpeech, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessSpeech,
pmNoRabEstablishAttemptAmrNb, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessAmrNb, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptAmrWb, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessAmrWb,
pmNoRabEstablishAttemptCs64, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessCs64, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptCs57, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessCs57,
pmNoRabEstablishAttemptPacketInteractive, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessPacketInteractive, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptPacketStream,
pmNoRabEstablishSuccessPacketStream, pmNoRabEstAttemptPsStreamHs, pmNoRabEstSuccessPsStreamHs,
pmNoRabEstablishAttemptPacketInteractiveHs, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessPacketInteractiveHs, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptPacketInteractiveEul,
pmNoRabEstablishSuccessPacketInteractiveEul, pmNoRabEstablishAttemptPacketStream128, pmNoRabEstablishSuccessPacketStream128,
pmRabEstablishEcAttempt, pmRabEstablishEcSuccess, pmNoInvalidRabEstablishAttempts, pmNoRabEstablishFailureUeCapability,
pmNoRabEstAttemptPsIntNonHs, pmNoRabEstSuccessPsIntNonHs, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlHwBest,
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlHwBest, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlHw, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlHw,
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlAse, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlAse, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptExceedConnLimit,
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlChnlCode, pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlPwr, pmCmAttUlSf2, pmCmSuccUlSf2, pmCmAttDlSf2,
pmCmSuccDlSf2, pmCmAttUlHls, pmCmSuccUlHls, pmCmAttDlHls, pmCmSuccDlHls, pmCmStop, pmNoReqDeniedAdm,
pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedSpeech, pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedCs, pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedInteractive, pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedPsStreaming,
pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedPsStr128, pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedHs, pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedEul, pmNoRabEstBlockRnPsStreamHs,
pmNoRabEstBlockRnBestPsStreamHs, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrHs, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrHsBest,
pmNoRabEstBlockNodePsStrHsBest, pmNoRabEstBlockTnSpeech, pmNoRabEstBlockTnSpeechBest,
pmNoRabEstBlockNodeSpeechBest, pmNoRabEstBlockTnCs57, pmNoRabEstBlockTnCs57Best, pmNoRabEstBlockNodeCs57Best,
pmNoRabEstBlockTnCs64, pmNoRabEstBlockTnCs64Best, pmNoRabEstBlockNodeCs64Best, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrNonHs,
pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrNonHsBest, pmNoRabEstBlkNodePsStrNonHsBest, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsIntNonHs,
pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsIntNonHsBest, pmNoRabEstBlkNodePsIntNonHsBest, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsIntHs, pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsIntHsBest,
pmNoRabEstBlockNodePsIntHsBest
24 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment >
rab establishment counters
› Some of counters related to RAB Establishment procedure are described below:
pmNoRabEstablishAttemptSpeech: Number of RAB establishment attempts for CS Conversational speech RABs.
of Includes AMR-NB, AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs. Incremented in the best cell in the active set.
pmNoRabEstablishSuccessSpeech: Number of successful RAB establishments for CS Conversational speech
RABs. Includes AMR-NB, AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs. Incremented in the best cell in the active set.
pmNoOfNonHoReqDeniedSpeech: Number of RAB establishments rejected by admission control for CS
Conversational speech RABs. Includes AMR-NB, AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs. Counter is applicable to
all Speech RAB establishments, including establishment on a Speech+Interactive multi-RAB configuration.
Incremented by one when a Speech RAB establishment is rejected by admission control.
pmNoInvalidRabEstablishAttempts: RNC-level counter. Number of invalid RAB establishment attempts.
pmNoRabEstablishFailureUeCapability: RNC-level counter. Number of failed RAB establishments due to
insufficient UE capabilities.
25 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment >
Hardware Fault
Node Blocking
Check for node
configuration error,
node limitations or
transport network
layer service
unavailability.
CS/PS Accessibility
(RAB)
Transport Blocking
a) Check for congestion on user
plane (AAL2)/ control plane
(UniSaal /SCTP) for IuB
resources.
b) Expand TN bandwidth
•Check T1 Errors
Check Locked T1s
•Check Iub/TD (Vc/Vp)
Mismatches
•Share Traffic with Nbr or
Escalate
for expansion
•Reduce CPICH or Tilt to take
less traffic
•Increase Directed Retry to
Offload to GSM
26 (40)
UTRAN
Check for RRC
rejections due to
High MP Load,
Admission control,
failures due to DL
channelization
codes.
Congestion
Accessibility > rab establishment > node blocking
Rab establishment failure due to node Blocking
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to Node Blocking, following counter is
incremented:
pmNoRabEstBlockNodePsStrHsBest: Number of RAB establishment attempts for RAB-type PS
Streaming for HS that are blocked due to node congestion or node failure. Incremented in the best
cell in the active set. Incremented by one when the establishment of a PS Streaming RAB for HS
fails due to node configuration error, node limitation, or transport network layer service
unavailability.
pmNoRabEstBlockNodeSpeechBest: Number of RAB establishment attempts that are blocked
due to node congestion or node failure for CS Conversational speech RABs. Includes AMR-NB,
AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs. Incremented in the best cell in the active set. Incremented
by one when the establishment of a CS Speech RAB fails due to node configuration error, node
limitation, or transport network layer service unavailability.
› If RAB Establishment procesure fails due to Node Blocking, it is recommended to:
– Check for node configuration error, node limitations or transport network layer service unavailability.
27 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > transport blocking
Rab establishment failure due to Transport
Network Blocking
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to problems in Transport
Network, following counters are incremented:
pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrHs: Number of RAB establishment attempts for RAB-type PS Streaming for HS that are
blocked due to TN congestion or TN failure, counted on the blocking cell. Incremented by one when the
establishment of a PS Streaming RAB for HS, fails due to congestion on the user plane (AAL2) or control plane
(UniSaal or SCTP) of the transport network layer as a result of user dimensioned transport network capacity.
pmNoRabEstBlockTnPsStrHsBest: Number of RAB establishment attempts for RAB-type PS Streaming for HS
that are blocked due to TN congestion or TN failure, counted on the best cell in the active set. Incremented by one
when the establishment of a PS Streaming RAB for HS, fails due to congestion on the user plane (AAL2) or control
plane (UniSaal or SCTP) of the transport network layer as a result of user dimensioned transport network capacity.
pmNoRabEstBlockTnSpeech: Number of RAB establishment attempts that are blocked due to TN congestion or
TN failure for CS Conversational speech RABs. Includes AMR-NB, AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs.
Incremented on the blocking cell. Incremented by one when the establishment of a Speech RAB fails due to UNISAAL or AAl2 congestion, IP resource limitations or blocking as a result of user dimensioned transport network
configured capacity. The counter is incremented for the first cell in which the failure occurred but only if the cell is in
the SRNC.
pmNoRabEstBlockTnSpeechBest: Number of RAB establishment attempts that are blocked due to TN congestion
or TN failure for CS Conversational speech RABs. Includes AMR-NB, AMR-WB and AMR-NB Multi-rate RABs.
Incremented in the best cell in the active set. Incremented by one when the establishment of a Speech RAB fails
due to UNI-SAAL or AAl2 congestion, IP resource limitations or blocking as a result of user dimensioned transport
network configured capacity. The counter is incremented for the best cell in the active set but only if the cell is in the
SRNC.
28 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > transport blocking
Rab establishment failure due to
Transport Network Blocking
› If RAB Establishment Failure occurs due to TN blocking, it is recommended
to:
– Check for congestions on user plane (AAL2) and control plane (UniSaal /SCTP) for IuB
resources.
– Expand TN bandwidth
– Check T1 errors and locked T1s
– Check Iub/TD (Vc/Vp) mismatches
– Share traffic with neighbors or escalate for expansion
– Reduce CPICH or tilt to take less traffic
– Increase Directed Retry to offload to GSM
29 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > node & transport blocking
Rab establishment problems due to Transport
Network Blocking And Node Blocking Over Iub
› Transport Network Blocking is defined as blocking due to congestion on the Userplane or Control-plane of the transport network as a result of resource shortage in
the transport network.
› Node blocking is defined as blocking due to a node configuration error (node B, RXI
and RNC), node limitation or transport network layer service unavailability.
› During a call setup, one or more AAL2 connections must be setup as a part of:
-RAB Establishment
-RRC Establishment
-Channel Switching between dedicated channels
-Addition of a Radio Link to the active set
› Any failure in establishing the AAL2 connection will increase pmNoFailedAfterAdm
counter.
30 (40)
Accessibility >
failure after admission
› Counter pmNoFailedAfterAdm represents the number of Radio Resource Control (RRC)
or Radio Access Bearer (RAB) establishment requests failed after being admitted by
admission control. If either a RRC or RAB establishment procedure fails AFTER the
admission has been granted for the establishment (RRC or RAB) - this counter will be
incremented in the cell or cells where the UE is located or will be incremented for all cells
if UE is in macro diversity. This counter will increment on both Circuit Switched failures
and Packet Switched failures.
31 (40)
Accessibility >
Reasons for failures after admission
› Transport Network Blocking and Node Blocking Over Iub: High number of Failures
After Admission might occur due to congestion or node miss configuration.
› Core Transport Network Congestion: Accessibility issues are observed on all sites at
the RNC without major issues with Iub congestion (especially at peak hour)
› Parameter Settings: Failures after admission might occur if the admission thresholds
does not match to the original planned capacity
› Hardware and Transmission Problems
› Channel Code Allocation Failures
32 (40)
Accessibility >
Reasons for failures after admission
› RAB and RRC Establishment failures which occur after admission control
can be due to TN and non TN related,
– timeout in the UE, RNC or RBS.
– invalid parameter settings.
– TN failure reasons.
– coverage issues
– If the connection is suddenly lost with a RAB, you will get a system RAB
release
– If it disconnects with RRC you may get an abnormal Disconnect message
which is failure to setup a call.
33 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > utran
rab establishment failure due to radio network
problems (utran)
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to problems in Radio Network
(UTRAN), following counters are incremented:
pmNoRabEstBlockRnPsStreamHs: Number of RAB establishment attempts for RABtype streaming PS unknown HS that are blocked due to RN congestion or RN failure,
counted on the blocking cell. Incremented by one when a target configuration
containing Streaming PS on HS is selected when reconfiguring the connection to add
the new RAB, and the execution of the reconfiguration was blocked due to RN
resources.
pmNoRabEstBlockRnBestPsStreamHs: Number of RAB establishment attempts for
RAB-type streaming PS unknown HS that are blocked due to RN congestion or RN
failure. Incremented in the best cell in the active set. Incremented by one when a target
configuration is selected when reconfiguring the connection to add the new RAB, and
the execution of the reconfiguration was blocked due to RN resources.
34 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion >
CS/PS Accessibility
(RAB)
Congestion
DL Power
•Check if Maximum
Transmission Power is
aligned with MaxDlCapability
•Check Maximum
Transmission Power and
CPICH ratio
•Increase PwrAdm, Reduce
PwrOffset
•Explore IFLS with other
Carrier
•Enable or Increase Directed
Retry to GSM
Code
ASE
•Check dlCodeAdm
values if adjustment
is still possible
•Verify settings for
aseDlAdm
Hardware Resources
•
•
• Check for traffic
load on the cell.
•Reduce 384k Users
on DL (sf8Adm)
Check Locked Tx/Rax
Boards
Check hanging CE
(restart)
Check HS/EUL
resource allocation
•Optimize radio
network to reduce
interference / pilot
pollution.
•Reduce HS-PDSCH
Codes
•Reduce HS-SCCH
Codes
•Reduce sf16Adm/sf8Adm
•Consider changing to 60W
RU
•
ul/dlHwAdm
•
FIRS 16kbps
•
Channel Type
DCH to FACH
eulServing/NonServing
Adm
•Add another Carrier
•
35 (40)
•
Replace RAX/TX
Boards
Connection Limit
•
Verify Admission
settings /Usage
trends for
different SF RAB.
• Fine tune
parameter
settings to
maintain balance
between
Accessibility &
throughput.
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > dl power
congestion due to lack of dl power
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to lack of DL Power, following
counter is incremented:
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlPwr: Number of failed RAB establishment
attempts due to lack of DL power.
36 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > dl power
congestion due to lack of dl power
› In case of lack of DL Power for RAB Establishment, it is recommended to:
– check if Maximum Transmission Power (maximumTransmissionPower = 400 {0..500}
is maximum power for all downlink channels that are allowed to be used simultaneously
in a cell, added together) is aligned with Maximum DL Capability
(maxDlPowerCapability that is calculated on the RBS based on transmitter hardware
capacity, feeder lengths, and other factors. If the value is excessively low, it could be
either because the values for some of those factors have been incorrectly defined, or it
could be the result of faulty or overheated hardware.)
– check the ratio between Primary CPICH Power (primaryCpichPower = 300 {-99..500})
and Maximum Transmission Power. primaryCpichPower takes typically 5-20% of
maximumTransmissionPower.
37 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > dl power
congestion due to lack of dl power
› In case of lack of DL Power for RAB Establishment, it is recommended to:
– consider increasing pwrAdm and reducing pwrOffset, according to dependency:
pwrAdm + pwrOffset <= 100%.
pwrAdm (=75 {0..100}) is admission limit for downlink cell carrier power expressed relative to the lower of
maximumTransmissionPower (configured in this UtranCell instance) and maxDlPowerCapability (configured in
the corresponding instance of RbsLocalCell in the RBS). Changing this attribute will re-initiate Congestion
Control measurements.
pwrOffset (=15 {0..100}) is cell carrier power offset expressed relative to the lower of
maximumTransmissionPower (configured in this UtranCell instance) and maxDlPowerCapability (configured in
the corresponding instance of RbsLocalCell in the RBS).
– explore IFLS (Inter Frequency Load Sharing) with other carriers
– add another carrier
38 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > dl power
congestion due to lack of dl power
› In case of lack of DL Power for RAB Establishment, it is recommended to:
– enable or increase Directed Retry to GSM
loadSharingGsmFraction (=100 {0..100}) defines percentage of Speech calls that can be directed to GSM
after the loadSharingGsmThreshold has been exceeded. If the value of loadSharingGsmFraction is set to 0, this
means no voice calls subject to Directed Retry should be directed to GSM (no voice calls aredirected to GSM).
If the value of loadSharingGsmFraction is set to 100, this means that ALL of the voice calls proposed for
Directed Retry should be directed to GSM (all voice calls that are proposed for directed retry are directed to
GSM).
loadSharingGsmThreshold (= 75 {0..100}) defines percentage of the guaranteed non-handover admission limit
(pwrAdm) above which Directed Retry should be invoked. If the value of loadSharingGsmThreshold is set to 100
then this means that the threshold at which voice calls are directed to GSM is 100 % of pwrAdm. Therefore no
voice calls should be moved to GSM until the admission threshold pwrAdm is reached. If the value of
loadSharingGsmThreshold is set to 0 then this means that the threshold at which voice calls are directed to
GSM is 0 % of pwrAdm.
39 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > dl power
congestion due to lack of dl power
› In case of lack of DL Power for RAB Establishment, it is recommended to:
– consider reducing sf16Adm / sf8Adm
› sf16Adm (=16 {0..16}) is admission limit for non-guaranteed traffic class connections with DL SF = 16. Maximum number of radio links
with Spreading Factor = 16 in the downlink (DL SF = 16) for which new admission requests for non-guaranteed traffic classes will
continue to be allowed. Reaching or exceeding this number of DL SF = 16 radio links (regardless of their traffic class) will block setup
and addition in this cell of more non-guaranteed traffic class radio links that would require DL SF = 16. The default setting disables the
admission policy. However, the actual setting may need to deviate from the default, in order to limit the number of simultaneous high bit
rate connections in a cell, typically to deal with limitations in transport network dimensioning (to prevent all TN resources from being
claimed by non-guaranteed traffic class connections). The setting of sf16Adm and sf16gAdm needs be considered together. If sf16Adm
< sf16gAdm, then only new guaranteed traffic class connections are allowed at and above the sf16Adm threshold. Similarly, if sf16Adm
> sf16gAdm, then only new non-guaranteed traffic class connections are allowed at and above the sf16gAdm threshold. Below the
lower of the two threshold settings (sf16gAdm or sf16Adm), guaranteed and non-guaranteed services compete equally for DL SF = 16
cell resources on a first-come first-served basis.
sf16gAdm (=16 {0..16}) is admission limit for guaranteed traffic class connections with DL SF = 16. Maximum number of radio
links with Spreading Factor = 16 in the downlink (DL SF = 16) for which new admission requests for guaranteed traffic classes will
continue to be allowed. Reaching or exceeding this number of DL SF = 16 radio links (regardless of their traffic class) will block
setup and addition in this cell of more guaranteed traffic class radio links that would require DL SF = 16. sf16gAdm value: 16
means that no blocking of DL SF = 16 requests will occur.
› sf8Adm (=8 {0..8}) is admission limit for non-guaranteed traffic class connections with DL SF = 8. Maximum number of radio links with
Spreading Factor = 8 in the downlink (DL SF = 8) for which new admission requests for non-guaranteed traffic classes will continue to
be allowed. Reaching or exceeding this number of DL SF = 8 radio links will block setup and addition in this cell of more nonguaranteed traffic class radio links that would require DL SF = 8. The default setting disables the admission policy. However, the actual
setting may need to deviate from the default, in order to limit the number of simultaneous high bit rate connections in a cell, typically to
deal with limitations in transport network dimensioning (to prevent all TN resources from being claimed by non-guaranteed traffic class
connections).
– consider change RU to 60W
40 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > code
congestion due to lack of codes
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to lack of DL channelization
codes, following counter is incremented:
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlChnlCode: Number of failed RAB establishment
attempts due to lack of DL channelization codes.
› In case of RAB Establishment Failure due to lack of DL channelization
codes, it is recommended to:
– Check dlCodeAdm values if adjustment is still possible
› dlCodeAdm (=80 {0..100}) is admission limit based on downlink channelization code tree usage. Expressed as
percentage of the code tree currently in use. Used by Admission Control, in Admission Request Handler.
– Reduce 384k users on DL (sf8Adm)
– Reduce HS-PDSCH Codes
– Reduce HS-SCCH Codes
41 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > ase
congestion due to lack of ase
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to lack of ASE (Average
Speech Equivalent), following counters are incremented:
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlAse: Number of failed RAB establishment attempts due to lack of DL ASE.
Incremented by one when admission control fails with reject reason lack of DL ASE.
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlAse: Number of failed RAB establishment attempts due to lack of UL ASE.
Incremented by one when admission control fails with reject reason lack of UL ASE.
› If RAB Establishment Failure occurs due to lack of ASE, it is recommended
to:
– Verify settings for aseDlAdm
aseDlAdm (= 240 { 0..500 }) is admission limit on ASE in the downlink. Used by Admission Control, in
Admission Request Handler.
– Check for traffic load on the cell.
– Optimize radio network to reduce interference / pilot pollution.
42 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > hardware resources
congestion due to hardware resources
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to lack of hardware resources,
following counters are incremented:
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlHwBest: Number of failed RAB establishment
attempts due to lack of DL hardware resources. Incremented in the best cell in the
active set.
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlHwBest: Number of failed RAB establishment
attempts due to lack of UL hardware resources.
Incremented in the best cell in the active set.
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackDlHw: Number of failed RAB establishment attempts
due to lack of DL hardware resources. The counter is incremented for the IubLink
containing the first cell to fail admission in the active set.
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptLackUlHw: Number of failed RAB establishment attempts
due to lack of UL hardware resources. The counter is incremented for the IubLink
containing the first cell to fail admission in the active set.
43 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > hardware resources
congestion due to hardware resources
› If RAB Establishment fails due to some problem related to hardware resources, it is
recommended to:
– Check Locked Tx/Rax Boards
– Check hanging CE (restart)
– Check HS/EUL resource allocation
– Check ulHwAdm and dlHwAdm
› ulHwAdm (=100 {0..100}) is admission limit on RBS uplink hardware resource utilization, applicable to all
admission requests. Setting ulHwAdm to 100 % will disable the uplink hardware admission policy.
› dlHwAdm (=100 { 0..100 }) is admission limit on RBS downlink hardware resource utilization, applicable to all
admission requests. Setting dlHwAdm to 100 % will disable the downlink hardware admission policy.
– Adjust channel down-switch from DCH to FACH
› more downswitch attempts, decrease upswitch attempts, results in better usage of resources
– Check eulServingCellUsersAdm and eulNonServingCellUsersAdm
› eulServingCellUsersAdm (=32 { 0..100 }) is admission threshold for the number of E-DCH users having this
cell as serving cell. Includes both 2 ms TTI and 10 ms TTI users.
› eulNonServingCellUsersAdm (=100 {0..100}) is admission threshold for the number of E-DCH users having
this cell as non-serving cell.
– Replace RAX/TX Boards
44 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > congestion > connection limit
congestion due to connection limit
› When RAB Establisment procedure fails due to connection limit, following
counter is incremented:
pmNoFailedRabEstAttemptExceedConnLimit: Number of failed PS RAB
establishment attempts due to exceeding the configured connection limit when allocating
Spreading Factors. Incremented by one when admission control fails with reject reason
value SF4, SF8, SF16, or SF32.
› If RAB Establishment procedue fails due to connection limit, it is
recommended to:
– Verify Admission settings / Usage trends for different SF RAB.
– Fine tune parameter settings to maintain balance between accessibility & throughput.
45 (40)
Accessibility > rab establishment > hardware fault >
CS/PS Accessibility
(RAB)
Hardware Fault
RSSI
•Attenuation/Losses
•TMA Check
•Verify RFDS
Errors/Crashes
T1 Errors
Alarms
•Restart Board
Escalate
Escalate
•Cold Restart Node
•Verify SW on node
•External
Interference
•Swap Cards/Boards
•PIMs
•Replace
Cards/Boards
46 (40)
retainability
47 (40)
CS/PS
Retainability
Missing Neighbour
Soft Handover
•Check neighbor cell
availability
•Check RBS HW
Alarms
•Add suggested
Neighbors with
WNCS/GPEH/Drive Test
data
•Check T1 Errors
•Analyze existing
neighbors with 3G-3G
cell relation report
•Determine if the
issue affects only
one cell or a RBS or
cluster
•Analyze cell coverage
by RF Planning tool
/Drive Test data Plots
•Down tilts or other
•Check Cell
Availability
•Verify for SC
Clashes
Uplink Sync
IRAT
•Investigating the UE
TxPwr by using Drive
test data or WMRR
•Neighbor List
cleaning/ deletion
•Check parameter for
UE TxPwr & maxSir
•GSM coverage
area verification
for IRAT
neighbors
•Analyze cell coverage
by RF Planning tool or
Drive test data
•Use of GPEH to
determine the number
of Event 6d or number
of Event 2d
•Check Cells doe RSSI
Issues
physical optimization
•One way neighbor
relation
48 (40)
•Re-prioritization
the neighbor list
based on usage
Congestion
•Check down switch
counter for
congestion reason.
•Investigate the RRC
Access failure due to
lack of DL power &
codes
•Perform analysis of
coverage area and
reduce overshooting
•Verify CE usage
and HW allocation
and dimensioning
Others
•Transport Issue
•RBS / RNC HW
issue
•RF issues outside
of available counters
•UE issues
Retainability counters
› pmNoNormalRabReleaseSpeech: Number of successful normal RAB releases (Speech)
› pmNoSystemRabReleaseSpeech: Number of successful system RAB releases (Speech
drops)
› pmNoNormalRabReleasePacket: Number of successful normal RAB releases (PS)
› pmNoSystemRabReleasePacket: Number of successful system RAB releases (PS drops)
› pmNoNormalRbReleaseHs: Number of successful normal releases of packet RABs mapped
on HS-DSCH
› pmNoSystemRbReleaseHs: Number of successful system releases of packet RABs mapped
on HS-DSCH
› pmNoNormalRbReleaseEul: Number of normal RAB releases of PS Int. RAB mapped on EDCH/HS-DSCH
› pmNoSystemRbReleaseEul: No. of system RAB releases of PS Int. RAB mapped on EDCH/HS-DSCH
49 (40)
Handover counters
› pmNoTimesRlAddToActSet: Number of times RL is added/ replaced to an
active set
› pmNoTimesCellFailAddToActSet: Number of times a cell fails to be
added to an active set
› pmNoRlDeniedAdm: Number of RL setups or RL addition requests denied
by admission
50 (40)
IRAT counters
›
›
›
›
›
pmNoDirRetryAtt: Number of attempted outgoing inter RAT HO due to capacity
pmNoDirRetrySuccess: Number of successful outgoing IRAT HO due to capacity
pmNoAttOutIratHoSpeech: No. of attempted outgoing IRAT HO for speech
pmNoSuccessOutIratHoSpeech: No. of successful outgoing IRAT HO for speech
pmNoFailOutIratHoSpeechGsmFailure: No. of failed outgoing IRATs due to GSM allocation
failure
› pmNoFailOutIratHoSpeechReturnOldChPhyChFail: No. of failed outgoing IRATs due to
physical channel failure, where UE returns to present active set
› pmNoFailOutIratHoSpeechReturnOldChNotPhyChFail: No. of failed outgoing IRAT HOs due
to reasons other than physical channel failure, where UE returns to present active set.
51 (40)
counters for Drop Reasons
› pmNoSysRelSpeechNeighbr: No. of sys disconnects of a speech call due
to missing (non-valid) neighbor relation
› pmNoSysRelSpeechSoHo: No. of system disconnects of a speech call
due to soft handover (valid/non-valid)
› pmNoOfTermSpeechCong: Number of Speech Radio Connections served
by RNC terminated due to congestion
› pmNoSysRelSpeechUlSynch: Number of system disconnects of a speech
call due to lost UL synch
52 (40)
Counters quick reference
53 (40)
Ucell parameter quick reference
54 (40)