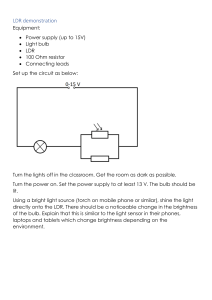
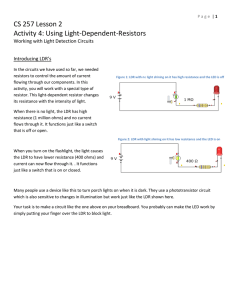
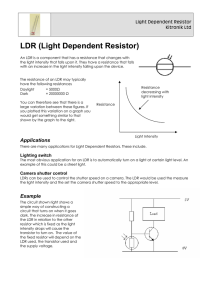
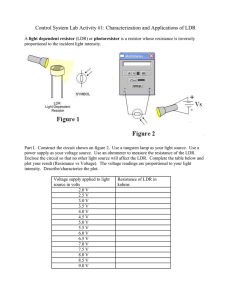
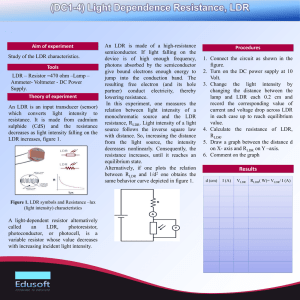
KOTHARI INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL NOIDA PHYSICS PRACTICAL FILE TO STUDY THE VARIATION IN CURRENT FLOWING IN A CIRCUIT CONTIANING AN LDR SUBMITTED BY: KRISH JAIN CLASS AND SECTION: 12 B BOARD ROLL NO: CERTIFICATE This is to certify that Krish Jain student of class XII “B” Kothari International School has completed the project titled “ To study the variation in current containing LDR” during the academic year 2023-2024 towards partial fulfilment of credits for the physics practical evaluation of CBSE 2023-2024, under the supervision on Ms. Samta Sharma Sign. of internal Examiner Sign. of external Examiner ACKNOWLEDGEMENT “There are times when silence peaks much more loudly than words of praise to only as good as belittle a person whose words do not express, but only put a veneer over true feelings , which are gratitude at this point of time “. I would like to express my sincere gratitude to our Physics teacher, Ms Samta Sharma for her vital support, guidance and encouragement- without which this project would have come forth. I wouldalso like to express my gratitude to the staff of the Physics Department at Kothari International School for their support during the making of this project. I would also like to thank my parents and friends who helped and supported me for this project. This project was an amiable as well as inspiring assignment to me for achieving success INDEX T TOPIC: PAGE NO. : INTRODUCTION 01 APPLICATIONS 02 AIM 03 APPARATUS 04 THEORY 05 PROCEDURE 08 OBSERVATION 11 PRECAUTIONS 13 SOURCE OF ERROR 13 CONCLUSION 14 BIBLIOGRAPHY 15 INTRODUCTION Light Dependent resistor also known as the photoresistor is a two terminal passive electronic component that is made up of a semiconductor element or compound. As the name implies the resistance of the Photoresistor depends upon the intensity of light projected onto it. With the increase in the intensity of light the resistance of the light dependent resistor decreases. The LDRs are used in a bridge sensor circuit on order to convert the light into the voltage and thus different actions can be performed for example by feeding the voltage signal into the microcontroller the circuit can be used to determine the darkness in the room and turn on or off the light. Two of its earliest applications were as part of smoke and fire detection systems and in camera light meters. There are two common types of materials found photoconductive cells. They are cadmium sulphide ( Cds) and Cadmium Selenide (CdSe) APPLICATIONS There are some applications of LDR which are given below: -> The LDR is used in the infrared astronomy. -> The LDR is used in light failure alarm circuits and used in light meter. -> The LDR used in smoke detectors. -> It is used for automatic contrast and brightness control in television receivers. -> It is used in photosensitive relay -> It is used in optical coding. -> It is used in street light control circuits. -> It is used in camera light meters. -> It is used in the security alarm. -> It is used as a proximity switch. -> It is used in light activated control circuits. APPARATUS 1)Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) 2)Connecting Wires 3)Source of different power rating (bulbs) 4)Bulb Holder 5)Metre scale 6)Multi Meter 7)Battery THEORY 1.) LDR and its characteristics When light is incident on it, a photon is absorbed and thereby it excites an electron from valence band into conduction band. Due to such new electrons coming up in conduction band area, the electrical resistance of the device decreases. Thus the LDR or photoconductive transducer has the resistance which is the inverse function of radiation intensity. λ0 = threshold wavelength, in meters e = charge on one electron, in Coulombs Ew = work function of the metal used, in Ev Here we must note that any radiation with wavelength greater than the value obtained in above equation CANNOT PRODUCE any change in the resistance of this device. The band gap energy of Cadmium Sulphide is 2.42eV and for Cadmium Selenide it is1.74eV. Due to such large energy gaps, both the materials have extremely high resistivity at room temperature. Characteristics of photoconductive cells Now when the device is kept in darkness, its resistance is called as dark resistance. This resistance is typically of the order of 1013 ohms. When light falls on it, its resistance decreases up to several kilo ohms or even hundreds of ohms, depending on the intensity of light, falling on it. The spectral response characteristics of two commercial cells were compared in our laboratory. And we found that there is almost no response to the radiation of a wavelength which was shorter than 300nm. It was very interesting to note that the Cadmium Sulphide cell has a peak response nearer or within the green color of the spectrum within a range of 520nm. Thus it can be used nearer to the infrared region up to 750nm. It was found that the maximum response of Cadmium Sulphoselenide is in the yellow-orange range at 615nm and also it can be used in the infra-red region up to about 970nm. Sensitivity The sensitivity of a photo detector is the relationship between the light falling on the device and the resulting output signal. In the case of a photocell, one is dealing with the relationship between the incident light and the corresponding resistance of the cell. Spectral Response Like the human eye, the relative sensitivity of a photoconductive cell is dependent on the wavelength (color) of the incident light. Each photoconductor material type has its own unique spectral response curve or plot of the relative response of the photocell versus wavelength of light. PROCEDURE •Choose a specific position for the source and mount it using a holder, make sure it is stable. • Select the bulb with the lowest power rating and connect it to the holder as shown in the figure. • Connect the LDR, battery(6V) and the multimeter in series. • Set the multimeter to ohm section and select suitable range and measure the resistance with a bulb on. • Similarly switch to current section and move to micro ampere in the multimeter. This gives the value of the current. • Repeat these steps with different power sources at different distances and note down observations OBSERVATIONS • The experiment has been conducted by using various sources with different power ratings. Voltage of the battery = 6 V SECOND TABLE ON NEXT PAGE--> GRAPHS RESISTANCE AS A FUNCTION OF ILLUMINATION RESULT • The LDR resistance decreases with increase in intensity of light and hence there is an increase in the flow of current. • There is an increase in the current as the distance from the source decreases. • The intensity decreases as the distance from the source increases ERROR • The error lies within the experimental limit. BIBLIOGRAPHY • NCERT physics class XII • Art of Electronics by Paul worowitz • www.wikipedia.com/ • www.electronics2000.co.uk/links/educationhobby/ • www.ecelab.com/ AIM To study the variation in current, flowing in a circuit containing an LDR, because of a variation A. In the power of the incandescent lamp, used to illuminate the LDR (keeping all the lamps at fixed distance) B. In the distance of an incandescent lamp ( of fixed power), used to ‘illuminate’ the LDR