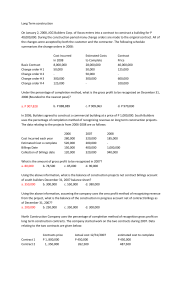
ASSIGNMENT- 1 ( NIA) CREATED BY: SHUBHAM VERMA ( 9871778008) 1. Can the gross domestic product be greater than the gross national product? (1) 1) No 2) Yes 3) Never 4) Can’t say 2. State which one of the following is true. (1) 1) Rent is a factor income 2) Royalty is not a factor income 3) Tax is a factor income 4) Subsidies is a factor payment 3. National Income is a (1) 1) Hypothetical concept 2) Non economic concept 3) Stock concept 4) Flow concept 4. Money flow is the flow of (1) 1) Goods only 2) Factor payments 3) Services only 4) Goods and services only 5. What do you mean by gross investments? (1) 6. Which of the following is an example of macroeconomics? (1) 1) Price determination 2) Consumer’s equilibrium 3) Producer’s equilibrium 4) Inflation 7. Define Domestic territory of a country. (1) 8. What is meant by Real Gross Domestic Product? 1 9. What is real national income? (1) 10. Find Net National Product at Market Price. (3) S.no. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) Contents Personal Taxes Wages and Salaries Undistributed Profit Rent Corporate Tax Personal Income Interest Net Indirect Tax Net Factor Income from Abroad Profit Social Security Contribution by Employers (Rs. in Crores) 200 1,200 50 300 200 2,000 400 300 20 500 250 ANSWER: 2970 crores 1 CREATED BY: SHUBHAM VERMA (9871778008) 11. Giving reason, explain whether the following are included in domestic product of India. (3) 1) Profits earned by a branch of foreign bank in India. 2) Payment of salaries to its staff by an embassy located in New Delhi. 3) Interest received by an Indian resident from its abroad firms. 12. From the following data, calculate “Net Value Added at Factor Cost”. (4) S.no. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Content Sales Change in Stock Intermediate consumption Net indirect taxes Exports Depreciation (Rs. in Lakhs) 400 (-) 20 200 40 50 70 ANSWER: 110 lakhs 13. State any precautions that are taken while calculating national income by expenditure method. (3) 14. Calculate the Net National Product at Market Price from the given details. S.NO. 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) CONTENTS Mixed income of self-employed Depreciation Profit Rent Interest Compensation of employees Net indirect taxes Net factor income to abroad Net exports Net current transfers to abroad (RS. IN CRORES) 8,000 200 1,000 600 700 3,000 500 60 (-) 50 20 ANSWER: 13,740 crores 15. Giving reason, explain how the following should be treated in the estimation of National Income. (6) 1) Payment of interest by a firm to a bank. 2) Payment of interest by a bank to an individual. 3) Payment of interest by an individual to a bank. 4) Stipend given by the government to the students studying for their master’s programme in economics. 16. Give one example of ‘externality’ which reduces welfare of the people. (2) 17. Explain how ‘ non-monetary exchanges’ are a limitation in taking domestic product as an index of welfare? (2) 18. Explain how ‘distribution of Gross Domestic Product’ is a limitation in taking Gross Domestic Product as an index of welfare. (3) 19. Distinguish between Real Gross Domestic Product and Nominal Gross Domestic Product. Which of these is a better index of welfare of the people and why? (4) 20. Calculate the operating surplus from the following date: (3) S. NO. 1) 2) 3) 4) ITEMS Sales Compensation of employees Intermediate Consumption Rent RS ( in crores) 4000 800 600 400 2 CREATED BY: SHUBHAM VERMA (9871778008) 5) 6) 7) 8) Interest NIT Consumption of fixed capital Mixed Income 300 500 200 400 ANSWER: 1500 crores 21.Which of the following is an example of transfer payment: (1) 1) Free meals in the company canteen 2) Employers’ contribution to social security 3) Retirement pension 4) Old-age pension 22. Microeconomics is different from macroeconomics because: (1) 1) Microeconomics deals with economic behaviour 2) Microeconomics deals with individual behaviour 3) Microeconomics deals with prices only 4) Microeconomics deals with the government’s decisions. 3 CREATED BY: SHUBHAM VERMA (9871778008)